Life expectancy over 100 years
Birch is actively used for economic activities and medicinal purposes.
Photo: stihi.ru Description:
- Birch - (lat. Betula) is a deciduous plant belonging to the dicotyledonous class. It takes its name from the ancient Gaulish language.
- The lifespan of the plant is approximately 100 - 300 years (rarely 400 years) . The age of the plant is influenced by the characteristics of the variety and external factors.
- The maximum height of the tree is 45 m . The trunk diameter can reach 1.5 m.
- The root system can be : superficial, with numerous thin processes, branched or deep. It depends on the conditions in which the tree grows.
Birch got its name from the ancient Slavic goddess Beregani.
The author of the story shares his experience of growing birch trees on the site. Recommends the use of trees in landscape design:
Variety of species
The exact number of birch species due to polymorphism has not been determined. But many scientists are inclined to believe that there are about 150 of them. There is no single classification, but the most successful is the division of all species into four groups:
- Costata - characterized by rough leaves due to protruding veins below and a ribbed trunk.
- Albae - includes birches with white and similar bark color.
- Nanae - includes all low-growing species with small foliage.
- Acuminatae are large-leaved species that grow in subtropical conditions.
Here are the most common types of birch trees.
Warty (hanging)
The most common type, the height of the birch is up to 35 m and has a trunk diameter of 80-85 cm. Young birch trees have brown bark, which turns white by the age of 10. In old trees, the lower part of the trunks turns black and begins to become covered with deep cracks. The branches are covered with a scattering of a large number of resinous formations that resemble warts, hence the popular name - warty birch . The branches of young trees hang down characteristically, which is why birch is often called silver birch. Grows in Asia, North Africa and Europe. The variety is demanding of the sun, easily tolerates drought, and is frost-resistant.
Hairy (fluffy)
The tree has a height of 20-27 m, a trunk diameter of about 75 cm. Young trees have red-brown bark, which after time becomes snow-white. The crown of a young tree is slender, narrow, with branches directed upward, becoming spreading and wide with age. This species grows in the European part of Russia, in Siberian forests, the Caucasus and Western Europe. The variety does not particularly need sun, it is shade-tolerant and winter-hardy. Feels very good in wetlands, prefers moist soil.
Sweet (sticky, cherry)
The tree is medium-sized, trunk diameter up to 65 cm, height 22-27 m. The crown is pyramidal, over time it becomes transparent, round, with drooping branches. The variety is characterized by dark brown, uneven bark, which is covered with pronounced cracks. The bark of young growth has a fragrant, spicy smell. This species grows quickly, preferring moist, light and well-drained soils , and is long-lived. It has average winter hardiness and often freezes in severe frosts. Due to its high demands on growing conditions, it never becomes a dominant tree. Grows well in Belarus and the Baltic countries.
Karelian
This species can reach 6-9 m, but often has the form of a small bush. The trunk is often covered with multiple irregularities (swells or tubercles) and is characterized by an unusual pattern that resembles marble veins. Wood is valued in furniture production.
Stone (Ermana)
This tree received its name in honor of the German traveler and physicist Adolf Georg Ermann. Among the birch trees it is a long-liver; some trees can grow up to 500 years. With a small height of 10-12 m, the tree usually has a curved trunk diameter of up to 1 m. The bark is flaky, dark gray or brown, and begins to crack with age. The branches are erect, pubescent and warty in young growth, forming a translucent, wide, very beautiful crown.
The species is unpretentious, shade-tolerant , cold-resistant, grows well on rocky soils. On swampy soils it is replaced by downy birch; it does not tolerate excess moisture well. It grows in Yakutia, Buryatia, China, the Far East, Korea and Japan.
Dwarf (dwarf, short)
This species is found on the plains and also grows in the mountains and tundra. It resembles a bush with powerful branching or is a low tree whose trunk is surrounded by warty branches. The bark of this tree is dark brown; young trees have a densely pubescent trunk. For growth and development, it prefers slightly acidic or acidic soil; it tolerates waterlogged, heavy soil well.
River (black)
The most heat-loving variety of tree with a trunk diameter of more than 1 m and a height of up to 35 m. The openwork crown is formed by ovoid or oval leaves, gray or whitish below, dark green above .
The bark can be brown, gray or rough, and in some cases there are even and smooth trees with creamy pink bark that peels off like paper. Widely distributed in America, heat-loving species.
Diseases and pests
| Cytorosis Ways to fight:
| |
| Silkworm caterpillars Ways to fight:
| |
| Bacterial dropsy Ways to fight:
|
Birch varieties
In addition to our well-known white-trunked birches with long catkins, there are species with a completely different appearance. For example, birch is black
I have light brown bark that peels off in curling strips.
Purple birch
is a small tree whose leaves are reddish-black when they bloom, and later become more reddish-brown. Very interesting, carved foliage of the Dalecarlian birch.
But the following species can boast of bright white bark: Chinese white birch
,
Jacqueman's birch
,
paper birch
and, of course,
silver birch
- one of the symbols of our nature.
In landscape design, birch trees with a crown hanging down to the ground are often used. These are varieties of weeping birch Tristis (Tristis)
and
Youngii
.
Reviews from gardeners
Newratka 18, Moscow
We water regularly, abundantly, but the birches drink their own and others’. Everything that is planted within a radius of 5 meters from the trunks is significantly lower than its counterparts growing in other conditions.
Source: xn--80abck7dtd.xn--p1ai
Sirina, Tyumen
For a long time I wanted to plant a birch tree in my dacha. I really love this tree. Finally, the fall before last I planted a very tiny one (so that it would take root better). Summer has stood still, but next year, I think, my beauty will begin to grow.
Source: dacha.wcb.ru
Popular types
As mentioned earlier, there are a large number of varieties of birch trees. Today we will talk about some of the most popular of them.
Hanging
The most common variety of birch in Russia is silver birch. It looks like a tree, up to 3 meters high with smooth white bark. In young trees, it is noticeable that the top layer of bark peels off easily. In “retired birches,” deep gray furrows are visible, penetrating the entire upper layer of bark. The trunk of this variety is quite flexible, straight with drooping branches, wedge-shaped leaves and catkins.
The average lifespan of this tree can be from 100 to 120 years. The tree becomes an “adult” by the age of 8, at which time the color of the bark also changes: from brown it becomes white. It is also worth noting that silver birch becomes drooping in old age; young representatives of the species have ordinary straight branches.
This plant is distributed throughout the country, but most often it can be found in the central regions and Western Siberia. Due to its unpretentiousness, it can grow in various climatic regions: it is found both in the tundra and in the steppe. Birch grows quite quickly, occupying any free plot of land, displacing other tree species.
This plant is widely used in human economic activities. So, resinous birch trees are almost collected in early spring, and young leaves are collected immediately after that. Birch bark is usually collected from the middle part of a growing tree or dead wood. In early spring, birch sap is also extracted, which, due to its composition (water, chemical elements of a special order and organic compounds), has a lot of useful properties. It is known that up to 10 tons of sap can be obtained from one hectare of silver birch. Chaga (a medicinal mushroom that chooses the trunks of this type of tree as its place of residence) is also collected all year round.
The collected material is widely used in medicine. Decoctions are prepared from the kidneys, which are used as a urine or choleretic agent. Infusions of young leaves are also good for these same remedies. But birch bark is necessary for creating various ointments for fungal, parasitic and infectious diseases, such as scabies, lice or lichen). The silver birch wood itself is used after dry distillation, which results in carbolene (charcoal). It is widely used in the treatment of poisoning. In addition, dense and heavy wood is used to prepare fuel coal or plywood.
Dwarf
The appearance of the dwarf birch is much more reminiscent of a low-growing branchy shrub than a tree familiar to everyone. Its other name “Ernik” seems to emphasize the predilection of this shrub for the formation of thickets. It grows in northern Russia, as well as in Europe, Canada and China. It can be found in the Alps or mountainous areas of Scotland. In our country, it can most often be found in Yakutia, Chukotka, Kamchatka or the Amur region. This is understandable, because this plant prefers mountainous or marshy areas and damp soils.
Dwarf birch is a shrub whose growth usually does not exceed 2-2.5 meters. The trunk of the dwarf species is also smooth, but the foliage is small (up to 2 centimeters), with a darker upper part. The branches are usually straight. The bark is not the usual white, but brownish-brown. It is important to note that this shrub grows very slowly, but is one of the most frost-resistant in the world. It is rarely used in economic activities: only among the northern tribes it is used as fuel or reindeer feed.
Karelian
Karelian birch is a variety of low-growing trees, distinguished by the presence of a strange growth on the trunk (burl) and a very beautiful patterned cut of wood. It grows, as the name implies, in Karelia, but not only. This type of birch is also found in other territories of Russia, as well as in Lithuania. This species is divided into three more varieties: low-growing, medium-height, tall.
When processed, the wood gives dark brown and yellowish shades. The unusual pattern of wood allows the Karelian tree to be used for making dishes, boxes, vases, watches and any other souvenirs.
Paper
Paper birch is a fairly powerful tree, the growth of which easily reaches 30 meters. It got its name because of the wide, dense bark, which, being pink in young animals, becomes white over time. The leaves of this tree are quite large, reaching a length of 10 centimeters. This plant is very unpretentious and can grow in any soil, with any lighting.
Cherry
North American species of birch. It is a tree up to 25 meters high. Young plants have a pyramidal wide crown, which with age begins to droop, forming a ball. The bark is of an unusual dark color (mostly cherry or red). It has fairly large leaves, up to 12 centimeters long, with pubescent veins along the perimeter. In spring, the tree blooms profusely, producing a large number of long catkins. The tree grows quite quickly and lives a long time. Prefers deep, moist bud.
Yellow
This is a large tree, reaching 30 meters in height. North America is considered its homeland (hence its other name - American birch). It has a very interesting bark color, which can be light orange or gray, or reddish-brown. The leaves are also large: up to 12 centimeters. The plant is very tenacious and grows quickly. Prefers moist but drained soils. It can live calmly for up to 300 years.
Small-leaved
A relatively short tree (up to 15 meters), it can often grow as a gnarled shrub. Distributed in desert valleys, rivers and swamps of Western Siberia, Altai or Mongolia. The bark is yellowish-gray or even pink. The leaves are quite small.
Fluffy
A low tree, distinguished by a 15-meter white trunk and a wide crown, which is formed by branches directed strictly upward. The leaves are shiny, small (up to 6 centimeters). Immediately after formation, the foliage is sticky and very fragrant. The plant tolerates shade and marshy soils well.
Far Eastern
Perhaps the hardiest plant in this group. It is a slender, straight tree with a 30-meter trunk and a spreading crown. Very shade tolerant. Young plants, for example, are not able to develop at all unless they are in the shade. Prefers foothills. Far Eastern birch can be found in Primorye, Khabarovsk Territory, as well as in the vast expanses of China and North Korea.
It is distinguished by the presence of a shaggy wide trunk covered with light yellowish bark. The leaves are oval, large and dense. This type of birch can live up to 80-100 years.
Woolly
This is a representative of the flora of mountains and mountain clearings, dark coniferous forests of Eastern Siberia, the Far East of Russia and Korea. It is a 15-meter tree with a large number of fluffy buds. The leaves are wide, up to 9 centimeters, covered with soft edges along the lower veins.
Where does Birch grow?
Birch is widespread throughout Russia and the Northern Hemisphere as a whole, even beyond the Arctic Circle. Birch is undemanding and tolerates both heat and cold.
Dwarf Birch grows in the tundras of Europe and North America and the mountain tundras of Siberia. It does not even reach 1 m in height. During the glacial and post-glacial periods, this Birch was distributed much further to the south; now it is found there only in swamps as a relic.
Cherry birch
Unusual decorative properties that persist throughout the year are what distinguishes the cherry birch species from all other listed species. In the spring season, it has an abundance of hanging stamen catkins of sufficient length.
Fruiting catkins, which are already summer, are often large in size and can remain on the branches until spring, enduring severe winter frosts.
Beautiful bouquets can be made right in winter if you carefully cut off several of these branches with earrings without damaging them.
Types of birch: photo of cherry birch
Karelian silver birch (Betula pendula f.carelica)
Karelian birch is sometimes considered an independent species, but it is one of the forms of European silver birch. The famous Karelian birch wood has sinuous fibers that create a very beautiful pattern in products made from it, but in gardening this feature is not important. There are several types of growth of Karelian birch - from creeping to straight-trunked. A bush form 3-4 m high with twisting trunks is suitable for gardens. Tall forms reach 15-18 m.
Winter-hardy, light-loving, drought-resistant, undemanding tree, effective in single plantings and in groups.
Description of the tree
Birch is a tree no more than 25 m high. The trunk is smooth, white and straight, with black lines on the bark. Branches with resinous warts, thin, well developed and dense. Mature trees have drooping branches.
The leaves are smooth on both sides, long-petiolate, pointed at the end and wide at the base, diamond-ovate or triangular in shape , 3-4 cm long. Young birch trees have fragrant and sticky leaves. Buds form in March. They are elongated, reddish-brown in color, astringent in taste and resinous.
Birch is a monoecious crop. The tree has staminate (male) and pistillate (female) catkins. Staminate catkins are located in 3-4 pieces at the ends of branches, 6-7 cm long, pendulous. Pistillate catkins are 2.3-3.5 cm long, erect, axillary, located one at a time on short lateral branches.
Begins to bloom in April-May. Male inflorescences develop in autumn and continue to remain in winter; female inflorescences are formed when the leaves bloom. Pistillate inflorescences are connected in 3-4 pieces, have 3-lobed scales. The fruits begin to ripen in August-September. One earring contains approximately 600 seeds. The fruit is a flat single-seeded nut of elliptical oblong shape, with two wings, they are 3-4 times larger than the nut itself. The seeds are carried by the wind and take root well when placed on moist or dry, loamy, sandy, rocky-gravelly or black soil. The tree grows very quickly and renews itself beautifully by self-seeding and shoots.
Wood
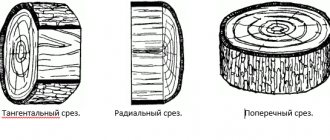
White birch has strong, dense, light-colored wood with a slight pink or yellowish tint. The pattern on it is weakly expressed, wavy, the growth rings are almost not visible, and reddish, chaotically scattered spots are characteristic.
One of the most beautiful woods is the Karelian birch - a low plant that has a highly deformed trunk in the form of spherical swellings and tubercles. Previously, the Karelian birch was considered a separate species, but now biologists have come to the conclusion that it is a warty (silver) birch, the trunk of which is deformed under certain conditions. That’s why the life of the tree is short: the Karelian birch lives for about forty years (some species live up to one hundred and eighty), and therefore does not have time to grow, and its height is about twenty-five meters. Karelian birch became famous for its marble-like texture and color: brown spots on a golden background (due to its properties, expensive products have long been made from it: furniture, decorative fakes, souvenirs). Scientists have still not come to a common opinion about the reasons for the appearance of such an amazing pattern.
Among the main assumptions why Karelian birch has patterned wood, the following versions are put forward:
- violation of mineral nutrition;
- viral infection;
- hereditary disease.
Despite the fact that when crossing two plants of this species, the Karelian birch passes on its amazing structure by inheritance, the decorative characteristics are not always completely transferred, and it is possible to determine whether the wood will have a pattern no earlier than after five years. Karelian birch is also of particular value because it is very rare, and therefore its cost exceeds 1.5 thousand dollars, and is sold not by cubic meters, but by weight, in kilograms.
Interesting Facts
- Sometimes on Birch you can see growths - caps - on a section they have a peculiar complex and beautiful pattern. Processed burl has long been used to make elegant crafts: boxes, snuff boxes, and decorative furniture parts.
- Birch is also characterized by specific types of fungi that destroy dead wood (saprotrophic), which play a vital role in the process of self-cleaning of forests from dead wood and windbreaks.
- Why is Birch white? The cavities of Birch bark cells are filled with a white resinous substance - betulin, which gives birch bark its white color.
- In beekeeping, Birch is important as a pollen carrier. After all, bees collect not only nectar, but also pollen - the main source of protein and vitamins.
- People living near a birch grove are much less likely to suffer from colds, since the volatile phytoncides released by the tree suppress the growth and development of bacteria.