Externally, wood looks like a dense fibrous material that is part of the trunk, roots and branches of trees of any species. Different types of wood differ in mechanical properties, thermal conductivity, ring pattern, and color.
Despite the differences, almost any type brings its own benefits to humans; it is used in construction, for heating, home decoration and for many other purposes.
Wood species and their use
Certain types of trees and their species are classified according to a number of characteristics. The most well-known division is into deciduous and coniferous species. There are species that grow on the territory of our state and other countries. From an economic and geographical point of view, this is a very important division, since the cost of imported wood may be higher than domestic wood in some cases.
Deciduous species, in turn, are divided according to their shape: ring-vascular and diffuse-vascular. And the latter can be distinguished by soft or hard wood.
Ring-vascular wood (ash, acacia, elm, oak, pistachio) received this name because the largest vessels are located closer to the center, in the early zones of the growth rings. In scattered vascular rocks (beech, hornbeam, rowan, maple), large vessels are dispersed more or less evenly. This changes the grain of the wood.
Both deciduous and coniferous trees are widely used in house building and other areas of construction technology. They are traditionally used to make such elements of building structures as walls, frames, partitions, rafters and other roofing elements. They are widely used in the manufacture of fences, porches, verandas (terraces), gazebos and a number of ancillary buildings.
Valuable wood
Speaking about different species, it is worth mentioning valuable species that are distinguished by their hardness, beautiful texture and other positive qualities, but are less common than other types of trees in a particular region. Valuable wood includes oak, walnut, alder, Karelian birch, maple and many exotic species. They are traditionally used in finishing decoration, as well as in the manufacture of furniture and shipbuilding.
Note! Fruit trees (cherry, black cherry, pear, apple, plum, persimmon and others) have an interesting texture and special physical and mechanical properties, so their wood is also considered a valuable species.
Certain types of cherries, for example, make wonderful inlaid souvenirs (snuff boxes and other attractive crafts). Finely chopped apple wood chips are traditionally used for smoking meat and fish. Pear is very popular among wood carvers; parquet, furniture, panels, and souvenirs are made from it.
Types and differences of wood
There are many types of wood, and you need to choose them depending on the purpose. Differences may be in:
- degree of hardness, and therefore durability of wood;
- characteristics of rings;
- sensitivity to moisture;
- resistance to solar radiation;
- blossom.
There are three main types of wood: hardwood, softwood and exotic.
Mechanical properties
Each of the rocks has certain physical properties, among which their ability to actively resist deformation and other mechanical influences is of particular interest.
The mechanical properties of wood are traditionally understood as its hardness, density, strength and elasticity to bending. The complexity of wood processing and the functionality of the future product depend on these qualities.
Strength and elasticity
The strength indicator refers to the ability of a material to resist deformation stresses leading to fiber rupture (for bending deformation, the strength indicator corresponds to the elastic modulus of wood).
The strength of the material critically depends on the following factors:
- direction of external force (along the fibers or across) and its speed;
- type (species) of wood;
- its density, humidity and the presence of obvious flaws (knots and cracks).
The presence of flaws in wood blanks significantly reduces their strength, but to a greater extent it depends on the vector of external loads.
With stresses along the grain, the maximum tensile load for most types of wood is 130 megapascals. The same parameter for compressive loads corresponds to 50 units, and for bending deformations it has a value of the order of 100 (note that for shearing effects it is only 0.5 megapascals).
Hardness
This indicator is directly related to the previous one and is understood as the resistance of wood material to the penetration of another dense body into it. It has been practically established that hardness in the longitudinal direction (along the fibers) always exceeds the same parameter in the cross section by approximately 30-40%.
For wood pieces dried to 12 percent moisture content, it is 1.5-2.0 times the hardness of the rawer material. As this indicator increases, the complexity of processing products also increases.
The hardness of a particular rock is determined experimentally using the Brinell method, and the data is entered into a table. The result is a hardness scale. At any time you can look at this indicator and draw conclusions about the hardness of the rock. There is a method and, accordingly, the Janka scale, as well as other methods named after the researchers who introduced them, but they are less common.
Plastic
When considering the characteristics of the structure of wood, its ability to hold various types of metal fasteners and hardware in the body of the material, as well as its resistance to impact splitting, is taken into account.
When assessing this property, it was found that to remove nails driven into wood across the grain, it is necessary to apply a force approximately 1.5 times greater than that driven into its end.
Important! It should be noted that the ability to hold nails and other fasteners increases in proportion to the increase in the density of a particular type of wood material.
Plasticity is directly related to resistance to splitting, that is, resistance to the separation of raw material when driving a wedge. The resistance of the material to this influence increases with increasing viscosity, and the presence of flaws such as knots, on the contrary, reduces it.
Main conifers
Of the coniferous species, pine should be especially highlighted, which occupies about 16% of the area of all forests in Russia. The most widespread is the so-called Scots pine, which mostly grows in the Crimea and the Caucasus. Wood of this species is classified as a soft material that can be easily processed and is most often used for the manufacture of windows, doors, and other building elements (staircases, for example).
Note! This easy-to-use type of wood material is often used in the manufacture of some furniture and household utensils.
Another representative of this group, spruce (fir), occupies up to 12 percent of all forested Russian areas and is widely used in the national economy. Coniferous spruce material, due to its increased knotiness, can be processed with great difficulty, but despite this, it attracts the user with its uniform structure, pleasant white tint and low content of resinous substances.
This grade is often in demand in the manufacture of building blocks, floorboards, platbands and baseboards. Selected spruce wood can also be used in the production of household furniture for the purpose of decorating residential interiors. From its bark they learned to make tanning materials widely used in the leather industry.
Larch is very common in our country and occupies most of the forest plantations. Its material has excellent physical characteristics and is noticeably superior in density and strength to those of pine. In addition, larch fibers are practically resistant to rotting and provide products made from this material with high strength properties.
The areas of use of larch wood are wide. It is used in the construction of hydraulic structures, in the manufacture of piles, sleepers, telephone poles and support posts for mines. Another representative of coniferous species (cedar) is very similar in its properties to spruce and can be used to make sleepers, racks, furniture and pencils.
The yew wood material is valued for its attractive appearance, which allows it to be used in the manufacture of luxury furniture, as well as in the decoration of interiors. The familiar juniper should also be included in the category of coniferous wood.
Furniture
Wood is the main raw material for the production of furniture, including luxury furniture. At the same time, different types of wood are used to create different types of furniture:
- Softwood (cedar, spruce, pine, chestnut, alder, willow, poplar, etc.)
- Hardwood (apple, walnut, ash, rowan, birch, beech, etc.)
- Very hard species (boxwood, hornbeam, pistachio tree, acacia).
The hardness of the raw materials has a direct impact on the service life of furniture sets and individual products made from natural wood. However, furniture is made from wood of all listed types, and in all cases it can be of high quality. The main influence on the formation of the cost of the finished product is the finishing of the material and the final appearance of the furniture.
Exotic wood species
Exotic wood species for our latitudes include sequoia, ebony and mahogany, as well as buckout and rosewood. Sequoia is a family of the largest and most durable woody plants and is found primarily in North America.
There are known examples of these trees with a height of almost 120 meters and a girth diameter of up to 15 meters (their estimated age is about 6 thousand years). Sequoia is successfully cultivated in the southern extremities of Crimea and in other areas of the Black Sea region. In its properties it resembles Russian spruce, but unlike that it is more resistant to rotting. It, like African abacha, is often used in the production of furniture and pencils, as well as in interior decoration.
The name “mahogany” in the generally accepted classification refers to a number of durable wood species (including merbau) that have a characteristic reddish tint.
Additional information: the most popular and unsurpassed variety of mahogany in color and beauty is American mahogany, found only in Central America.
One of the varieties of exotic wood called African padauk is widely used in the production of luxury furniture. Due to its strength characteristics (high hardness), trees of this variety are used for finishing carriage interiors and cabins.
Black refers to species that have a characteristic dark shade of fibers (these include elite varieties of ebony from India, in particular). This type of “colored” wood is used for the manufacture of piano keys, wind instrument bodies, and also for inlaying luxury furniture.
Buckout is an evergreen woody plant, often found in the subtropics, with a dense and hard structure with a vanilla scent. It is very difficult to machine and is most often used for the manufacture of especially durable parts of machine tools and machines. Somewhat similar to backwood, rosewood is very hard, but easy to polish. It is in demand in the manufacture of luxury furniture, parquet sets and musical instruments (pianos, in particular).
Hardwood
Particular attention should be paid to deciduous trees. After cutting down the coniferous forest, they fill the empty area. Deciduous types of wood are used most widely and variably.
Ring-vascular structures
The basis of deciduous species is made up of such ring-vascular representatives as elm, elm, ash, elm and oak. The last of this family - oak - is found in many places in European Russia, and also grows in the southern outskirts (in the Crimea and the Caucasus). The peculiarity of its wood is its high hardness, strength and resistance to rotting. In addition, common English oak is distinguished by its bending ability, very attractive texture and rich color.
Common ash is often found in most regions of the European part of Russia. The properties of this type of wood are very similar to the characteristics of oak already discussed above (it also has a high hardness index and bends well, that is, it has good ductility).
Due to its properties, ash is used in the production of various types of sports equipment (tennis rackets, skis and oars), as well as in the automotive, aviation and ship industries. In addition, it is often used to make stair railings and handles for various tools.
Disseminated-vascular soft rocks
Birch is the tree symbol of Russia and grows everywhere on its territory. It is widely used in the domestic industry for the manufacture of plywood, butts of hunting and sporting rifles, skis and veneer. In addition, wood boards of various classes, parquet floors and tar are made from birch.
Poplar, aspen, alder, willow and linden have a very similar structure and, due to their softness, are most often used as ornamental wood to satisfy household and construction needs. These wood structures are used to make troughs, shovels, household utensils and pulp.
In addition, some of them are used to produce box containers, viscose, wood shavings, toys and roofing tiles.
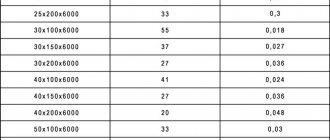
Timber
Wood materials and products are usually divided into several main groups:
- Timber produced by mechanical processing of wood. These include round, sawn, peeled, and planed materials.
- Chips and by-products: wood flour, sawdust, shavings, wood chips.
- Modified wood treated with synthetic resins, plasticized with ammonia, etc.
- Wood products (plywood, chipboard, wood panels, fiberboard, wood-laminated plastics, etc.)