The desire of consumers to have furniture, interior and interior structures made of natural wood is not always feasible due to the high cost of natural material. There is no point in especially regretting this, because products made from solid wood have a lot of weight, and, moreover, over time they can dry out and become deformed. In this regard, veneer is often used for finishing.
Products made from natural veneer are very similar in appearance to solid wood, while the products cost much less and can be used without problems.
What is veneer called?
Veneer is a word of German origin meaning wood chips. Apparently, at the time the term was borrowed, they were synonymous. Nowadays, wood chips mean chopped wood. There are several types of wood chips, the best of which are called technological. After additional chemical treatment, some of them are used in the production of boards from wood fibers and chips.
All modern types of veneer are obtained by more subtle mechanical methods of wood processing, for which special technological equipment is used. As a result, plates of small thickness and relatively large (for crushed raw materials) surface area are formed. They don't look like wood chips at all.
The advantages of veneered products are as follows:
- the coating has a beautiful pattern, which is further enhanced during processing;
- veneer of exotic species can be used to decorate a base made of inexpensive wood;
- in case of minor damage, the appearance of the surface can be easily corrected by minor repairs;
- veneer allows you to restore old structures and products without large financial costs;
- a thin layer of coating allows you to carry out the work yourself using ordinary tools.
When working with solid natural wood, you have to make a lot of physical effort, use woodworking machines and special tools, but working with veneer is much easier.
Advantages and disadvantages
Veneer has many advantages for which consumers value it and choose it. It is worth mentioning the following advantages:
- Economical array replacement. If you purchase products finished with natural veneer, the visual difference is not immediately noticeable, but you can save significantly.
- Environmentally friendly material. Any veneer, even second-grade, consists of at least 75% wood, which allows it to be used in the manufacture of all kinds of interior items (unlike film).
- Different shades. A variety of colors and shades of material allows you to create a combination in your work (for example, on doors or wardrobes);
- The coating gives additional strength to structures.
Wood cutting methods
Veneer panels can be removed from semi-finished wood products in several ways. Their choice is determined by the type of raw material, its condition, the direction of future use of the product, and the equipment of the manufacturer.
The main types of mechanical actions are as follows:
- planing;
- peeling;
- Sawing
Each procedure requires special equipment, the use of wood of the required quality, and the degree of its preparation. Finished veneer differs in aesthetic features, respectively, in its usability and price.
Planed material
Planing produces veneer of oak, mahogany, ash, beech and two main conifers: pine and larch. The products have a beautiful texture and are used primarily as a facing material. For the production process, sawn beams or so-called vanches are taken, which, after steam treatment, are cut on special planing machines.
Note! Planing can be carried out in different directions, resulting in different patterns on the plates.
After radial planing of the veneer, carried out strictly along the end, a pattern of parallel rings is formed on it, located evenly over the entire surface. Radial veneer made in this way is designated by the letter R.
Due to half-radial planing, the pattern of rings occupies approximately ¾ of the area of the resulting layer. The veneer obtained as a result of such a mechanical action is designated by the letter combination PR.
As a result of tangential processing, the rings have the appearance of curved strips. The plates obtained by planing along a tangent (tangent to the annual ring) are designated by the letter T. Sometimes the name “tangential” is found. It cannot be called incorrect, since masters often use such a term.
After tangential-end planing, the pattern is formed by looped oval curved lines, on which dashed core rays are visible. The type of such veneer, formed as a result of planing technology along the axis between the end and the tangential plane, is designated by the letter combination TT.
Types and thickness of sliced veneer
According to the quality of wood and the thoroughness of processing, planed products are divided into two grades. Types of natural veneer from group 1 have minimal defects in the form of spotting, internal sapwood, dark growth, cracks, scratches or do not contain them at all. Types of veneer from the 2nd grade group are controlled much more loyally, because the standard allows for the presence of defects in products.
The thickness of wood plates varies from 0.5 to 1 mm. Veneer obtained by tangential, full or half radial cutting has a length reaching 900 mm and a width reaching 120 mm. Products with the TT designation are usually smaller in size. The permissible surface roughness indicator varies. For oak, mahogany, ash, pine, larch it is 200 microns, for other wood - 100 microns.
All veneer produced by planing is dried until a moisture content of 8% is reached and then packaged.
Peeled veneer
Ribbon-like veneer is called peeled veneer. It is removed from the surface of the wood using a special machine. Long strips are dried, cut into pieces of specified sizes and used as a semi-finished product for the production of plywood, multilayer panels, glued elements of building structures, cladding, and food packaging.
The outer coverings that rotary cut veneer creates look a little worse than those made from planed pieces. The advantage of this type is the larger surface area of the plates. It is not always advisable to process valuable wood species by peeling, but a semi-finished product from common raw materials, such as poplar, after veneering turns into a sought-after product.
The length of each product varies from 800 to 3750 mm. The width varies from 150 to 3750 mm, the pitch in the line varies from 50 mm to 100 mm. Requirements for thickness indicators depend on the type of wood. For thin plates made of hardwood, the maximum is 4 mm, for thicker ones 6.5 mm.
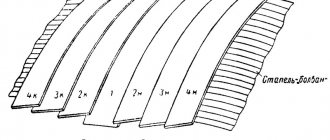
Veneer is divided into 5 grades: elite and others, including from 1st to 4th grade. Next to the digital designation of the grade of coniferous wood products there is the letter X.
The moisture content of the finished veneer should not exceed 6%, the roughness index for hardwood products cannot exceed 200 microns, and for coniferous products - 320 microns.
Sawn veneer
Man learned to saw wood into layers a long time ago. Making thin sheets using a saw, even the most modern form, is difficult, and the process is accompanied by a large amount of waste. Lamels made by sawing have a thickness from 1 to 12 mm.
Note! Sawn veneer is used for inlaying expensive furniture and decorative interior elements.
The peculiarity of sawn veneer is that it can be selected according to the pattern of the main part of the wood of the product. The result will be very beautiful and impressive, but you will have to pay a lot of money for it. Sheet veneer, sawn from cedar, spruce, and fir wood, is often used to form bent design elements for furniture or stairs. The products are used individually or in combination with MDF material.
In some sources you can see information about the use of sawn veneers for finishing musical instruments. The content of the state standard indicates that peeled or planed veneer plates are used for these purposes. Thus, for rough veneering of pianos, types obtained by peeling hardwood are used; for finishing veneering, planed pieces of veneer of ash, pear, walnut or American walnut, maple, elm, oak and even mahogany (for the most expensive instruments) are used.
What are the benefits of veneered furniture?
- in a variety of textures and colors, since both pine wood and expensive wood species are used for their production. The appearance of veneered furniture depends on the type of wood used to make the veneer. Depending on the varnish or paint used, veneer surfaces can be matte or glossy; in addition, they are often combined with enamel and film facing materials;
- in ease of processing, which makes it possible to obtain veneered blanks of various shapes for the manufacture of furniture for kitchens, living rooms, etc.;
- in the external attractiveness of veneered furniture. Gluing valuable wood veneer onto an MDF or chipboard base gives the products a beautiful, noble look. Its naturalness is palpable and clearly visible up close;
- in practicality. High-quality kitchens made of veneer are reliable and durable, since they are resistant to high humidity and temperature fluctuations - factors that have a destructive effect on furniture facades. Veneered furniture does not crack or deform during use, so it is often chosen as the bottom part of the set;
- in maintainability. Minor scratches on veneered surfaces are eliminated by sanding, deep damage - with veneer patches;
- in accessibility. The cost of veneered sets is much less than products made from natural solid wood.
Veneer, as a facing material, also has certain disadvantages:
- under the influence of the sun, such a coating can change color;
- it does not tolerate cleaning with aggressive chemicals, which cause bubbles and peeling on their surface. The exception is products made from eco-veneer - they can be cleaned with various means, but without abrasives and solvents;
- the unique pattern of each sheet of natural veneer makes it difficult to select a pattern at their joints;
- higher cost of products made from oak, ash or beech veneer.
Modern production technologies
In addition to traditional methods, many enterprises have introduced and are successfully using new approaches to the production of veneer products.
Variegated, multi-character multi-veneer is popular, the surface of which may have light or dark brown shades, gray tones with different textures. There are design works that create a strictly defined or chaotic pattern, unlike natural colors, but with the texture of wood. The products are in demand among connoisseurs of non-standard solutions in interior design.
Where is it used?
Finishing with this decorative material can be found quite often. The interior door leaf can be fully or partially decorated with veneer. You can find canvases with artistic inserts.
Important! Decorative sheets are used in the assembly of cabinet furniture and kitchen units. There are thick tabletops and bar counters covered with veneer and varnish. It looks very impressive and expensive.
It is not uncommon to use MDF (pressed inserts with veneer) in interior design and car finishing. It is allowed to cladding window frames and window sills, musical instruments.
Fine-line features
Products with a unique name, understandable to anyone who studied English at school, indeed have beautiful lines on the surface. The material is made from wood waste, as a result of which its cost is more affordable than that of first-class natural veneer. This type of veneer is also called reconstructed. Fine-line products are presented in an assortment, have a wide range of colors, and can easily undergo further processing.
The technological cycle for the production of reconstructed veneer includes the following stages:
- removal of plates on peeling machines;
- drying and sorting;
- impregnation with dye in containers;
- treatment with adhesives;
- pressing;
- formatting by planing.
Thus, the products are peeled and at the same time planed. The moisture content of the material should be in the range from 8 to 12%. The types of reconstructed fine-line plates with a thickness of 0.35...5 mm and a density of 450 to 600 kg/m3 are in greatest demand. The final product contains up to 94% natural wood, approximately 6% adhesive, and no more than 2% color pigments.
Fine-line coatings can imitate the texture of any wood species and create textile patterns, such as a satin surface pattern. Fine-line veneer has great plasticity and heat resistance, does not react to humid air conditions, and is easily varnished.