We tell you everything about plywood from A to Z.
What is plywood? Plywood is a versatile material that is used for various purposes almost everywhere. Externally, plywood looks like rectangular sheets of certain sizes of varying thickness, consisting of many layers (at least 3) of wood fiber raw materials. Plywood can be made from wood or tree veneer.
Most often, plywood is made from wood veneer, the layers of which are laid perpendicular to each other and glued with special compounds. This manufacturing technology provides excellent strength and wear resistance, and also increases the material’s ability to resist moisture penetration.
Plywood grades - classification by type of adhesive composition
The performance properties of plywood largely depend on the substance used for gluing the sheets. The quality of impregnation affects the moisture resistance and environmental friendliness of plywood, as well as its ability to withstand temperature fluctuations, humidity and other external influences. Based on the adhesive components used in production, many grades of plywood are distinguished.
FBA plywood
FBA is the least resistant material to a humid environment. However, the use of albumin casein glue makes it absolutely safe from an environmental point of view. This plywood is only suitable for rooms with low humidity levels. In particular, it has found its application in the production of furniture, and is also used to create all kinds of decorative interior elements.
Plywood FC
FC is a material with fairly low moisture resistance. The function of the binder in this case is performed by urea glue, which does not emit harmful substances, which allows this type of plywood to be used for finishing work inside residential premises. A moderate level of humidity is allowed.
FKM plywood
FKM – veneer sheets joined together using melamine glue. In terms of moisture resistance, the material is average.
Plywood FSF
FSF are especially durable wood boards, the layers of which are impregnated with phenol-formaldehyde resin. The material is able to withstand significant loads and resist moisture. However, the amount of toxins contained in the adhesive makes it possible to use such plywood exclusively outside the premises. In particular, it is ideal for cladding external walls in frame housing construction, erecting enclosing structures, and making outdoor furniture.
FB plywood
FB is a material in the production process of which bakelite glue is used. Sheets impregnated with this composition are characterized by increased moisture resistance and can withstand almost any temperature conditions. Impregnation reliably protects wood from negative environmental influences, which allows this type of plywood to be used in almost any area.
At the same time, FB-type boards may have characteristic differences, depending on the composition of the adhesive and sizing technology, which affects their characteristics.
Materials treated with alcohol-soluble impregnations are moisture resistant and are divided into three types:
- FBS is the highest quality plywood, each sheet of which is impregnated as thoroughly as possible;
- FBS1 – plywood boards, during the manufacturing process of which the method of coating veneer sheets is used, due to which the quality indicators of the material are reduced;
- FBS1A - belongs to the lowest class of bakelite plywood, in the production of which the amount of alcohol-soluble substance applied is limited, which involves processing exclusively longitudinally located sheets.
Another type is FBV plywood, in the manufacture of which water-soluble adhesive compositions are used.
There are two types of such plywood:
- Plywood, with the inner layers treated by the coating method, but the outer sheets impregnated.
- Plywood boards marked FBV1, for all layers of which only the coating method is assumed.
Some of the uses of plywood
- construction (service bridges and loading docks, outbuildings and structures, fencing structures and fences, agricultural buildings, bases for roofing materials, partitions, doors, scaffolding, flooring, formwork);
- interior and exterior design (soundproofing panels, lecture halls, concert halls, wall panels, window sills, doors, facade decoration, gates and fences);
- furniture production (facade, side and back walls of cabinets, cabinets for upholstered furniture, furniture for gardens and cottages, furniture for bathrooms, tables and countertops, cabinets and shelves, kitchen furniture, shelving);
- shipbuilding (interior decoration of yachts and ships, sides, partitions, decks of yachts, boats and vessels, seats on boats, catamarans and passenger ships);
- transport engineering (trailers, trim, doors, bodies and floors of trucks, commercial trailers, delivery vans, trolleybuses, containers, buses, trailers, campsites, pickup trucks, wagons);
- packaging (containers and packaging, decorative boxes and boxes);
- trade, service and warehouse equipment (trade and service equipment (cabinets, counters, racks), equipment for hotels, bars and restaurants, hairdressing salons, laundries, medical offices and pharmacies, beach houses, cabins and showers, furniture for street restaurants, cladding of warehouse premises , fitting rooms and partitions, information desks);
- children's furniture and playground equipment (children's furniture (tables, chairs, benches, cabinets, etc.), equipment for children's and playgrounds,
- sports and playgrounds (hockey rinks, skateboard ramps, snow slides, seats for spectators on sports grounds, benches, bumpers, flooring), school furniture, children's toys, children's slides);
- other areas of application (road signs, billboards, elevators, templates, etc.).
Plywood varieties
Today, GOST standards define five grades of plywood, differing in the presence of certain natural wood defects or those formed during its mechanical processing.
Grade E
Grade E is a high-quality elite material intended primarily for fine finishing. The presence of any foreign inclusions, as well as all kinds of deformations, is not allowed, with the exception of minor deviations in the structure of the wood, which are random. Pin knots on coniferous plywood are acceptable, but not more than 3 pieces per 1 m2. The aesthetic perfection of E plywood makes it the most expensive of all manufactured materials.
1st grade
1 – grade for which some defects in the form of knots, light porosity, repair inserts for sealing knots are acceptable. Such wood boards are used for both interior and exterior finishing work.
2nd grade
2 – grade of plywood, in which cracks up to 20 cm may be present, and the presence of small repair inserts for sealing knots, knots and wormholes, light and dark porosities is also allowed. It is permissible for glue to seep through in certain areas within 2% of the total area of the plywood sheet.
3rd grade
3 – grade of plywood, in many ways similar to the second grade, but here the restriction on the number of closed cracks and the number of knots of coniferous plywood has been removed. The maximum possible diameter of knots has been increased to 70 mm. In conditions of fine finishing, such defects can be hidden using special paints and varnishes.
4th grade
4 – grade, which includes the lowest quality and most affordable materials. Wood with numerous defects, including wormholes, as well as unjoined falling out knots, can be used in production. Uneven edges of glued sheets are allowed with deviations within 0.5 mm. The main purpose of such plywood is the production of packaging materials. However, it is often used for rough finishing indoors.
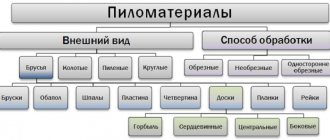
Plywood by type of front surface
One of the parameters by which this material is classified is the technology used in production for processing the external surfaces of plywood. Based on this criterion, several types of plywood are distinguished.
1. Unsanded (NS) - the outer surface of the veneer is not subjected to additional processing, as a result of which it has a fairly rough structure. The risk of cracking increases. Mostly such materials are used for rough work, where the condition of the surface of the slabs is not of fundamental importance.
2. Ш1 – sanded plywood, processing of which is carried out on one side. Practically not prone to cracking.
3. Ш2 – material that is subjected to grinding on both sides. The ability to absorb moisture is minimized. As in the cases with Sh1 plywood, it can be used for finishing work, as well as in the manufacture of decorative products and individual structural elements of furniture.
4. Laminated plywood sheets , for the processing of which special resins are used that contain phenol and melamine. It is also relevant to apply PVC film to the surface of plywood. Thus, the moisture resistance of the material improves. Lamination allows you to extend the service life of wood boards. In addition, the external surface looks quite aesthetically pleasing. This type of plywood is often used in interior design.
Wooden plywood - quality and types
Various types of wood are used to make the material. Several layers of veneer are securely connected to each other.
In each adjacent layer, the fibers are located perpendicular to those of the previous one. This feature increases the strength and wear resistance of the sheets.
If it is necessary to obtain plywood with higher torsional and bending resistance, the fibers in the product should be located at an angle of 60,30 or 45 degrees with respect to each other. A standard sheet of plywood has an odd number of individual layers.
There is a type of plywood where the fibers of all existing layers are directed in one direction. It is called layered pressed wood.
This material bends well, has a certain flexibility and elasticity, and is suitable for the production of various types of furniture. What method is used in the manufacture of plywood?
It can be peeled, sawn or planed
The first method is used most actively. The process goes like this:
- a narrow layer of wood is cut from the ridge;
- Separate sheets of veneer are cut out according to predetermined dimensions;
- the cut sheets are glued together with synthetic or natural glue;
- Under the influence of high temperature, several layers of veneer are pressed into bags, then they are cut to specified sizes.
Plywood for environmental safety
Since the production of wood-based panels uses a substance such as formaldehyde, a generally accepted scale has been developed that determines the level of permissible formaldehyde emissions. Based on the level of emission of harmful substances, plywood can be classified as class E1 or class E2.
E1 grade plywood
Class E1 includes materials that emit no more than 10 mg of harmful substances per 100 g of dry wood. Such indicators are considered acceptable for the use of plywood in residential premises.
E2 grade plywood
E2 class boards are recommended for use only for outdoor use, as the emission level can reach 30 mg.
At the same time, some unscrupulous manufacturers often indicate in the annotations to their products a class that does not correspond to reality. Using such materials in certain conditions is quite risky, so it is advisable to give preference to trusted manufacturers.
Types of plywood according to the composition of raw materials
Based on the composition of raw materials, all plywood offered today can be divided into three categories.
Hardwood Plywood
The hardwood species from which plywood sheets are made primarily includes birch. The veneer made on its basis is characterized by increased density and uniformity of structure. At the same time, in comparison with other types of materials, strength indicators are higher on average by 20%. The only conditional disadvantage of birch plywood can be considered its cost, which is higher than that of coniferous plywood.
Slabs made from hardwood are in demand not only in private construction. These types of plywood are used as packaging elements for the transportation of goods, in the field of shipbuilding and carriage building, as well as in various areas of the automotive industry.
Softwood plywood
Coniferous wood is usually cheaper. Domestic manufacturers of such plywood mainly use pine, which has high strength indicators. The finished products are quite light, and the natural wood grain adds aesthetic appeal to them. Due to the presence of natural resin, the material has a longer service life. Coniferous plywood has found its application in house construction, and is also actively used in arranging the interiors of residential premises.
Combined plywood
Combined plywood sheets include both hardwood and softwood veneer. This combination allows you to reduce the cost of products, practically without compromising their quality, since the technical characteristics are as close as possible to sheets made from birch. This type of plywood is mainly in demand in the furniture industry.
How to level plywood floors
Plywood floors can be installed in different ways. It depends on the required result and initial parameters. Most often, plywood is used for leveling and as a base for other coverings. Let's look at the most common options.
Method I
Laying on a concrete screed. This procedure provides three alignment options:
- sheets 10-12 mm thick are glued directly onto the concrete base with a special two-component glue, the concrete base in this case must be smooth and of high quality, and the gap between the sheets, sheet and wall must be left at least 3-4 mm so that the material “plays”;
- plywood is installed on anchor studs, they can be twisted, adjusting the evenness of the surface; this method is used when there is a difference in height;
- a frame is made from logs and sheathed with plywood; the most labor-intensive option, used when insulating floors or raising them to a certain height.
Gluing plywood onto a concrete base Source remont-samomy.ru
Types of plywood by purpose
Plywood boards are used not only in the construction of buildings and interior decoration. The scope of their application is much wider.
Furniture plywood
It is wear-resistant and also environmentally friendly. In most cases, this is a combined FC plywood, suitable for use in conditions of moderate humidity.
Construction plywood
Birch-based slabs are ideal for almost all types of rough finishing.
Formwork plywood
Thanks to its increased strength and moisture resistance, FB plywood is capable of being used in aggressive environments.
Decorative plywood
In the production of plywood intended for fine interior finishing, high-quality veneers are usually used. In this case, ideally smooth outer surfaces of the outer sheets are assumed, on which textured patterns are also visible.
Automotive plywood
FSF plywood is used to cover the body parts of trucks. The boards typically have a laminated or sometimes mesh-ribbed outer surface.
Marine plywood
In shipbuilding, there is quite a demand for moisture-resistant FB sheets, the production of which uses bakelite adhesives.
Which plywood is best for flooring?
Before answering this question, there are two main aspects that need to be clear:
- what kind of floor you want to make from plywood: rough (underlay) or finishing (front);
- in which room will you lay the plywood floor: in residential (especially the bedroom and children's room) it is allowed to use only the FC brand: it is safe (there are no formaldehydes in the composition) + has a satisfactory level of moisture resistance; for industrial premises where there is good ventilation, you can take FSF plywood (only class I, which contains no more than 100 mg of formaldehyde per kg of sheet).
Only taking into account the above nuances can you choose the right plywood for the floor in each specific case. But there are a number of other parameters that a simple consumer cannot do without taking into account.
Base for laminate made of FSF plywood Source strojka-gid.ru
Plywood sheet sizes
The standard width of plywood sheets can be either 1220 or 1525 mm. The minimum length is 1525 mm, and the maximum reaches 2500 mm. Modern manufacturers mainly offer rectangular slabs with dimensions of 2440x1220mm, as well as square ones, for which the dimensions of the plywood sheet are 1525x1525mm. The exception is large-format products, for which the permissible length can reach 3050 mm.
Standard dimensions of plywood, mm.
1220x1220; 1525x1220; 1525x1525.
Large format plywood dimensions, mm.
1830x1525; 2440x1220; 2500x1250; 3000x1500; 3050x1525.
The thickness of plywood depends primarily on the number of layers. According to GOST requirements, there are regulated minimums and maximums - from 3 to 30 mm. At the same time, there are approved standards that allow some specialized enterprises to produce slabs with a thickness of 1 mm or more.
What criteria are important to follow when choosing
If you need to choose plywood for your floor among a wide variety of materials, you should pay attention to the following aspects:
- marking (only FC is suitable for living rooms);
- grade (the material is available in 4 grades: for rough coating you can take 3 and 4, for finishing you need to take 1 or 2 grades);
- class (for flooring only plywood of class E-1 is allowed;
- humidity (the quality of the sheets will depend on this, % should not exceed 12-15%);
- the number of layers in the sheet (the level of strength depends on it, but the thickness of the material should be chosen depending on its purpose: sheets of 12-18 mm are taken for the subfloor, and 10-12 mm for the front floor);
- sheet sizes (format and large-format plywood are produced, sheet parameters are prescribed in GOST 3916.1-96 and 3916.2;
- manufacturer (high-quality plywood, according to experts, is produced by European and domestic enterprises, while Chinese ones often do not meet the declared characteristics.
Main types of plywood Source stranapap.ru
Attention!!! It is important to remember that plywood is not suitable for buildings with significant temperature changes (country houses, premises for temporary residence). This also applies to rooms with a high percentage of humidity (bathrooms, baths, saunas, swimming pools, etc.).
See also: Catalog of companies that specialize in the design and construction of turnkey country houses.