5 years ago
Add a comment
- Anastasia
3,462 views
In Rus', houses, baths and sheds were traditionally built from wood. Today, timber and logs are popular materials for the construction of buildings. In order to protect the house from fire and fungus, fire bioprotection is used for wood. What is the best way to choose a high-quality fire retardant? Let's look at the characteristics of different formulations and reviews of their use.
Classification, characteristics and application features
Substances that impede the combustion of wood include fire retardants.
They envelop the tree and significantly slow down the combustion process. In addition, antiseptics are added to the mixture to protect against mold and rot. The nature of the action of the remedies differs greatly:
- the composition melts. When exposed to fire, a protective film is formed on the wood. It prevents oxygen from reaching the wood, thereby slowing down combustion;
- the composition swells. When the combustion temperature rises, the mixture begins to swell, blocking the path of the flame;
- the composition decomposes. When fire protection decomposes, gases are released that do not support combustion.
Attention! If, in the event of a fire, an untreated log house is destroyed in 15–20 minutes, then a used one can last a day.
Wood processing is carried out:
- step by step, first antiseptic, then fire bioprotection;
- two types of impregnation at the same time.
Based on consistency, protective substances are divided into:
- impregnation. They are odorless, capable of revealing and improving the structure of wood;
- coatings (enamels, pastes, varnishes). They deteriorate the structure of the tree and smell bad. Used for finishing elements.
The composition of the mixture is:
- water-soluble, more natural and durable;
- organically soluble, they must be diluted with toxic flammable compounds.
Purpose and methods of fire protection of wood
For what?
Today, much attention is paid to ensuring the fire safety of load-bearing, enclosing and other building structures made of wood. Of course, no impregnation will preserve the structure in the event of a full-fledged fire.
The rate of charring of coniferous wood due to the high content of resinous substances is high - 0.7-1 mm/minute. Therefore, at the advanced stage of combustion, surface impregnation will not be able to affect the rate of charring, but will only delay ignition for up to 4-5 minutes, which will allow the fire to be extinguished.
According to statistics, 80% of fires are caused by so-called low-calorie fire sources (cigarette butts, burning matches, welding, electrical short circuit, etc.). Fire-retardant impregnation is provided against these accidents, which will “mute” the interaction of wood and sparks, making it possible to prevent a fire at the stage of its occurrence.
The main fire protection methods used in wooden house construction:
- structural - cladding with non-combustible materials;
- chemical - the use of impregnating compounds, paints, enamels.
In the production of rounded logs, fire retardants are used for fire protection - they practically do not change the color of natural wood and meet the requirements of fire safety standards.
The methods of applying fire protection do not differ from antiseptics; they are also applied with a brush/roller, spray or immersion in a bath.
Features of applying impregnating agents for fire protection
- Fire retardants are applied to finished products that will not be subjected to further mechanical processing.
- Wood moisture content should not exceed 15%.
- Processing is carried out at a temperature not lower than +5, and air humidity not more than 70%;
- The composition must be applied in an even layer, without sagging or omissions.
- Quality control is carried out using PiP-1 (a portable device designed by VNIIPO) or by assessing the ignition of chips from a simple match. To do this, chips up to 1 mm thick are removed in 4-5 different places per 1000 m 2 of the finished product. If the wood is well processed, the shavings will not ignite when lit with a match.
The right choice of protective compounds
Fire protection products are so important that you need to choose them not only on the advice of the seller, but also based on your own knowledge.
Points to consider when purchasing:
- Does the seller have a certificate of conformity and a conclusion from the sanitary and epidemiological station?
- Efficiency group.
- The basis of the composition (salt or non-salt).
- Consumption.
- Absorption depth.
Treatment with fire protection agents is necessary for every wooden structure
Consumption of bioprotective composition
This is also an important point. As a rule, the cheaper the impregnation, the higher the consumption declared by the manufacturer. Therefore, when you see a seemingly inexpensive product on a store shelf, do not rush to choose it. Calculate how much impregnation will be required to treat your structure, following the manufacturer's recommendations for consumption. The average consumption rate should ideally not exceed 200-250g/m². While on some products you can find figures of 500-600 g/m², which is quite typical for FIRE-retardant materials, but cannot in any way be the norm for BIO-protective compounds.
Composition and documents
Each wood processing product must have documents, without which the sale is considered illegal. When purchasing, be sure to ask the seller to bring a certificate of conformity and a conclusion from the sanitary-epidemiological station. The certificate must contain all information regarding the features of application and the group to which the product belongs.
Another important characteristic is the composition of the impregnation. They can be:
- saline. Easily washed out with water, the validity period is only 3 years. Suitable for indoor wood processing;
- non-salt. Lasts 10-15 years, non-toxic, effective for external use.
How to choose the right means of fire and bioprotection
When choosing preparations for impregnation, special attention should be paid to possible fumes and their effect on human health. Main criteria:
Main criteria:
- absence of organic solvents, heavy metal salts (chromic acid anion, arsenic, copper cations, etc.) in chemicals;
- durability - compositions for impregnation of internal structures should not be washed out by water, destroyed under the influence of ultraviolet radiation and remain functional for at least 5-7 years (for internal structures - at least 30 years);
- stability - during operation, the product should not evaporate or decompose.
The provision of a quality certificate, a sanitary-epidemiological report, a package of documents from the manufacturer indicating the components of the mixture and recommendations on safety measures when working with the product and its disposal will help you decide on a purchase. The presence of only a sanitary-epidemiological conclusion is not a guarantee of safety. Many chemical components that we are allowed to use for wood processing according to old GOSTs are recognized in many countries as harmful to human health.
It is best to trust a large manufacturing plant with a good reputation. Thus, among imported manufacturers, the brands Tikkurila, Ici Paints, Caparol, Bochemie, Sadolin, Remmers, Belinka, Osmo are distinguished. In the domestic market, they have worthy competition from the products of Senezh-Preparaty LLC, NPO NORT, JSC Rogneda, and JSC Antiseptic.
Protecting wooden buildings from fire invariably remains one of the most important tasks when constructing wooden houses or other buildings. Protective compounds for wood processing significantly complicate fire and reduce the rate of fire spread.
Treating wood with fire-bioprotection slows down the ignition process and also repels insects.
Efficiency group
The most important difference between different compositions is the 1st or 2nd degree of protection. GOST divides fire retardants into 2 groups:
- Effectively protects throughout the fire.
- They prevent fire, but do not last long.
Advice. The more layers, the better the protection. 6 layers of the 2nd group have properties similar to the 1st layer of the 1st group.
If the 2nd group is indicated on the product, the wood acquires the properties of low flammability. If 1, then it becomes fireproof. In residential buildings, only group 1 is allowed.
Fire retardant treatment for wood
Fire protection involves applying special compounds to the surface of wood. As a result, a fire protection layer is formed on it. Impregnations can also be used, which penetrate into the wooden structure under pressure. In the event of a fire, all untreated structural elements will quickly ignite, which contributes to the large-scale spread of the flame.
When treating with protective coatings, you need to pay special attention to the wooden elements used in finishing residential premises and escape routes, and forming the roof. There is a particularly high risk of fire where wooden structures come close to heating devices, pipes, electrical wiring, and chimneys.
Experiment with untreated wood and wood coated with a fire retardant:
What is a fire retardant compound?
To protect wood from fire, fire retardants are used, which are a thermodynamically balanced mixture of fire retardants. Also, paints and putties can be used as fire protection, to which substances have been added that increase fire retardant properties, for example, potassium liquid glass.
Impregnations activate substances that prevent wood from igniting. It just starts to smolder a little. If you remove the source of fire, the smoldering will stop. Varnishes and paints with fire retardants simply foam when exposed to high temperatures, and the coating layer increases several times. Thanks to this, the fire is simply not able to heat the wood very much.
Fire retardant consumption
The peculiarity of protective compounds is that when purchasing, you need to pay attention not only to the price tag, but also to the consumption. After all, a cheaper product can be wasted more, and in the end it will cost more.
Attention! Cheap salt formulations are consumed in 2-3 rubles. faster than expensive non-salt formulas.
For example, “Senezh”, a salt mixture of group 1, consumes approximately 600g/sq.m. if you process wood 6 times. Neomid is more expensive, but provides similar effectiveness at a consumption of 250g/km.m.
Features of fire protection treatment
Fire protection treatment is considered as one of the main measures for passive protection of an object from fire. A set of measures carried out by specialists allows:
- increase the actual fire resistance limit of structures,
- limit the spread of fire in case of fire,
- reduce the flammability of materials,
- provide conditions for spontaneous extinction of fire when interacting with treated surfaces,
- facilitate fire extinguishing work in case of fire.
offers professional services for fire protection of facilities and guarantees their high quality, complying with current fire safety regulations and government standards.
| № | Services list | Unit | Cost including VAT, rub. |
| Metal structures | |||
| 1 | Preparing the surface for fire protection6 degreasing, priming the surface with GF-021 or UKHRA-1503 | sq.m | 200 |
| 2 | Application by airless spraying of fire retardant paint VUP-2, VUP-3R, up to fire resistance limit R30 | sq.m | 350 |
| 3 | Application by airless spraying of fire retardant paint VUP-2, VUP-3R, up to fire resistance limit R60 | sq.m | 750 |
| 4 | Application by airless spraying of fire retardant paint VUP-2, VUP-3R, up to fire resistance limit R90 | sq.m | 1200 |
| 5 | Coating with OZS-MV composition up to fire resistance limit R90 | sq.m | 550 |
| 6 | Coating with OZS-MV composition up to fire resistance limit R120 | sq.m | 650 |
| 7 | Coating with OZS-MV composition up to fire resistance limit R150 | sq.m | 750 |
| 8 | Coating with OZS-MV composition up to fire resistance limit R180 | sq.m | 1150 |
| 9 | Coating with OZS-MV composition up to fire resistance limit R240 | sq.m | 1500 |
| № | Services list | Unit | Cost including VAT, rub. |
| Wooden structures | |||
| 1 | Impregnation with fire retardant composition MIG-09, KOS-D, VANN-1, Vuprotek up to efficiency group 1 (obtaining wood that is difficult to burn) | sq.m | 100 |
| 2 | Impregnation with fire retardant composition biopyrene Piralax up to group 2 | sq.m | 50 |
| 3 | Impregnation with fire retardant composition biopyrene Piralax up to group 1 | sq.m | 150 |
| 4 | Application of fire retardant paint Terma, VUP-2, OZK-45D, up to (R30) | sq.m | 320 |
| 5 | Application of fire retardant paint Terma, VUP-2, OZK-45D, up to (R120) | sq.m | 400 |
| 6 | Coating with fire retardant varnish Pirilax-3000, Nortex Lacquer, Shield-1 to group 2 | sq.m | 300 |
| 7 | Coating with fire retardant varnish Pirilax-3000, Nortex Lacquer, Shield-1 up to group 1 | sq.m | 450 |
| № | Services list | Unit | Cost including VAT, rub. |
| Air ducts | |||
| 1 | Application of fire retardant composition OZS up to fire resistance limit EI30 | sq.m | 600 |
| 2 | Application of fire retardant composition OZS up to fire resistance limit EI60 | sq.m | 850 |
| 3 | Application of fire retardant composition OZS up to fire resistance limit EI90 | sq.m | 1150 |
| 4 | Application of fire retardant composition OZS up to fire resistance limit EI120 | sq.m | 1500 |
| 5 | Combined fire protection system ET Vent (fire retardant adhesive + basalt material reinforced with foil) up to EI30 limit | sq.m | 500 |
| 6 | Combined fire protection system ET Vent up to EI60 limit | sq.m | 550 |
| 7 | Combined fire protection system ET Vent up to EI90 limit | sq.m | 600 |
| 8 | Combined fire protection system ET Vent up to EI120 limit | sq.m | 650 |
| 9 | Combined fire protection system ET Vent up to EI150 limit | sq.m | 750 |
| 10 | Combined fire protection system ET Vent up to EI180 limit | sq.m | 900 |
Fire protection work is carried out in a complex. At the facility the following are treated with special compounds:
- metal supporting structures,
- ventilation system elements,
- wooden structures,
- light fencing,
- floor coverings,
- decorative textile materials.
BRAND LLC carries out the following types of fire protection work:
- impregnation of structures and elements with a fire retardant substance;
- surface treatment;
- filling voids and cavities, including in walls and other floor structures.
The cost of fire protection measures depends on the area of the surfaces being treated and the price of the materials used.
Work order
The algorithm for carrying out fire protection of buildings and structures at a facility consists of a preliminary stage and the immediate implementation of surface treatment. At the preliminary stage, specialists develop a plan diagram, which indicates all the surfaces that are intended to be treated, all the cavities that will be filled with special compounds.
After studying the technical features of the object and the materials for its construction, experts determine the compositions and materials that are optimally suited for a particular case and can guarantee maximum protection of the building from fire.
has the necessary experience, knowledge and resources to develop a fire protection plan and implement it at a high professional level. We use only certified compounds approved for use in the Russian Federation.
Absorption depth into wood
Based on the depth of penetration, two types of compositions are distinguished:
- superficial, penetrating to a depth of 6 mm;
- deep penetration. Penetrate to a depth of 12 mm.
Advice. Impregnation with color makes application easier, because you can see where you have already touched with a brush and where you have not yet. But the color remains for a long time, so it is better to use a colorless product on the facade and in any visible places.
The more common option is option 1, because it can be applied by roller or brush. In addition, such impregnation does not reduce the strength of the wood product.
In residential buildings it is necessary to use fire protection equipment of the 1st degree of protection
Means belonging to the second group are specialized. Special equipment is required to apply them.
Types of protective impregnations
There are two large groups of fire protection products.
Organosoluble
These products are dissolved by organic solvents, which most often have a pungent odor. Since ancient times, wooden sleepers have been impregnated with creosote compounds; the wood has lain in damp soil for decades without damage. Modern silicon-phosphorus fire-bioprotection compositions effectively protect wood from fire and disease, do not have specific odors and are suitable for use in residential buildings. They do not wash out and are durable. There is a drawback - they form a film on the tree, which changes its appearance, but with closed structures this is not important. A number of manufacturers use such compositions to give wood a decorative effect (Pinotex).
Salt water soluble
They consist of salts of boric, phosphoric or silicic acids. Fire protection impregnates the wood without chemically bonding with it. Salts clog the pores of wood, making it “dead” and unattractive to fungus and insects. The fire protection mechanism operates on the principle of a “melted jacket” or the release of non-flammable gases when heated. The composition prevents ignition and delays the occurrence of a combustion source. It is a mistake to assume that the treated material does not burn at all! If the heat is maintained externally, the machined part will eventually ignite.
Most salt impregnations have a low level of penetration and are easily washed out. They are not suitable for external use, and even in a place protected from precipitation they last for several years. After this time, the wood will have to be processed again.
Explanation of symbols
As a rule, on packaging with impregnation from any manufacturer the following letter code is indicated:
- "B". Contains boric acid;
- "D". Under the influence of flame it forms a protective film;
- "M". Contains copper sulfate, which protects against mold;
- "WITH". Contains baking soda that protects against fire;
- "F". Indicates the presence of sodium fluoride, a toxic substance that destroys pests and fungi;
- "X". Toxic composition that destroys wood borers and bark beetles;
- "HA" is a gas-releasing agent.
How does wood fire protection work?
The treatment is carried out at the first stages of construction, impregnating all the main and auxiliary wooden elements. Antiseptics and fire retardants for fire-bioprotective treatment of wood are used both individually and as part of complex products. The latter are more profitable and convenient - costs are reduced and processing time is reduced. However, this is controversial from the point of view of protective properties, so there is no clear solution. Flame retardants act as follows:
- gases released during combustion of the active substance reduce the concentration of oxygen in the air, preventing combustion;
- fill the pores of wood with non-flammable substances, reducing the surface susceptible to combustion;
- a protective, fire-resistant film with low thermal conductivity appears, increasing the time and temperature required for the combustion of wooden structures;
- the protective layer swells, preventing contact between fire and wood.
Chemicals used as fire retardants are diammonium phosphate, ammonium sulfate, sodium fluoride, boric acid, its salts and other compounds.
It is important to remember that even after treating a house with fire protection, fire safety must be observed. Wood will not cease to be a flammable material, but impregnation allows you to gain time to eliminate the threat or evacuate residents.
Most fire protection compositions contain antiseptics and fungicides that prevent the development of pathogenic microflora. These are special compounds that are poisons against groups of insects and fungi that destroy wood. To destroy mold fungi, fungicides are used as part of wood bioprotection products. These substances prevent infection and eradicate fungi by acting on mycelium and spores and causing their death, thus protecting against rotting and mold development. Chemicals used against fungi in fire bioprotection include imidazole derivatives, triazoles, ammonium compounds, etc.
Antiseptics are broad-spectrum drugs that act on both mold and harmful insects (in particular grinder beetles).
Some impregnations, in addition to their protective functions, tint the wood, giving it a beautiful shade.
Treating wooden elements with fire-bioprotection increases the operational safety of log houses and is necessary for residential and public buildings.
Tips for use, reviews from practitioners
Professionals advise that before processing wood, thoroughly clean the surface of cobwebs, dust, old impregnation or paint.
The protective composition is applied to treated, sanded wood with a humidity level of no more than 30%.
It is advisable to carry out all work at positive air temperatures, otherwise water frozen in the capillaries will reduce the efficiency of processing.
Active participants in construction forums argue about the need for fire protection. Some are absolutely confident in its effectiveness, and some claim that if the room is well ventilated, the composition will disappear in 1-2 years and suggest covering the wood with a mixture of copper sulfate and lime. One forum member conducted an interesting experiment: he treated a newspaper with fire-bioprotection and tried to light a fire with it. The newspaper did not catch fire.
Application Features
When treating wood with fire-bioprotection, the moisture content of structures should not exceed 30%. It is not recommended to use at sub-zero temperatures - lude crystals in the capillaries of the wood interfere with the absorption of the solution. Also, do not treat with fire protection in the rain, when the air humidity is more than 70%. The impregnation is washed out by rain, so in regions with heavy rainfall it is processed 1.5 times more often.
The treatment of lumber with a fire-retardant composition is carried out at the last stage, after planing and sanding. Before treatment, the surface is cleaned of dirt, cobwebs, paint, and dust. The product is distributed in an even layer without sagging. By varying the number of layers of the substance, the degree of protection is increased. By applying 6 layers of group 2 fire protection to the wood, they obtain group 1 fire resistance.
When infected with mold and rot, the surface is cleaned with a spatula, including the uninfected layer. After cleaning, cover with an antiseptic.
Popular brands of impregnation
The market is filled with worthy products from domestic and foreign manufacturers. They differ in group, purpose and cost.
The most common ones are:
- "Senezh". Used for external and internal work. The period of protection against fire is 5 years, against bugs and mold – 20 years.
- "Olympus". Treatment with the composition of the 1st group is possible indoors and outdoors. The fire retardant is valid for up to 7 years, protection against insects and fungi – 10 years. For the 2nd group, the period is shorter - fire protection - 5 years, bioprotection - 10 years.
- "Pirilax." The formula of the composition is distinguished by the presence of preservatives that protect the wood from cracking and aging. Available with two protection groups. The validity period directly depends on the climate zone. If external walls are rarely exposed to rain, the fire protection will last for 5 years. The term for internal premises is 12 years.
Frame construction is breaking all records in popularity. Glued laminated timber and rounded logs are also actively used. Builders remind you that wood can be used for construction only after appropriate protective treatment. Fire-retardant compounds selected according to the specified criteria will help ensure the safety of any building.
What is fire protection for wood?
The use of fire-bioprotection is a necessary procedure, since according to building codes and regulations, wooden elements, in particular interior partitions, attic structures, rafters, must be treated. Complex fire-bioprotection compositions for wood can be impregnated on an organic or water basis, including antiseptics and fire retardants. The antiseptic component prevents biodestruction:
- protects against wood-staining (giving a bluish or greenish tint) and wood-destroying fungi (capable of destroying a wooden house, turning it into dust). In addition, microorganism spores cause serious chronic diseases in humans;
- prevents the proliferation of grinder beetles, which destroy the crowns of log houses, rafters, partitions, as well as furniture and parquet.
Although fire retardants do not make wooden structures non-flammable, they do make it difficult for fire to spread. Used for both external and internal work.
Properly treated wood is protected for 5–20 years (depending on the product used), then it is recommended to repeat the impregnation. Unfavorable conditions, such as freezing, high humidity, heavy rainfall, cracks, chips, reduce the duration of fire bioprotection.
Hydrothermal wood treatment
Compositions used for fire and bioprotection of wood can be applied to the surface of the wood using sprayers, brushes, rollers, etc. In the case of using impregnations, it is advisable to use hydrothermal wood treatment technology.
This term refers to the treatment of wood with hot water, steam, gas or liquids. The main purpose of this technology is to change the moisture content of wood for its further use in industry.
If impregnations are used, they are preserved inside. This helps to increase the service life of the product several times. The use of impregnations without hydrothermal treatment is possible, but the maximum effect will not be achieved.
Wood can also be treated with special oils. They do not leave a film on the surface of the material and are applied in a thin layer. Among the entire range of oils presented on the construction market, it is worth highlighting the Osmo brand material.
Types of sales of funds
For ease of application, refractory raw materials are sold in several forms:
- Impregnations. It is divided into two subtypes according to the depth of absorption: surface - penetrates 6 mm deep into the beam, more advantageous due to the ease of application using a brush, sprayer, roller; deep penetration - impregnate the wood 12 mm deep; professional equipment will be required for use. When applied, impregnations change the structure of the paint, so they are applied before final finishing. The advantage of impregnations is the absence of odor, which facilitates indoor use.
- Enamels, varnishes, paste mixtures. They significantly change the color and structure of the materials they are applied to, and also have an unpleasant, strong or weakly expressed odor, so they are used only before the final stage of finishing work.
According to the method of dilution, fire retardants are divided into water-soluble and soluble with the help of special liquids.
- Water-soluble compounds, in turn, are divided into two more types: saline and non-saline. The advantages of the salt product are high in cost, but there are many more disadvantages: short service life (3-5 years), when exposed to moisture, it quickly loses its physical properties, high consumption of material. The fireproof substance without salt content provides a longer protection period (15-20 years), is non-toxic, can be used indoors and outdoors.
- A solvent-based product is used to protect the exterior of the structure due to its increased toxicity. The advantage of applying such a liquid is the formation of a protective film that repels moisture and protects against the effects of fire. The disadvantages, in addition to toxicity, include the narrow focus of the composition: they do not have antiseptic properties.
To treat wooden surfaces from the inside, you should choose the least toxic products
Cause of biodestruction of wood
Microorganisms affecting wood spread under conditions of “warm and humid and no ventilation.” Exactly in this combination.
First of all, boards with natural moisture are at risk, since they are often affected by spores already at the sawmill. During the drying process, these spores in most cases die under the influence of temperature.
Moreover, even an affected board, if it lies in a puddle in the fall, will not “bloom” more strongly. Because you also need warmth.
Since we use only dry and planed boards, there are no “natural reasons” for biodestruction, like a board with natural moisture. If your structure creates “warm and humid” conditions, bioprotection may not help; it is not a panacea.
If the conditions are damp, warm and there is no ventilation, biosecurity will not help
An example - when I built my personal house, I treated part of the dry board with one of the most “vigorous” compounds - XM11. But one of the household members carefully wrapped the pack of boards, wet after the rain, with film on all sides, essentially placing the board in a greenhouse, creating the same conditions - warm, humid and no ventilation. As a result, 50% of the boards developed some kind of fungus.
Conclusion - we must do so to avoid such conditions, and not rely on bioprotection and antiseptic treatment of wood.
Does the house need to be treated?
Many developers are inclined to believe that it is necessary to treat their wooden houses with fire protection , in principle, which does not contradict logic. But there are owners who are categorical on this issue and are of the opinion that it is not necessary to saturate the house. They justify their statements by the fact that if a fire starts, no fire protection will help.
This is debatable. A certain organization , we will not name it, so as not to create advertising for it, conducted an experiment with the combustibility of houses with different fireproof characteristics. They took three mock-ups of houses: one was covered with pyrilax , the second was opened with salt impregnation , and the third was without any treatment.
They were placed in a row in the following sequence: a house without impregnation , and the other two were placed along the edges. They set fire to the central house and began to wait. The fire from the burning house, after some time, spread to the house with salt impregnation - and it burned down, and the house with pyrilax was only slightly burned on the outside - it can be restored.
So, whether to cover the house or not is your choice.
What materials are used to protect wooden houses?
Today, there are many different active ingredients on the market to protect wood from biological damage and fire. Most owners of country houses treat the wood with an antiseptic , after which fire retardants . This is a rather lengthy process, since before applying each subsequent layer, you must wait until the walls are completely dry.
The procedure became simpler as soon as complex products appeared, the so-called fire-bioprotection of wood. It takes on the functions of both an antiseptic and a fire retardant, costs less and saves time for owners, which is why it is most often preferred.
Use of fire and bioprotective agents
Following Russian traditions, we visit baths and saunas not only for hygienic purposes, but also go there to relax and unwind from the hustle and bustle of everyday life. As a rule, all internal surfaces of baths and saunas are made of natural wood, which feels most natural to the body and, importantly, does not heat up so much. All surfaces are sheathed with it: the floor, the walls, and the ceiling. It is best to use wood from species that are resistant to moisture, are naturally resistant to the development of mold, and are poor conductors of heat.
Use of fire and bioprotective agents.
However, even the most resistant wood will be affected by mold if the bathhouse is not used properly. If mold has settled in the bathhouse, then there will be no health benefits from such a vacation. In addition, the development of mold in the bathhouse harms wooden surfaces. In a favorable humid environment, various fungi and bacteria develop well, causing darkening and destruction of wood. Untreated wooden surfaces under these conditions are prone to cracking and the formation of deep fungal lesions.
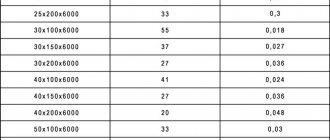
Acceptable indicators of consumption of antiirenes.
Without timely treatment, a bathhouse will not last long. A means of saving a bathhouse is wood impregnation, which stops the development of mold, rot, and wood-boring beetles.
It is known that during the operation of a bathhouse there is not only increased humidity and condensation, but also abundant exposure to water on almost all surfaces. Therefore, when choosing protective impregnations for a bath, pay attention to the presence of highly effective washout-resistant components. Impregnation for wood must be resistant to the difficult operating conditions of the steam room and washing room. The protective coating must be renewed as necessary.
What are MDF panels What is veneer All about mahogany What to choose: MDF or laminated chipboard
When choosing a protective agent for a bath, you should take into account the safety characteristics of the composition. Washrooms and steam rooms are characterized by sharp changes in temperature and humidity. In a hot, well-heated bath, the human body warms up, blood flow and metabolic processes increase.
The protective agents used to treat wooden surfaces inside the bathhouse should not emit substances harmful to health when the temperature in the steam room increases. Otherwise, unwanted side effects may occur in the body. Impregnating compounds provide high-quality protection of wood from fire, rot, the development of mold and wood-staining fungi, and wood-boring beetles.
Mold on floors.
Fire-retardant impregnation
In order to protect the wooden surfaces of the bathhouse from fire, use biopyrene (fire retardant-antiseptic) “Pirilax”-Terma. This is a fire retardant composition with strong antiseptic properties. This wood impregnation is designed specifically for the purpose of treating rooms characterized by temperature changes and high humidity.
Biopyrene has been tested for safety at high temperatures. Protective impregnation tints the wooden surface an amber color and does not form a film. If the walls near the stove in the steam room are made of coniferous wood (pine, spruce, larch), then Pirilax-Terma is the best option.
Fire-retardant impregnation.
Bath antiseptic agent
To treat the bath, we recommend using a highly effective antiseptic that destroys biological lesions and prevents their reappearance even in conditions of high humidity. The antiseptic does not tint the surface, does not form film coatings, and free moisture exchange is maintained in the wood. A composition that provides water- and dirt-repellent protection. The protective composition has high antiseptic, bactericidal and water-dirt-repellent properties. Destroys mold, algae and prevents their reappearance.
Bath antiseptic agent.
Protects against wood-boring beetles:
The composition for baths has an antimicrobial effect, protects against bacteria, viruses, and prevents their reproduction. Also protects against water, soot, dirt, soapy water, grease, and leaf stains. The treated surface acquires hydrophobic (water-repellent) properties.
The composition is tested for safety at high temperatures. Preserves the natural appearance and smell of wood. Does not interfere with the natural breathing of wood.
Why fire protection of wooden structures is important
The importance of fire protection of wooden structures Fire protection of wood is now no less relevant than ever. Indeed, despite the emergence of a large number of new fire-resistant building materials, buildings made of wood are widely popular. People prefer environmentally friendly housing that is easy to breathe, warm and comfortable.
The number of wooden houses increases every year, and where there is wood, there is a danger of fire. In dry summer weather, an ordinary tree can catch fire with just one match. Therefore, fire protection of wooden structures is a necessary condition for wooden construction, ensuring the safety of people’s lives and their property.
Today, fire-retardant wood treatment can be carried out in several ways. It is immediately worth noting that none of them is capable of making wood non-flammable. All these methods are aimed only at maximizing the time of ignition of wood, as well as preventing further spread of fire.
Fire retardant treatment of wood can be carried out by coating or plastering it. These methods have been used for a long time and consist of increasing the ignition time of wood by covering it with a protective layer of considerable thickness. In the case of coating, high-quality fire protection of wood is ensured with a layer thickness of at least 3 mm; when plastering, the thickness of the protective layer should be at least 20-30 mm. Coating is especially often used for fire protection of wooden roof structures.
Modern methods of fire protection for wood include painting and impregnation. Special fire-retardant paints for wood swell when exposed to flame and block fire from reaching the wood. An example of such paint is “Krauz-D”. Fire retardant impregnation of wooden structures is carried out with special compounds that penetrate deep into solid wood, increasing its fire resistance. Additional advantages of impregnations are the provision of not only high fire protection for wood, but also bioprotection from pests and rotting through special additives in impregnations.
Wood treated with special compounds.
What does fire bioprotection consist of?
The composition of the fire-bioprotective coating may vary. These can be water- and organic-soluble modifications. The latter option requires the use of flammable and toxic solvents. That is why preference should be given to water-based formulations.
They, in turn, are divided into 2 types:
- Salt compositions . They have been used for a long time and are inexpensive. But this is where their advantages end. Applying impregnation requires the consumption of a huge amount of material. Among other disadvantages, it should be noted that such compositions cannot be painted in the future. Atmospheric precipitation quickly washes them from the surface. And they have a short shelf life. It is only 3 years. The use of salt fire protection is often possible during internal processing of the material. But at the same time, it is desirable that the room is not damp;
- Non-salt solutions . They are able to protect from fire for almost 15 years. These compositions provide protection against biological factors for up to 20 years. The appearance of the tree under the influence of this composition does not change. Non-salt solutions are not toxic and are used more economically than analogues.
Non-salt formulations are more expensive, but justify their price. Thanks to their use, you save on both the volume of material and the frequency of processing.
Biosecurity
Fungi, mold, salt deposits and other biodegraders pose no less a threat to wooden structures than fire and moisture. To protect against them, special antiseptics are used.
Some of them can not only prevent the development of fungal plaque, but also save the wooden structure from destruction. The latter is especially true if sufficient attention was not paid to the processing of the material before construction began.
Insects can grow in the ceilings and walls of houses, which threaten the strength of the structure. To combat them and create an unfavorable environment for reproduction, various antiseptic and insecticidal preparations are used. It is advisable to treat wood before using it in construction. This way you can avoid the appearance of untreated areas.
It has been noted that the development of fungi and the vital activity of insects is possible only in a certain environment. With critical changes in humidity, they are simply unviable. Therefore, one of the ways to combat them is to dry the wood or over-moisten it.