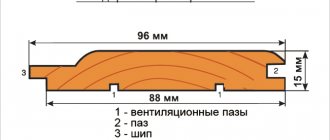
Chipboard (chipboard) is made by hot flat pressing of wood particles (shavings and sawdust) mixed with a binder, mainly synthetic resins (urea-formaldehyde, urea-formaldehyde, formaldehyde resins). A valuable raw material for chipboard is any low-value wood, both coniferous and deciduous. The performance properties of chipboards mainly depend on their density, shape and size of wood particles, as well as the quantity and quality of the binder.
The raw materials for particle boards are:
— chips obtained in planing production;
— sawmill waste: slats, obapol and trimmings after trimming boards, etc.;
- specially chopped wood chips.
Chipboard is free from the disadvantages inherent in wood, such as knots, internal voids and cracks. Important advantages of chipboard include high strength, rigidity, uniformity, ease of processing, and the ability to firmly hold nails and screws. Another advantage of chipboard is its low price. That is why chipboard is the most widely used material for economy class furniture; Most office furniture is made from chipboard. For kitchens and baths, a special type of chipboard is used - with increased moisture resistance. Plates can be given biostability, hydrophobicity and fire resistance. The slabs are well glued along the sides and edges, they can be painted or finished with paints and varnishes, lined with veneer, paper, and plastics.
Chipboard varieties
There are chipboard slabs of 1st grade, 2nd grade, as well as non-grade slabs, used, as a rule, for construction purposes. The main differences between grades 1 and 2:
No protrusions or depressions, resin or paraffin stains are allowed on the first grade chipboard board;
On a first-grade chipboard slab, chipping of edges and chipping of corners is not allowed (with the exception of single chips (chipping) up to 3 mm and extending along the edge up to 15 mm); on a second-grade chipboard slab, chipping of the edges is allowed within the limits of deviations along the length (width) of the slab;
there may be grinding defects on the surface of the second grade chipboard slab (no more than 10% of the area);
On the surface of a chipboard slab of the second grade, inclusions of bark and large fractions of chips may be present to a greater extent compared to the first grade.
Basic parameters of particle boards
Despite the fact that at first glance all slabs of equal dimensions look approximately the same, in fact they differ in a number of parameters. The basic requirements for chipboard are contained in a special standard (GOST 10632-2007), according to which several different classes of these products are distinguished.
Chipboard varieties
Depending on the quality of surface treatment, three types of the material under discussion are distinguished:
- First grade. Complete absence of chips on the surface of the sheet, perfectly smooth edges, no swelling. Most often, first grade chipboard is used for further processing, in particular for lamination.
First grade chipboard sheets - Second grade . The sheet has minimal deviations: small chips, scratches, delaminations. Such slabs are used mainly in the production of furniture, flooring or cladding for finishing.
- Third grade . This is a rejection of high-quality material, which may have differences in thickness, large delaminations, low density and other defects. The standard does not indicate how many chips there must be to classify a sheet as third grade.
Water resistance of chipboard
Chipboards come in regular and increased (letter “B” in the marking) water resistance. In the vast majority of cases, chipboard with ordinary water resistance is used. Chipboard with increased water resistance is advisable to use for the manufacture of countertops for kitchens, furniture for bathrooms, as well as for special construction purposes. When making waterproof chipboard, before pressing, a special paraffin emulsion or molten paraffin is introduced into the chip mass. An indicator of water resistance is swelling in thickness (over 24 hours, upper limit):
• regular chipboard, grade P-A - 22%,
• regular chipboard, grade P-B - 33%,
• waterproof chipboard - no more than 15%.
Advantages and disadvantages of chipboard for finishing
Most of the advantages are due to the homogeneity (homogeneity) of the structure and the fact that the basis of production is wood.
- Relative safety for health (if chosen correctly).
- Ease of installation and maintainability of the structure.
- Fire resistance when impregnated with special compounds - fire retardants.
- Good ability to hold fasteners.
- Inert to temperature changes and chemical reagents.
- Perfectly suitable as a finishing layer for installing a base floor made of finishing coatings.
One of the manufacturing shortcomings is the fact that the sheets sag and cannot withstand high bending loads. High humidity deforms the pressed material. The composition contains formaldehyde resins.
Furniture manufacturing
Laminated panels are in great demand in this area. Everyone is well aware of what laminated chipboard is in furniture. These are all visible parts of upholstered and cabinet furniture: walls, shelves, tabletops, bed frames, as well as cabinet fronts in the inexpensive segment. Hidden parts and those located under the upholstery can be made of slabs without a decorative coating.
Furniture made from chipboard is the most affordable Source mblx.ru
In terms of manufacturability in the manufacture of furniture, this composite material is superior to wood in many respects, especially when it is necessary to create large-sized structures. It is not needed:
- plan;
- polish;
- paint;
- splice or glue together several elements to produce wide parts.
To make furniture from laminated chipboard, it is enough to cut and cut out the parts, mark and drill holes for fasteners, and use it to assemble the product and install the fittings. But this material forces us to include an additional stage in the technology, which is absent in the production of wooden furniture. We are talking about finishing the ends. This can be a problem when making it yourself; in production, the edge is glued using special equipment.
Variety in quality
There are three quality options available.
The highest quality is class 1. There is an ideal surface and compliance with certified performance characteristics. It is used in residential areas.
Next comes class 2, which may have various scratches and flaws on its surface. Can be used in economy class residential premises.
The worst quality is class 3, this material is used in technical rooms.
Standard dimensions of chipboard sheets
The production offers several standard sizes of chipboard sheets:
- 2440x1220 mm;
- 2440x1830 mm;
- 2750x1830 mm;
- 2800x2070 mm.
The last format in this list is not provided for by Russian GOST, but some foreign companies supply laminated sheets of these sizes. The thickness of the material usually corresponds to the standards accepted in furniture production: 10, 16, 18, 22 and 25 mm.
Maximum permissible dimensional deviations according to GOST 10632-2014:
| Thickness, mm | Length, mm | Width, mm |
| +/- 0.3 - for polished | +/- 0,5 | +/- 0,5 |
| -0.3/+1.7 — for unpolished |
Reference materials
Here are some reference materials on the technical and physical characteristics of chipboard. They can be useful if it is necessary to calculate the volume, weight, area of sheets during transportation or ordering.
Density of chipboard
| Thickness, (mm) | 8 | 10 | 16 | 20 | 22 | 30 | 32 | 38 |
| Density, (kg/cubic meter) | 740 | 720 | 680 | 670 | 660 | 620 | 600 | 600 |
Areas and volumes of chipboard
| Width, mm | Length, mm | Area, square meter | Volume (with a thickness of 10 mm), cubic meter. | Volume (with a thickness of 18 mm), cubic meter. | Volume (with a thickness of 20 mm), cubic meter. | Volume (with a thickness of 38 mm), cubic meter. |
| 2440 | 1830 | 4,47 | 0,045 | 0,080 | 0,089 | 0,170 |
| 2750 | 1830 | 5,03 | 0,050 | 0,091 | 0,101 | 0,191 |
| 3060 | 1830 | 5,60 | 0,056 | 0,100 | 0,112 | 0,213 |
| 3060 | 1220 | 3,73 | 0,037 | 0,067 | 0,075 | 0,142 |
| 3060 | 610 | 1,87 | 0,019 | 0,036 | 0,037 | 0,071 |
Chipboard weight
| Thickness, mm | Size, mm | ||||
| 2440x1830 | 2750x1830 | 3060x1830 | 3060x1220 | 3060x610 | |
| 10 mm | 26 kg | 29 kg | 33 kg | 22 kg | 11 kg |
| 18 mm | 33 kg | 37 kg | 41 kg | 27 kg | 14 kg |
| 20 mm | 60 kg | 67 kg | 75 kg | 50 kg | 25 kg |
| 32 mm | 86 kg | 97 kg | 108 kg | 72 kg | 36 kg |
What it is?
Chipboard is a sheet composite material produced by pressing sawdust and shavings at high temperatures with a non-mineral binder and the introduction of various additives, which are necessary in various cases to improve certain properties of the resulting sheet. The production of this material is quite expensive, but at current prices for the finished product, the purchased equipment pays for itself in 1-2 years.
Depending on different indicators, there are several classifications of chipboard. Some classifications are given below.
Main types
The CIS GOST documentation identifies the following characteristics for classification:
- Based on the number of layers, chipboard is divided into single-layer, two-layer, three-layer and multi-layer. Moreover, the trend is this: the greater the number of layers, the more dense and durable the resulting slab.
- By emission class. Emission determines the amount of formaldehyde that, when added during production, is released into the air from 100 g of slab. There are 2 classes: E1 and E2, while the first is more environmentally friendly, harmless to people, the content of harmful substances in it is less than 10 mg. Another class contains more than 10 mg of formaldehyde. Boards of this class are suitable for use in construction and production with good ventilation or outdoors. There is also a certificate for chipboard that confirms its emission class. The certificate is issued by a special body, has an established model and is distributed throughout the CIS. The current standards for assessing the toxicity of formaldehyde in Europe differ from those adopted in the CIS countries.
- Based on the density of chipboard, slabs are distinguished with low density (550 kg/m³), with medium density - 550–750 kg/m³, with high density - more than 750 kg/m³.
- There are 2 types of chipboard, P1 and P2, and depend on the physical and mechanical characteristics of the sheets: resistance to bending, curvature, hydrophobicity, etc. In this case, type P1 is intended for use in conditions of absence of humidity, and P2 is intended for use indoors, including including furniture production, for use in conditions without humidity.
- There are 2 grades based on the characteristics of the external condition of chipboard sheets: grade I (without flaws or almost without defects), grade II (large defects of the top layer are allowed). For slabs with significant deficiencies, the name without grade is also used; it can be used in repair and construction work.
- The outer layer of chipboard is divided into sheets with a fine-grained top layer (coating with polymers is acceptable), regular (can be covered with veneer) and coarse-grained (used for repair and construction work)
- There are also sanded (Sh) and unsanded (NS) chipboards based on the level of processing of the outer layer.
Difference from MDF and fiberboard
In addition to chipboard, there are also fiberboard and MDF. They are very similar, but in order to learn to distinguish them, it is better to learn more about the last two materials.
So, MDF is made from the finest sawdust. Experienced builders say that the difference between it and chipboard is about the same as between ingredients crushed with a mixer and a meat grinder. You can even tell them apart by their appearance.
And although there is more filler in chipboard, MDF still outperforms it in terms of environmental friendliness. After all, inside it, the bonding of the chips occurs with the help of paraffin and lignin. Because of this, it is gradually replacing the usual particle boards.
In addition to high quality and environmental friendliness, MDF also wins in terms of plasticity. Despite its strength, it can even be subjected to fine processing. This panel lasts longer than regular wood, so it is used to create furniture. For the CIS countries, there is still one drawback - the price is too high, since MDF production is poorly organized.
Fiberboard or, simply, fiberboard, is much more common than both materials described above. Drawers, cabinets, other furniture - run your palm along their bottom or back wall. If you feel a rough surface, then this is fiberboard.
It is made by compressing wood dust and then gluing it together. But, most importantly, in this case, wet pressing technology is used in production, and the wood shavings are steamed first.
The difference with chipboard is less strength. Moreover, it is always thin, since a larger size cannot be made due to special technology. Fiberboard is sometimes laminated on one side, but on the other it always remains rough.
Despite not so good strength indicators, it is quite durable and has a lower price. But, of course, it will not be possible to make a complete furniture structure from it, and the narrow range of applications is the main disadvantage of fiberboard. You need to decide for yourself what is better than MDF, fiberboard, laminated chipboard or chipboard at the planning stage, since the final cost of the finished object will depend on this.
The video will help you understand the wide range of materials for furniture production: