Wood pyrolysis: concept and products
Wood pyrolysis (dry distillation of wood) is the decomposition of wood when it is heated to a temperature of 450 °C without oxygen. As a result of this process, gaseous and liquid (including tree resin) products are formed, as well as a solid residue - charcoal.
The technology and process of wood pyrolysis is one of the first technological chemical processes known to mankind. Starting from the mid-12th century, this technology was widely used in our country to produce pine resin (which was used to impregnate ropes and tar wooden ships). This trade was then called tar smoking.
When metallurgy began to develop, another trade arose, which was also based on the dry pyrolysis of wood - charcoaling. In this case, the final product of pyrolysis was charcoal.
The beginning of the spread of industrial use of wood pyrolysis can be considered the 19th century.
The main product of pyrolysis then was acetic acid, and only hardwood was used as a raw material.
The process of wood pyrolysis is based on various free radical reactions of thermal destruction of cellulose, lignin and hemicelluloses, occurring at temperatures from 200 to 400°C. Wood pyrolysis is an exothermic process, which produces a fairly large amount of heat (about 1150 kJ/kg).
The technological scheme of wood pyrolysis includes the following stages:
- cutting wood raw materials into pieces
- drying cut wood
- direct pyrolysis
- cooling and stabilization of coal (to prevent spontaneous combustion);
- complete condensation of vapors of volatile products.
The longest and most energy-intensive stage of all those listed above is drying the wood to a moisture content of 15%.
Wood pyrolysis products
Currently, hardwood is usually used to carry out the process of wood pyrolysis, but sometimes (mainly during complex processing of raw materials) coniferous wood is also used. Modern pyrolysis technologies make it possible to obtain from birch wood:
- charcoal - 24-25% charcoal,
- liquid waste (so-called slurry) - 50-55%
- gaseous products - 22-23%
The larger the size of the pieces of wood taken for pyrolysis, the larger the solid residue will be. The charcoal obtained as a result of pyrolysis, after the sorting procedure according to the size of the pieces, is sent directly to the consumer or for processing.
When processing the liquid obtained as a result of pyrolysis, wood resin (which is approximately 7-10%) settles and at the same time numerous transformations of the components occur.
A wide range of valuable products can be distinguished from resin. As a rule, acetic acid is isolated from the liquid.
It is usually extracted from the liquid by extraction, and then, through rectification and thorough chemical purification, it is processed into a food product ready for sale.
Gaseous products of wood pyrolysis (non-condensable gases) include:
- carbon dioxide CO2 (approximately 45-55%)
- carbon monoxide CO (28-32%)
- hydrogen H2 (1-2%)
- methane CH4 (8-21%)
- other hydrocarbons (1.5-3.0%).
The composition of gaseous products of wood pyrolysis depends on the pyrolysis temperature, speed and heating method. The heat of combustion of gaseous products ranges from 3.05 to 15.2 MJ/m³. All of the above factors, as well as the type of wood, its quality and humidity, determine the final yield of pyrolysis products.
With increasing temperature, the yield of wood resin and gaseous products increases, but the yield of charcoal, alcohol products and acetic acid decreases. Coal, as a result of increasing temperature, is formed with a higher percentage of carbon. The average yield of the main products of wood pyrolysis is (based on dry wood):
- charcoal - 23-24%
- tree resin - 10-14%
- acetic acid - 5-7%
The technology for wood pyrolysis is quite diverse, but most of the devices used in world practice are hopelessly outdated and do not meet all modern requirements.
In addition, the need for wood pyrolysis is constantly decreasing, since destroying such environmentally friendly raw materials is quite wasteful.
However, the technology of sawdust pyrolysis is beginning to become increasingly popular.
Pyrolysis of sawdust
Pyrolysis of sawdust is the most profitable way to dispose of wood waste. Thanks to this technology, waste from the wood processing industry does not need to be taken to a landfill for disposal, but can be used to generate heat and electricity.
In recent years, this use of wood waste has begun to be seen as an excellent alternative to traditional fuels. All this is directly related to the fact that sawdust as a fuel has a number of advantages:
- they belong to renewable sources of thermal energy
- are completely CO2 neutral
- There is practically no sulfur in sawdust
- it is possible to burn wet waste (containing up to 55 - 60% moisture)
- The corrosiveness of flue gases is quite low
- low, compared to fossil fuels, price of raw materials
Using wood waste as fuel is not only much less harmful to the environment, but also saves money.
This way of saving non-renewable natural resources can allow Russia to get closer to more developed countries in terms of such an indicator as the specific energy intensity of industrial production, which makes it extremely attractive.
And all this leads to the fact that sawdust pyrolysis technologies have been constantly developing and improving in recent years.
Sawdust disposal
The service life of most devices used for dry distillation of wood in industry is ending, and there is a need to update the technical equipment at enterprises. The processing of sawdust is becoming an increasingly popular pyrolysis technology. Companies install special equipment for this.
Constantly disposing of trees is a wasteful activity, but recycling sawdust is a rational use of a resource.
The product obtained from pyrolysis is a cheap fuel that can be produced regularly if there is enough wood.
Wood pyrolysis: process description, raw materials, gas composition
Most of the wood is made up of organic compounds.
Under the influence of high temperatures under vacuum or minimal air flow, they break down into solid, semi-liquid and gaseous components.
This process is called dry distillation, tar smoking, pyrolysis. It differs from combustion in the greater preservation of decomposed components. Chemical reactions take place very quickly and without the formation of flames or smoke.
Distillation technology appeared in the 12th century . At that time, pine and other coniferous species were used as raw materials. From them they extracted resin for impregnating wooden parts of ships and ropes, and charcoal. In the 19th century, acetic acid was produced through the destruction of carbon-containing mass.
The essence of the process
Normal combustion of wood with the participation of oxygen leads to ignition and evaporation of the released gases, the complete destruction of solid components, turning them into smoke, soot, ash and ash. The flame temperature reaches 1000°C. Pyrolysis is also thermal destruction.
The result of this process is the formation of decomposition products of lignin, cellulose and hemicellulose. Dry distillation is carried out in a closed space at a constant temperature of 250–450°C; the resulting gases and liquid components released are immediately removed and cooled. The process is accompanied by a large release of heat, but smoke and soot are not formed .
The resulting residues can then be used for industrial or household purposes.
Procurement of raw materials
The starting material used is wood that is of little use for other needs, and production waste, including sawdust. It is customary to distinguish several groups of raw materials:
- hardwoods: beech, birch, elm, oak, hornbeam, maple, ash;
- soft-leaved: linden, alder, aspen, poplar;
- conifers: larch, pine, cedar, fir, spruce.
There are strict production regulations, according to which all timber arriving at processing plants is sawed, cut and collected into piles of a certain width and height in special warehouses. They are placed on flat areas, providing access to air and lighting.
Preparation for pyrolysis involves preliminary drying . This process can be difficult, especially when working with solid aspen or poplar, which, with increased dampness, are prone to fungus infection and the development of rotting.
Drying is carried out naturally in the ventilated area of warehouses. To speed up the process, the material is split into small pieces. Air-dry wood is considered suitable for further processing: about 12–15%.
Sometimes quick drying is used: the massif is crushed, placed in an oven or blown with dry hot air.
Equipment
Wood decomposition is carried out in retort ovens. The bodies are cylindrical containers welded from metal. The thickness of their walls is about 15 mm. There is a loading opening, inside there are gratings for placing raw materials, a system for supplying coolants, removing and cooling the released liquid products, gases and charcoal, at the bottom there is a port for unloading the resulting components.
Industrial equipment comes in different sizes. More often, large furnaces are used, the combustion chambers of which are about 2–2.5 m in diameter. The following heating systems are used:
- external: the metal walls of the retort heat up, starting the process of wood decomposition;
- internal heat supply: the temperature is maintained by a mixture of released gases; their efficiency is usually several times lower than that of those heated from the outside.
Equipment can be continuous, semi-continuous and batch . In the first case, all stages of the cycle occur simultaneously.
When the next batch of wood comes inside, the finished coal is unloaded from the outlet. Semi-continuous devices have an orderly process. First, the first batch of raw materials undergoes complete processing; after unloading, the next one arrives.
The type of equipment affects the rate at which wood decomposes.
There are boilers similar to industrial ones, but more compact. They are designed for pyrolysis on a small scale.
The result of distillation is influenced by the conditions in which the process occurs and the state of the incoming material.
Distillation process
If the loaded batch of wood is not dry enough, after grinding it is dried in a closed chamber at a temperature of 130°C. This stage is the most energy-intensive, since it requires an external heat source. The evaporation of moisture is accompanied by the primary decomposition of some wood components.
Further heating to 155–200°C leads to the beginning of the release and evaporation of gaseous substances.
Direct decomposition of the entire mass of material occurs upon subsequent heating to 280–420°C. In this case, resins, acetic acid, and carbonyl compounds are released and removed. At the same time, charcoal is formed.
The final stage is calcination. The temperature inside the retort rises to 500°C and above. Heavy resins and carbon compounds are removed from wood residue. Then the products are cooled and unloaded from the chamber.
The amount of material obtained, the speed of the process and energy costs depend on the type and size of pieces of wood and equipment systems . Fast pyrolysis using external heat sources produces larger quantities of coal and high purity at relatively low energy costs.
Pyrolysis products
The main components for which wood is distilled are coal and acetic acid.
Coal
The amount of solid residue obtained depends on the type of wood. For hardwood beech and birch, the yield is about 25% of the primary material. In coniferous species it is slightly higher. Soft-leaved plants produce the least coal. Pyrolysis of sawdust produces coal flour. At the same time, the yield of liquid residue is higher.
High-quality coal has no cracks, brown or whitish deposits, and burns without smoke. A defective product is obtained when the pyrolysis technology is violated: insufficient temperature, air penetration into the furnace.
Charcoal is an environmentally friendly and affordable type of fuel, which is used for industrial and household stoves and home fireplaces.
It releases a large amount of heat, produces virtually no by-products or odor during combustion, and has a low cost.
Coal is used in the metallurgical industry, agriculture, for the production of filters, plastics, dyes, glass, and medicines.
Condensate
Liquid pyrolysis products, or condensate, contain resinous compounds called slurry. Its amount reaches 50% of the total residue and depends on the type and moisture content of the wood, and the type of pyrolysis.
The liquid contains ketones, resins, aldehydes, alcohols, esters, and water.
As a result of multi-stage reactions, acetic acid is formed from it - a compound used in the chemical, textile, pharmaceutical, cosmetology, and food industries.
Formic and butyric acids, acetone, methyl and isopropyl alcohols, formaldehyde, and resins are obtained from the liquid.
Gases
Gaseous compounds released as a result of distillation are formed in an amount of 20–25%. The composition of pyrolysis gases includes:
- CO: 40–50%;
- CO2: 28–38%;
- CH4: 8–20%;
- H2: 1–2%;
- carbon impurities: about 1%.
On average, during dry distillation of 1 m³ of wood, about 70–80 m³ of gaseous compounds are released.
Distilling wood at home
You can also perform pyrolysis of wood or its waste at home. In this case, you will only be able to get coal.
Large-volume metal barrels are used as a retort . Chemical containers must not be taken. A clean container with several small holes to allow gases to escape is required.
First, prepare the platform:
- A large sheet of iron is placed on the ground.
- Several refractory bricks are placed on the edge, and firewood is laid between them.
- They make a fire.
The barrel is filled with dried chopped wood and hermetically sealed. After that, it is placed on a platform with a fire. When the container gets hot and oxidation begins, gas will come out of the holes. The process may take several hours.
When the gas output stops, the barrel is left on the fire for 30 minutes . After cooling, remove the lid and take out the finished charcoal. It can be used to kindle baths, home stoves, and fireplaces. After distilling the sawdust, the resulting flour is added to garden soil and used to process plant cuts.
What is pyrolysis - description of the process
Theoretically, you can burn any substance that includes compounds of carbon and hydrogen, for example:
- coal;
- natural gas (methane, propane, etc.);
- biomass – fresh, dry;
- wood products, cellulose, ordinary firewood;
- various types of plastics;
- rubber made from natural or artificial rubber;
- oil, its derivatives;
- other carbon-containing waste.
At the output you will receive a certain amount of thermal energy, depending on the initial moisture content of the burned mass. To describe the processes, we use the chemical formula:
Combustion is a rapid oxidation reaction. Under ideal conditions, each carbon atom combines with two oxygen particles, and 2 hydrogen atoms interact with 1 oxygen particle. As a result, harmless compounds are formed - carbon dioxide CO2 and water. The latter evaporates when heated, taking away part of the released heat.
Important point. In real conditions, not all hydrogen and carbon atoms find a pair due to the lack of oxygen molecules. Therefore, the composition of combustion products includes a small proportion of harmful flammable compounds - carbon monoxide (CO), free hydrogen (H2) and carbon in the form of soot.
Even in a fire, pyrolysis gases are released - they burn above the main flame, combining with free oxygen.
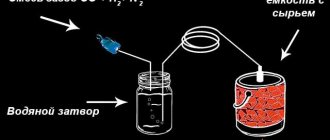
Pyrolysis is a decomposition reaction of a substance that occurs when heated and there is a lack of free oxygen. This principle is used in gas generating plants:
- Fuel (in particular, wood) is placed inside a closed metal vessel - a reactor.
- The container is heated from the outside to 500...900 degrees, and a dosed amount of air is supplied through special holes - tuyeres.
- Under the influence of high temperature, the substance decomposes into 3 main components - carbon monoxide (CO), hydrogen (H2) and solid or liquid carbon residue. At the same time, a small amount of carbon dioxide and water vapor is formed.
- The volatile products constitute pyrolysis gas, a flammable mixture of hydrogen and carbon monoxide that leaves the container through a separate pipeline. The separated gaseous fuel is purified, cooled, and then pumped into the tank.
Diagram of the simplest gas generator installation with a water seal
Reference. Under production conditions, the resulting synthesis gas is sent to heat the same gas generator tank.
Combustion and pyrolysis are 2 different processes that can occur simultaneously. Example: during intensive burning of wood, a small volume of carbon monoxide is formed in the boiler furnace, while harmless CO2 is much larger. And vice versa, in smoldering mode, firewood releases a lot of hydrogen and carbon dioxide, some of which manages to turn into CO2 and oxidize. That is, it all depends on the amount of oxygen involved in the reaction.
Wood pyrolysis
Wood pyrolysis is also called dry distillation. This process is the decomposition of wood under high temperature conditions of up to 450 °C without oxygen. As a result of this process, gaseous and liquid (including tree resin) products are obtained, as well as solid material - charcoal.
Wood pyrolysis technology
Pyrolysis is one of the first technological chemical processes known to mankind. Back in the middle of the 12th century, this technology was actively used to obtain pine resin, which was used to impregnate ropes and tar wooden ships. This process was then called tar smoking.
With the beginning of the development of the metallurgical industry, another industry arose, based on the dry pyrolysis of timber - charcoaling. In this process, the final material was charcoal.
The beginning of the spread of industrial use of wood pyrolysis can be considered the 19th century. The main product of pyrolysis in those days was acetic acid.
The raw materials were only deciduous timber.
The pyrolysis process is based on various free radical reactions of thermal destruction of cellulose, lignin and hemicelluloses. These reactions occur at temperatures ranging from 200 to 400°C. Wood pyrolysis is an exothermic process that produces a large amount of heat (approximately 1150 kJ/kg).
The technological scheme for pyrolysis of timber consists of the following stages:
- wood shredding
- drying chopped wood
- pyrolysis
- cooling and stabilizing coal to prevent spontaneous combustion
- the process of condensation of vapors of volatile products.
The most time-consuming and energy-consuming stage is drying the wood to a moisture level of 15%. Drying is carried out at temperatures of 130-155°C using external heat. This removes water from the timber and changes some of the wood components.
After this, the wood begins to decompose. This happens within the temperature range from 155 to 280°C. At this stage, its least stable components disintegrate. In this case, carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, and acetic acid are released.
Then the temperature rises to 280-455°C. Under these conditions, evaporation begins and the formation of the main volume of wood decomposition products begins.
In this case, there is an active release of heat (exothermic process) with the release of large amounts of CO2, CO, CH4, ethers, carbonyl compounds, hydrocarbons, acetic acid, its homologues and methanol. At the very end, the resin is removed.
Then the calcination of the wood residue begins. The temperature rises to more than 500°C. During this process, heavy tar is released and removed, as well as CO2, H2, CO and hydrocarbons. This is the end of pyrolysis, and the resulting residue is charcoal.
The volume of wood pyrolysis products obtained varies greatly, it all depends on the size of the pieces of timber, the temperature of the process, its duration, and the moisture level of the raw materials.
Devices for pyrolysis
This process takes place in retorts. A retort is an all-welded cylindrical metal vessel. Inside, it has a diameter of 2.5 to 2.9 m, and the wall thickness is 15 mm.
At the top of the device there is a loading device for raw materials, and at the bottom there is a conical part and an unloading device for coal. The retort has a height of about 25 m. The retort is equipped with four pipes.
The vapor-gas mixture is removed through the upper pipe, the coolant is introduced through the second, the third removes heated gases from the coal cooling area, and through the fourth, the lowest, cold gases are introduced that cool the coal.
Retorts are:
- continuous action
- periodic action
- semi-continuous action.
In addition, based on the heating principle, there are:
- devices with internal heating. In such devices, heat is supplied to the timber from the coolant through direct contact. The coolant is hot flue gases, which are forced into the device. In this case, the pyrolysis process is carried out more gently, but the volume of decomposition products is approximately 7-10 times less
- devices with external heating. In such devices, heat is supplied through the metal walls of retorts, which are heated by hot flue gases.
The most common are semi-continuous devices. Wood is loaded into them periodically, in small quantities at equal intervals of time. The steam-gas mixture is taken continuously, and coal is unloaded periodically, in portions.
In continuous devices, all stages of the process occur simultaneously: drying occurs in the upper part, then the timber is heated to the decomposition temperature, in the middle part the wood decomposes, and in the lower part the coal is calcined and cooled.
Rapid pyrolysis of wood
A fairly common type of pyrolysis can be called fast pyrolysis, during which thermal energy is supplied to the original mixture at high speed. The entire process takes place without oxygen.
The process of slow pyrolysis can be compared to bringing water to the boiling point, but the fast pyrolysis method can be compared to dropping a drop of water into hot oil, which is otherwise called explosive boiling.
The main features of rapid pyrolysis of timber:
- the possibility of forming a closed, continuously flowing technological production process
- significant “purity” of the final pyrolysis products, which is achieved due to the absence of a resinization stage
- low energy intensity of this process compared to other types of pyrolysis
- in this process, a large amount of thermal energy is released (exothermic reactions during rapid pyrolysis are superior to endothermic ones).
Yield of thermal decomposition products
Raw materialsThermal decomposition products, wt. % by weight a. With. e.coal,tars,volatile components,gases,water
| Spruce | wood | 37,9 | 15,3 | 6,3 | 18,2 | 22,3 |
| bark | 42,5 | 18,4 | 1,9 | 19,8 | 17,4 | |
| Pine | wood | 38,0 | 16,7 | 6,2 | 17,7 | 21,4 |
| bark | 40,5 | 18,2 | 5,7 | 19,7 | 15,9 | |
| Birch | wood | 33,6 | 14,3 | 12,3 | 17,0 | 22,8 |
| bark | 37,9 | 24,0 | 4,7 | 18,6 | 14,8 | |
| Aspen | wood | 33,0 | 16,0 | 7,3 | 20,4 | 23,3 |
Handyman
What is the very essence of dry distillation of wood?
The essence of dry distillation of wood is to separate the required substances from the wood. To do this, the wood is pressed into the apparatus and subjected to heating without access to fire or air. Under the influence of heat, sometimes very high, wood decomposes and releases the required products. These products are light - gaseous, volatile and heavy - liquid. This means that an apparatus is needed, i.e. .room for wood. The device, of course, obviously must be iron, well closed so that air and fire do not penetrate into it. The device must have two outlets - tubes: one up for light gaseous products, and the other at the bottom for heavy, liquid products. Gaseous volatile products must then be cooled. As a result of cooling, they turn into droplets and will flow out of the tube as a liquid. This means that the upper tube needs to be inserted into another device - a refrigerator. The refrigerator can be made of wood. The longer the tube that removes volatile products is, the more complete their cooling will be, they will completely turn into liquid, and not a drop of them will fly into the air. Therefore, the outlet tube is made elbow or helical. Such a tube is called a coil. Cold water must flow into the refrigerator to cool the walls of the coil tube . The colder the water, the better. The water will heat up. The heated water will have to be removed from the refrigerator. Therefore, it must have a tap for draining water or a wooden plug (plug). The coil will cool the gaseous products. They will turn into liquid. The liquid will flow along the coil. This means that in order to collect it, the end of the coil needs to be taken out of the refrigerator. Under the end of the coil coming out of the refrigerator, you need to place a container to receive liquid. Heavy products will collect at the bottom of the apparatus, which is filled with wood. To release them, there must be a hole in the bottom of the apparatus with an outlet tube. A vessel should be placed under this tube to collect them.
What basic requirements must a device for dry distillation of wood meet?
The apparatus into which the wood is loaded must be heated strongly by fire. Therefore, it needs to be covered with bricks so that the flame covers it all the way. Below is a firebox for firewood. The apparatus is placed on the walls of the firebox. Slots need to be made on all sides of the apparatus - chimneys for smoke and flame. These chimneys must go into a common chimney - a pipe. The apparatus itself should not release gaseous products. It must be well riveted from thick iron. To load the material, there must be a hole in it - a cover. When the device is loaded, the lid must be well lubricated so that gaseous products do not escape into the air. The tube for removing gaseous products must be well soldered so that these products do not escape through its seams. The longer the tube, the better it will cool the basin. The refrigerator must be so spacious that the coil tube fits freely in it and that the water covers the coil in a thick layer on all sides.
How to start producing experiments. It goes without saying that funds are needed to construct the apparatus. Not everyone can spend these funds. Besides, every person may have doubts: I will spend money, but will anything come of this venture? Therefore, first try to make do with the means that can be found everywhere, in every household, without special expenses. Take a cast iron pot, in which water is heated in a bathhouse, and adapt it to load wood.
Rice. 1. On the left is a cross-section of a cast iron boiler. There is a brick at the bottom. There is an iron grate on the brick. On the right is the grate.
Heavy foods should accumulate at the bottom of the pot. Therefore, you need to make sure that the bottom of the pot is free. To do this, place a brick on the edge on the bottom of the cauldron in the middle. From a sheet of old roofing iron, make a circle of such a size that it fits on the brick. Punch holes in this circle so that heavy food can flow through them to the bottom of the pot (Fig. 1). Load the material onto the iron circle-grid. Lay it more tightly (Fig. 2). Make a wooden lid for the pot so that it fits tightly into the edges of the pot. Make a round hole in the lid to allow gaseous products to escape. The hole should be 4 1/2 centimeters (1 inch) in diameter. For the refrigerator, take an ordinary tub - 6 buckets of water. Take an old, used tub. It doesn't matter if it leaks a little water. Make two holes in the tub. One hole is needed to release heated water. Its diameter is not required.
Rice. 2. On the left is a sectional view of a boiler loaded with material and covered with a wooden lid. On the right is the cover.
Fit a wooden plug to this hole. The other hole should be in the lid of the tub, slightly larger than the diameter of the end of the coil tube that discharges gaseous products (Fig. 3). The tube that removes gaseous products must consist of two components. The first part should have the shape shown in Fig. 4.
The part of the tube that connects to the lid of the pot should be widened and have bent edges so that it can be attached with nails, or even better, screws, to the lid of the pot. Three holes for nails or screws should be punched in the bent edges (Fig. 4). The diameter of the coil tube should be 2 centimeters (Fig. 5). The pipes must be ordered from a roofer or tinsmith. It would be nice to make them out of white iron. The refrigerator needs to be 1 meter away from the stove in which the pot is embedded so that it does not warm up from the stove. Therefore, the length of both tubes will depend on the installation of the entire apparatus. The tubes must be well soldered and fit tightly into each other at the junctions. The refrigerator should be placed on a stand to make it easier to place the product receiver. Any utensil can serve as a receiver: a pot, bowl or bucket. When everything is ready, you need to put everything together into one whole, into one system. After loading the wood, the lid of the pot must be coated with crumpled clay. To make the coating stronger, sifted ash should be added to the clay.
Rice. 6. The entire device is assembled. To the left is the stove for heating the boiler. It would be a good idea to place the outlet tube on glass. You can prepare the putty yourself: take powdered chalk and knead it, like kneading dough, in boiled linseed oil (linseed oil). How to arrange everything is shown in Fig. 6. This device will suffer from some disadvantages. Firstly, liquid products will burn at the bottom of the pot, and as a result, their quality will deteriorate. The coil and refrigerator may not cool all the gases and the product yield will be less than it should be. But you will have to come to terms with these shortcomings for the first experience.
The site contains:
Decoupage styles Types of bathtubs and their care We repair them ourselves We install ventilation grilles ourselves Floor coverings made of quartz vinyl tiles How to make a kitchen floor Methods for extracting essential oils How to extract tar from birch bark (birch bark)
We use sawdust pyrolysis at home to produce fuel
Any wood waste can be used to produce flammable pyrolysis gas.
In terms of volume/heat release ratio, pyrolysis gas is inferior to natural gas (the difference is 25–50% in favor of natural gas), so it can be used in conventional boilers , but in larger volumes.
In addition, pyrolysis gas can be used as fuel for automobile engines, but the power will be lower by:
- 20–40% compared to liquefied natural gas (propane, methane, butane);
- 30–50% compared to gasoline.
Nevertheless, the car will drive , and fuel costs will be significantly lower. After all, when driving in normal modes, the engine is never used at full power.
The only disadvantage of using pyrolysis gas will be lower acceleration during acceleration, that is, it will be more difficult to overtake cars on the highway.
In this article we will talk about:
- what is pyrolysis;
- what equipment is used for pyrolysis;
- how pyrolysis gases are purified;
- How are pyrolysis gases used?
What is pyrolysis?
Pyrolysis is the thermal decomposition of wood , as a result of which cellulose breaks down into:
- hydrogen;
- carbon monoxide (CO);
- nitrogen;
- water vapor;
- carbon dioxide (CO2).
Pyrolysis begins at a temperature of 300–400 degrees and occurs in the absence of oxygen.
However, a self-sustaining reaction requires a small amount of oxygen to keep some of the wood burning and maintaining a high temperature. Therefore, in pyrolysis plants the process occurs with a strong oxygen deficiency (15–30% of the required).
If more oxygen is supplied, the pyrolysis gases will burn directly in the installation.
During the pyrolysis process,
wood breaks down into various gases and a small amount of inorganic residues, so the formation of ash in pyrolysis plants is tens of times less than during conventional combustion of wood waste.
The efficiency of pyrolysis directly depends on the moisture content of the wood - the wetter the wood, the more heat is needed for thermal decomposition and the more water vapor in the pyrolysis gas.
Therefore, wood waste is pre-dried in special installations, which you can read about in the article Equipment for wood processing.
The process of pyrolysis can occur in any organic matter, but most often wood waste, branches and other similar materials are used to produce gas.
The calorific value of the finished fuel is affected by the density and humidity of the source material, and by density we mean the specific gravity of the wood.
The wetter the fuel, the more energy will be expended to maintain the pyrolysis process and the higher the water vapor content at the outlet.
Along with sawdust, shavings and chips from healthy or diseased wood, as well as any waste from dry wood processing and processing, can be loaded into the gas generator.
In addition, even fallen leaves and tree bark can be used as fuel, but their calorific value is much lower than that of healthy wood, so the operating time of the gas generator on one load of fuel will be much shorter.
Gas generating units
Apparatuses and devices for producing pyrolysis gas are called gas generator units.
They are a sealed stove with adjustable air supply and the ability to shut off the chimney.
To reduce the requirements for the chimney, air is forced into them using centrifugal pumps.
Moreover, they either use a pump with variable performance (this is done using a frequency converter), or install several pumps to ensure maximum air supply in ignition mode.
When the contents of the installation flare up,
the air supply is reduced, leaving only the minimum necessary to maintain the optimal temperature.
As a result, thick black smoke begins to emerge from the installation, which contains unburned carbon (soot) and pyrolysis gases.
This gas cannot be used immediately due to the large amount of soot, so it is purified using various devices, the most popular of which are cyclones.
The soot collected by the cyclone can either be loaded with wood waste into a gas generating plant or sold to tire manufacturers. After all, soot is one of the main components, the share of which reaches 30%.
In addition, water vapor is removed from the pyrolysis gas, which increases its combustion temperature. To do this, the gas is passed through a cooler, where the water vapor condenses into water droplets.
As water accumulates, it is drained through a special tap located at the bottom of the cooler.
After this, the gas is fed into a fine filter, which uses electrostatic devices, cardboard cartridges and a container of water.
Electrostatic devices operate due to the different electrical capacitance of gas and any solid particles.
Under the influence of static electricity, solid particles stick to the positive or negative electrode (depending on the electrical potential of the particle), and the gas passes through without obstacles.
The electrodes must be periodically
cleaned of soot adhering to them.
Cardboard filters work on the principle of a mesh - they allow gases and solid particles to pass through them, which are smaller than the size of the pores that permeate the entire cartridge, so it has to be changed regularly, which is not cheap.
The water in the container does not retain the gas, but does trap the smallest solid particles of soot. As the water becomes dirty, drain it and add new water. The drained water is evaporated to produce soot, which is then either sent to a gasification plant or sold to tire manufacturers.
Despite the fact that sawdust is also wood and the basic principles of obtaining gas from it are the same, conventional gas generators cannot be used .
This is due to the peculiarities of air movement through the fuel mass.
Large wood waste does not adhere tightly to each other , so air between them easily passes in any direction.
When the fuel container is filled with sawdust, air passes between them very little, just as pyrolysis gas cannot pass through.
Therefore, in installations designed to produce pyrolysis gas from sawdust and shavings, air is supplied in several places , and the gas outlet hole is located at the top.
When planning to buy a gas generator, do not forget to check whether it is designed to work on sawdust and shavings. After all, generators designed for processing large waste do not work well with small ones , but those designed for small waste can process large ones.
Cost of gasifiers
We have prepared a table that includes the most popular models of gas generator units.
Most of them are designed for use with heating boilers, but they can be adapted for other purposes.
In addition, we included a semi-industrial gas generator for a car in the list. To clarify its parameters and select the most suitable one for your car, you need to contact the supplier using the link given in the table.
| Model | Additional functions | Power/Performance | Price thousand rubles | Seller or manufacturer website |
| KDO-1 | A gas generator with a combustion chamber and a heat exchanger for heating water (boiler). Possible purchase without heat exchanger and combustion chamber | 15-100 kW | 169 | bmpa.info |
| KSDO-125 | Gas generator with control panel and water heating boiler. If desired, another boiler can be installed, and it is also possible to purchase a complex without a boiler | 125 kW | 495 | tayur-kotly.ru |
| KH-100V | Gasifier without additional equipment | 100 m3 of gas per hour | 2700 | ooo-smog.promportal.su |
| UGK | Gas generator for car | 50-100 kW | 460 | belgorod.promportal.su |
| UDSO-60 | Gasifier without additional equipment | 60 kW | 300 | pifmaster.ru |
The high cost of industrial and semi-industrial gas generators forces many to make these devices themselves. Moreover, there is nothing particularly complicated about it.
We have prepared links to thematic forums where the manufacture of various models of gas generators is discussed.
There you will also find tips to make it easier to find materials for making this device, as well as various recommendations that will help you choose one or another model for self-production.
Here are links to thematic forums:
- Forumhouse – manufacturing of an automobile gas generator.
- Moonshiners forum - making a gas generator from a pyrolysis boiler.
- Vasdom - making a gas generator and discussing various models.
- OstmetallInfo - manufacturing a gas generator for a forge and discussing its advantages and disadvantages.
Methods of using pyrolysis gas
This gas is used for various needs.
connect a kitchen stove to the gas generator and the fire on it will be only slightly less than that obtained by burning propane or butane.
You can connect an autogen to it (better cleaning will be required) and when oxygen is supplied, the flame temperature will reach two thousand degrees.
electric generators and car engines work well on this gas .
A gasoline car engine, after a little modification, works well on gas produced by a gas generator unit.
A diesel engine can also run on such gas, but a more serious modification of the fuel system will be required.
full power from such an engine , but it will produce ¼ to ½ if the gas generator’s performance is sufficient.
In the context of constantly rising fuel prices, a gas generator installed in the trunk of a car will significantly reduce fuel costs. This is especially true for tractors whose engines operate in the same mode.
However, most often pyrolysis gas is used for heating . After all, 3–4 kilograms of sawdust provide the same thermal energy as 1 m3 of natural gas.
If you can for free or cheap , the savings are quite significant. Therefore, wood processing enterprises, workshops and sawmills can be heated without spending money on purchasing energy resources, because shavings, chips and sawdust appear at such enterprises constantly and in huge volumes.
Due to the high nitrogen content, the calorific value of pyrolysis gas is lower than that of any natural or liquefied gas.
For proper combustion and release of the required amount of heat, it is necessary to increase the gas supply .
To do this, nozzles are drilled out in kitchen stoves and heating boilers without electronic control.
In electronically controlled boilers, the diameter of the jets is increased and the firmware (software) is changed.
In cars, it is necessary to completely redo the fuel system, so the easiest way is to convert carburetor cars to pyrolysis gas.
We recommend converting only inexpensive equipment that is not under warranty.
The use of fuel that does not meet certain standards is often grounds for refusal of warranty repairs .
In addition, it is necessary to convert any equipment to natural gas only after carefully studying forums where users share their experience of such work.
We also recommend that you take fuel cleaning as seriously as possible; this will not only increase its calorific value, but also reduce the risk of clogging the fuel system of the heating device.
on this topic
About the pyrolysis of wood processing waste, watch this video:
Conclusion
Pyrolysis gas, which is produced from sawdust and other wood waste, is an effective and inexpensive fuel .
Therefore, the use of pyrolysis gas generators is justified in cases where there is access to very cheap or free wood waste.
Wood pyrolysis process
Wood pyrolysis is a process that ensures the decomposition of wood into two components. One of them is the dry residue, which is called charcoal. The second is pyrolysis gas.
It is necessary in order to ensure the functioning of devices such as long-burning boilers.
Such boilers are popular and do an excellent job of maintaining the optimal temperature level even in the coldest winter.
Types of pyrolysis boilers
Wood pyrolysis is a process that is only possible under certain conditions. The first requirement is that there should be no access to oxygen in the chamber in which this action is carried out. The second requirement is that the entire process occurs at sufficiently high temperatures.
Deciduous wood is used as a raw material to produce pyrolysis gas.
Their properties are the most optimal for carrying out this action. However, coniferous species are no exception, although their efficiency is an order of magnitude lower.
The structure in which this action is carried out is a retort. It has a closed shape, and its oxygen level is extremely low. It is equipped with a pipe through which the formed gas is removed. Subsequently, the pyrolysis gas can be burned and ensures the operation of a long-burning boiler.
- 1 Process stages
- 2 Pyrolysis products
Process stages
Pyrolysis fuel is formed as a result of a series of processes, the sequence of which cannot be disrupted. If you neglect at least one of them, then all the work done will not bring any results. It is worth highlighting the main stages of this process:
- Drying. At this stage, the wood is completely stripped of all its moisture content. This action is carried out at temperatures from 0 to 150ºC.
- The pyrolysis process itself. It is at this stage that gas is released and production waste is generated. This stage varies in temperature from 150 to 350ºС. At a temperature of 280ºС, the most effective stage is observed, at which more than half of all raw materials are formed.
- Calcination. At this stage, the separation of resins from charcoal occurs more clearly. In addition, certain gases are released that were previously not subject to temperature parameters. This stage occurs in two stages, and the temperature is 350-550ºС.
Wood itself is a fairly complex component that contains a huge amount of different substances. The pyrolysis process makes it possible to separate them and obtain each in its pure form.
Each temperature stage is characterized by the release of a specific substance. That is why, in order to obtain absolutely all components in their pure form, it is necessary to carry out the pyrolysis process from beginning to end.