Charcoal is a product resulting from the heat treatment of wood. This material is highly porous and contains a large amount of carbon. It easily enters into a combustion reaction with the release of thermal energy, has high efficiency and is safe for human health. This product is an environmentally friendly source of fuel and is actively used in everyday life or industry.
What is charcoal
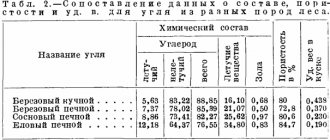
Charcoal is a microporous carbon product. The chemical composition of the material is represented by the following elements:
- carbon: 80 to 90%;
- oxygen: from 5 to 15%;
- phosphorus: from 0.01 to 0.03%;
- hydrogen: 4 to 5%;
- ash: from 1 to 3%;
- volatile substances (nitrogen, sulfur): from 7 to 20%.
The chemical formula shows that this material has a structure similar to coal. But it contains a small number of elements that do not participate in combustion reactions. The percentages of various substances may vary in the presence of moisture.
Charcoal is produced through heat treatment of wood. In chemistry, this process is called pyrolysis. As the temperature of the wood rises, most of the moisture evaporates. When burning, the percentage of phosphorus, carbon and oxygen decreases. In industrial conditions, this product is obtained using special technical equipment, which allows the chemical composition of the substance to be preserved.
Types and varieties of charcoal
There are 3 main types of charcoal:
- Black: It contains increased amounts of non-volatile carbon, water and ash. It is distinguished by its high density and strength. This type of coal is divided into 2 grades: first and highest. They differ in physical properties. The material is created by heat treatment of oak, ash, maple, beech, birch, hornbeam and elm wood.
- Red: has a high percentage of ash. Made from coniferous trees: pine, spruce, cedar, larch or fir. It has 2 grades: first and second.
- White: Crafted from hardwoods such as oak, ash, maple, beech, birch, hornbeam and elm. It is not divided into additional grades, but has the maximum quality parameters specified in GOST 7657-84.
This classification is actively used by Russian manufacturers. It determines the nuances of manufacturing a material in accordance with its physical or chemical properties. Foreign manufacturers rarely use these production standards. The world leaders in the supply of this material, located in Latin America, use only eucalyptus in production, which is not specified in world or state standards.
GOST 7657-84 Charcoal. Specifications
1 file 106.78 KB
Properties of charcoal
The chemical composition of charcoal is determined by the pyrolysis temperature. The mass fraction of oxygen, hydrogen and volatile substances depends on this process. During heat treatment of a substance, its structure becomes compacted. The proportion of O2 and H2 decreases, which leads to a decrease in electrical resistance and an increase in the density of the substance.
The presence of macroradicals (paramagnetic centers) in the composition of coal determines its high reactivity when interacting with oxygen. During this process, a combustion reaction occurs. As a result, low molecular weight products are released, including H2O. The characteristics of the reaction affect the specific gravity of the formed charcoal. Its average value is 210 g - 1 liter.
This mineral has the following physical characteristics:
- substance density: up to 380 kg/m2;
- specific heat capacity: up to 1.21 kJ/(kg×K);
- electrical resistance: up to 0.5×109 Ohm×cm;
- thermal conductivity: 0.058 W/(m×K);
- specific heat of combustion: 3.4×107 J/kg.
Charcoal is a porous material with a high carbon content. Due to the presence of pores, it has sorption properties. The material can absorb toxic gases, water and water vapor. Due to the presence of sorption properties, the substance is able to filter alcohols, amino acids and other liquid elements.
Due to the low ash content (up to 3%), the combustion of this substance practically does not form combustion products containing various chemical elements. For this reason, this material is one of the most environmentally friendly types of fuel and is actively used for cooking food in barbecues, ovens and retorts.
The combustion temperature of charcoal is 1200–1300 °C, which makes it possible to use this raw material when forging metal in forges. It has high thermal conductivity, which is ensured by the low humidity of the substance. This indicator is influenced by the combustion temperature of charcoal. When producing charcoal with your own hands or using industrial equipment, the material is charred when heated to combustion temperature. After the end of production cycles, it acquires a shine and a blue tint.
According to GOST 7657-84, this mineral belongs to low-hazard substances (hazard class: 4). Dust generated during combustion of material can have an irritating effect on the body and cause respiratory diseases. Under improper storage and operation conditions, it can pollute the environment. The substance has the ability to spontaneously combust.
Properties
During the pyrolysis of wood, the structure of its conductive tissues is preserved, therefore the resulting charcoal has a large number of capillaries and pores with a large total surface area, which contributes to its high adsorption capacity. At ordinary temperatures, charcoal can adsorb various substances from their solutions, as well as various gases, including inert ones. Moreover, the easier the gas is liquefied, the better charcoal adsorbs it. When heated, charcoal that has adsorbed substances releases them, again acquiring the ability to adsorb. To increase the adsorption capacity of coal, it is activated by heating without air access[2].
Application
Most often, charcoal is used as organic fuel. When burned, it releases a large amount of heat, which is required for cooking meat products in a barbecue grill. Grill fuel produces a stable flame and does not emit harmful gases into the atmosphere during combustion. This mineral is also used in everyday life to light home fireplaces. This material does not emit odors and does not pollute the room.
Some city residents do not know why charcoal is needed if alternative heat sources are available. The advantage of this material is its environmental friendliness. It does not have a negative impact on the environment or the human body.
There are the following areas of application of charcoal on an industrial scale:
- Ferrous and non-ferrous metallurgy: coal is used as a reducing agent due to its high carbon content. This material is one of the most important components of the charge used in the smelting of cast iron and other iron alloys.
- Production of aluminum, pure silicon for semiconductor devices, glass, crystal products, paints, plastic polymers and electrodes.
- Agriculture: production of natural fertilizers for cultivated plants and feed mixtures for cattle and poultry.
- Instrument making and printing production: production of anti-corrosion powders and lubricants. In these areas, softwood raw materials are used. Lubricants from this substance are made by mixing coal with residual ash. The resulting mixture is treated with a solution of potassium manganese and sulfuric acid.
- Production of black powder: a product from alder wood is used. It is highly flammable due to its high carbon content. The percentage of coal in black powder ranges from 12% to 20%.
- Manufacturing of electric coal products: during the technological process, the mineral is mixed with coal tar. These parts are used in engines, electric cars and electric vacuum equipment.
- Pharmaceutical and food industry: production of activated carbon, designed to remove dissolved organic matter. It is used as an adsorbent in wastewater treatment plants to filter natural waters.
The use of charcoal is limited by the shelf life of the material. It can be stored for 5 – 12 years. The shelf life of the product depends on storage conditions. It is recommended to keep the material in closed containers, under a canopy. The product must be stored at a temperature of 200 °C.
What is better to use for grilling kebabs? Briquette or coal?
Having considered all the pros and cons, we can say with confidence that both types of fuel are perfect for use in your barbecues, grills and barbecues. Here, as they say, it’s a matter of taste. For some, the minimum price is important, for others - longer burning.
If we consider charcoal, then this is a product whose main advantage is rapid ignition. It often takes just 10 minutes to reach the temperature required for roasting meat and cooking other dishes. However, a fire on coal will disappear as quickly as it appeared, so you must always add coal to the grill so that it does not go out.
In this regard, fuel briquettes are much more efficient. Although they are more expensive, you can be sure that your barbecue will always be at a high temperature, even after several hours. Thanks to this, we don’t have to constantly monitor the fire or constantly add something to the grill so that our dishes are properly cooked.
However, it is extremely important to choose a briquette that is completely natural. Briquette compositions containing harmful chemicals (for example, synthetic glue) should be avoided. Only natural briquettes guarantee us high quality and safety for health.
Did you find this article helpful? Please share it on social networks: Don't forget to bookmark the Nedvio website. We talk about construction, renovation, and country real estate in an interesting, useful and understandable way.
Production process technology
In ancient times, people used charcoal technology to produce coal fuel. They placed firewood in special pits and covered them with earth, leaving small holes. After the industrial revolution, the charcoal charring procedure began to be carried out using automated equipment capable of controlling the carbonization reactions of substances and heating the material to combustion temperature.
In industrial conditions, this material is produced in small quantities. Before producing charcoal, you need to choose the right raw materials, purchase specialized equipment and determine the manufacturing technology. The industry uses 3 main methods for producing charcoal:
- drying;
- pyrolysis;
- calcination
The resulting products are packaged in bags, briquetted and labeled. GOST 7657-84 describes how charcoal is made in production. It describes the process flow diagrams and provides precise information about the amount of temperature required to heat the raw materials.
Charcoal can be produced at home, forming a cottage industry. Most often, a personal plot is chosen as a place for the production of these raw materials. Before making charcoal, you need to arrange the premises in accordance with safety rules, choose a manufacturing technology and evaluate the prospects for the development of a business project.
Selection of raw materials
According to GOST 24260-80 “Raw materials for pyrolysis and charcoalization”, when creating charcoal, hardwood is required. This group includes birch, ash, beech, maple, elm and oak. Coniferous trees are also used in production: spruce, pine, fir, larch and cedar. The least used softwoods are pear, apple, plum and poplar.
GOST 24260-80 Wood raw materials for pyrolysis and charcoalization. Specifications
1 file 457.67 KB
Raw materials must have the following dimensions: thickness - up to 18 cm, length - up to 125 cm. The wood should not have a large amount of sap rot (up to 3% of the total area of the workpiece). Its presence reduces the hardness of the material and increases its ash content. Large amounts of water are not allowed. This substance leads to the appearance of cracks on the surface of the workpieces.
Drying wood
During the drying process, the raw materials are placed in a charcoal burning block. Wood is affected by flue gas. As a result of heat treatment, the temperature of the workpieces increases to 160 °C. The amount of water contained in wood affects the duration of the technological process. As a result of drying, a material with a moisture level of 4-5% is obtained.
Pyrolysis
Pyrolysis is a chemical decomposition reaction that involves heating a substance with a lack of oxygen. During combustion, dry distillation of wood occurs. The workpieces are heated to 300 °C. Pyrolysis removes H2O from the raw material, which leads to charring of the material. With further heat treatment, the wood is converted into fuel, the percentage of carbon is 75%.
Calcination
After pyrolysis is completed, the product is calcined. This procedure is necessary to separate resins and unnecessary gases. Calcination occurs at a temperature of 550 °C. After this, the substance is cooled to 80 °C. Cooling is necessary to prevent the product from spontaneous combustion upon contact with oxygen.
Production history
In order to answer the question of what is required to produce coal, one must look at the history of its production. The first producers of such coal dug special pits for it and burned wood in them.
Subsequently, firewood began to be piled up and burned on special sites. This production technology was called charcoaling, and some production plants still use it to this day.
Today, an improved technology for producing charcoal is called pyrolysis. It is characterized by better insulation of materials from oxygen, and also provides optimal thermal conditions for a higher quality final material.
Charcoal production equipment
To create charcoal, the following equipment is required:
- Pyrolysis barrel: dry distillation of raw materials is carried out here. This device is also used as a waste disposal device. For continuous production of raw materials, stationary pyrolysis barrels with large dimensions are used.
- Vertical retort: designed to reproduce chemical combustion reactions. Used for drying wood.
- Wood splitter: used for harvesting and sorting raw materials. Its distinctive feature is its high efficiency. Wood splitters are resistant to friction.
Coal production also uses a large number of auxiliary equipment. This category includes automatic filling lines, weighers and separators.
Wood pyrolysis
Pyrolysis, or dry distillation, is the decomposition of organic substances by heating without (or with limited) access of air to prevent combustion [1]. Also, pyrolysis is the first process that occurs when wood burns. Flames are formed due to the combustion not of the wood itself, but of gases - volatile pyrolysis products. During the pyrolysis of wood (450-500 °C) a number of substances are formed: charcoal, methanol, acetic acid, acetone, resins and others.
This process is used in pyrolysis boilers. The process of wood gasification (pyrolysis) occurs in the upper chamber of the boiler (loading space) under the influence of heat and with limited air access. The resulting wood gas flows through the heat layer, reaches the nozzle and mixes there with the secondary air.
How to make at home
Very often, the production of charcoal at home is carried out by people who own metal forging workshops. Homemade biofuel is made for domestic needs: cooking on the grill, refueling the forge. Before you make charcoal with your own hands, you need to choose a manufacturing method and organize production workshops, taking into account fire safety rules. You can make charcoal at home using available materials. At the same time, the manufacturing technology of the material is often not followed. In the production of this product, pits, barrels and stoves are used. Before you set up a coal production workshop yourself, you need to evaluate the amount of costs and profitability of the business project.
In the hole
This method assumes the presence of a pit located at a far distance from buildings. Its depth should be at least 150 cm, width - 80 cm. To make charcoal in the pit, you need to light a fire from small branches. It needs to be placed in a hole. Medium-sized pieces are thrown into the fire. After burning the wood, the pit must be covered with a covering and left for several days to cool. The resulting products can be removed within 2 days.
In a barrel
When making charcoal in a barrel, it is necessary to use containers made of heat-resistant materials. The bottom of the metal barrel is reinforced with bricks. Between them there is a fire, on which wooden blanks are placed. A metal grate is placed over the pile of firewood to allow heat and flames to pass through. This design allows you to produce several portions of coal in a barrel.
In the oven
You can make coal in a standard stove. To do this, you need to place the wood in the fuel compartment and heat it to 550 °C. You must wait until the wood turns red. The resulting fuel is removed using tongs, placed in a metal container and covered with a lid. After cooling, the product can be packaged in bags and used at home.
Method of obtaining in the pit
This method can be put in first place, since it was used by our ancestors.
It will be labor-intensive to make charcoal for one person, call some helpers - together the work will go faster.
You need to start by digging a small hole, which should be cylindrical in shape with strictly vertical walls. This will be the oven. If you want to get about two bags of coal, then the pit furnace should have a diameter of 70 to 80 cm and a depth of at least 50 cm.
In order for the finished raw material to be sufficiently clean, without any admixture of earth, the bottom of the resulting pit must be compacted; this can be done with your feet.
Then you need to make a fire in the pit, but do not add any chemicals to the fire, use dry birch bark, small branches and the like for ignition.
You need to monitor the fire and periodically add dry wood to the flames. The entire bottom of the pit should be covered with burning wood.
You should start burning only when the fire is well lit. You can add pre-prepared wood to it, which will subsequently turn into coal. For convenience, it is better to cut the firewood into pieces no longer than 30 cm.
It is important to know: firewood for charcoal must be cleared of bark. The raw materials from it are still of poor quality, and when burned it smokes a lot.
Firewood must be laid out in layers: when the first layer has already burned out, lay the next one. It is important to stack firewood tightly together. The pit should gradually fill to the top with firewood.
After this, the pit with the contents must be carefully covered with grass and leaves, then pour in a little earth and compact it very well. After 24 hours, sift the resulting coal.
Charcoal production as a business
It is recommended to sell coal in bulk. Buyers may be supermarkets, gas stations, cafes and restaurants, factories and other industrial organizations. To manufacture and export products, it is necessary to register the enterprise with the tax authorities, arrange the supply of raw materials, rent premises and purchase professional equipment. The cost of starting a business is on average 2,000,000 rubles. The wholesale price of 1 kg of charcoal is 100 rubles. A 3 kg bag costs at least 270 rubles. When selling 20 tons of coal, the total profit is 800,000 rubles. The business pays off within 6 months.
Personnel
As for workers, no more than 2-3 people are needed; no professionalism is required from them.
Workers are needed to:
- load the production line;
- unload raw materials;
- load finished products.
In addition to workers, you will need to hire:
- watchman;
- sales and purchasing manager (if you do not plan to engage in sales yourself);
- perhaps an accountant.