Basic wood building materials
Wood has always been used in the construction industry, even in the construction of pyramids and medieval granite castles. Today, wood materials are used no less widely, although with the invention of concrete, wood begins to yield to it its dominant position in the past. But even modern stone buildings cannot do without wood.
For example, not a single residential building today can do without a rafter system, which in 99% of cases is made of wood. It is also used for finishing work, and this is not to mention formwork, if any parts of the house are being concreted.
Yes, wooden house construction in our country is on the decline, and frame technologies have not taken root at all, and these are precisely those types of construction that require the use of large amounts of wood.
But even in stone house construction, wood is used quite a bit, so the woodworking industry today is developing at a fairly rapid pace. Many sawmills and factories produce a wide variety of lumber, the purpose of which is very wide. For each type of work, one or another type of material is used, in connection with this there is a classification of lumber. In addition to lumber, other wood materials are also used, such as plywood or particle boards, so we’ll talk about all of this.
Log
The most traditional lumber is a log, but today ordinary logs are used little, mostly builders give their preference to rounded logs. Such a log is lumber with an ideal round cross-sectional shape and is processed in factories.
All logs used to build a house have the same diameter, so there is no need to adjust them to each other; houses are built from such logs very quickly.
However, a rounded log is noticeably more expensive than a regular log, and a significant part of this difference is due to the preparation of the log for construction not only by carpentry, but by drying using not very cheap technologies.
Board
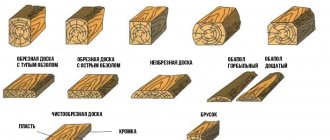
The most common type of lumber is board. A standard board is obtained by sawing a log, its length is within 2 meters, its thickness is up to 10 cm, and its width is up to 30 cm. The boards are used to lay floors in rooms, cover walls with them, and make ceilings between floors.
Boards vary by category, the most popular of which is unedged board, and the most elite is solid board, one of the options of which is lining. The difference is that solid boards are made from expensive types of wood, while lining is made from almost any kind.
They are united by the presence of tenons and grooves on the sides, thanks to which the laying of this material is done better than using nails or screws.
An unedged board is a board whose edges are not sawn, it is the cheapest, the only cheaper one is the slab, which is the outermost layer of cut logs with unprocessed edges. And if you can even make lining from an unedged board, then the slab is only suitable for sheathing or formwork, which, however, does not detract from its value when carrying out a variety of types of work, since formwork and sheathing are mandatory elements used in the construction of any house.
The industry also produces a wide variety of planed boards, which, however, are more often used not in construction, but in the furniture industry.
Boards are made from almost all industrial tree species, both deciduous and coniferous.
timber
The beam is also made from a solid log, and, in fact, it is a log, only its sides are not round, but cut. This lumber is mainly used for making rafters for houses of any type or for creating frames for frame houses.
There are different types of timber, the most popular is ordinary timber, which can have any thickness greater than 10 cm. The more expensive one is profiled timber. In a regular beam, all sides are smooth; in a profiled beam, the two opposite sides have a profile somewhat similar to the tongue-and-groove system.
Thanks to this profile, the installation of a log house from beams is of higher quality, but at the same time such timber is much more expensive.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JJmav4eCsBY
Today, glued laminated timber has become quite widespread. Strictly speaking, this is not even a beam as such, but a wooden mass similar to a beam, made from boards glued together. However, such timber is much stronger and more durable than conventional types of timber, and it does not shrink or warp under high humidity.
You can also mention such a type of timber as a block. It is made mainly by cutting thick boards and is most often used in finishing and repair work. Its usual thickness does not exceed 10 cm, the length may vary depending on the application.
What it is?
In a professional environment, timber products are wood blanks in which the original physical and chemical structure has been preserved; in everyday speech they also include lumber. To obtain timber the following is used:
- industrially felled trees;
- hand felled timber;
- suitable species of self-fallen trees (rare);
- whips and their parts.
In the process of timber production, various options for division in the transverse or longitudinal plane are used. We are talking primarily about the following processes:
- sawing;
- planing;
- processing with cutters;
- schism;
- peeling;
- crushing (grinding).
It is worth noting that timber products cannot be mixed with secondary whole products, for example, the following:
- with laminated timber;
- with different types of plywood;
- with chipboard, fibreboard, MDF.
The most important advantages of timber are, of course, their natural origin and ease of use in various cases. And also in favor of such a product is its accessibility to consumers. Wooden structures last a long time and are stable. When used correctly, this material is not too inferior to brick and concrete in terms of durability. The aesthetic flavor of anything made from timber is also very important.
But wood has more than just benefits. The disadvantages include:
- high flammability;
- susceptibility to dampness and mold (removable, but valuable environmental properties are lost during processing);
- tendency to absorb moisture in large quantities;
- high risk of shrinkage, warping and other similar deviations that provoke deformation of building structures;
- difficulties in choosing the appropriate species and category of timber.
Wood - types of wood building materials - Domomaster
Wood remains one of the most popular materials, and not a single construction site can do without it. Recently, it has been of particular interest: owners of residential buildings are interested in environmentally friendly construction and safe home decoration, and wood materials remain leaders in safety and usefulness for humans.
Preparing wood for the production of building materials
Coniferous and deciduous wood is used to make lumber.
Tree felling and stump uprooting in Moscow and the Moscow region is carried out in several areas; the harvested wood goes through several preparatory stages: bucking, debarking and sawing.
Bucking is the division of a trunk, which is first freed from roots and branches. Debarking is the process of removing the top layer of bark, after which the trunk is sawed using special equipment.
After this, planing is carried out - the tree trunk is freed from the upper layers, thin sections are removed with a special tool. Before making materials, the wood is also dried in special chambers to remove natural moisture. The final preparatory stage is protective treatment: the wood is impregnated with antiseptics to protect against fungus and bacteria.
Types of wood building materials
All types of materials can be divided into solid and composite. Solid ones are made from solid wood - these are timber, slabs, edged boards, rounded logs and other materials that are actively used in modern environmentally friendly construction. Load-bearing structures are made from solid wood due to its high strength.
Grade
Based on quality characteristics, timber is divided into four grades. When establishing the grade, the whip is divided into the butt, middle and apical parts. Butt wood has the highest physical and mechanical properties and does not have live knots on the side surface. In the middle part of the whip there is the largest number of overgrown and tobacco knots. The apical part is most abundant in healthy knots of different sizes.
- 1st grade: large-sized assortment from the butt part of the whip. Knot-free or low-knot logs are used for the production of wood materials for special purposes: aircraft, deck, veneer, etc.
- 3rd grade: such timber can be obtained from any part of the log. They are used both in round and sawn form. They are used in mechanical engineering and construction; they are used to make sleepers, railway transfer bars, and furniture. In coniferous timber, the number of healthy knots is not taken into account.
- 4th grade: used for lumber for construction, mechanical engineering, furniture, packaging. External rotten rot, the simultaneous presence of sapwood and heart rot in coniferous and sapwood deciduous species (birch, alder, hornbeam, maple), and heart rot in thin assortments of all species are not allowed[1].
Requirements
Lumber includes wood of different sizes and qualities. During its production, the logs are divided into parts and cut. Each type of lumber is subject to generally accepted state standards (for example, GOST 24454-80, GOST 8486-86, GOST 2140-81, etc.).
The quality of edged materials for export and domestic production is assessed by the surface or the worst edge. In doing so, pay attention to a number of important criteria:
- material defects (roughness, cracks, structural defects);
- permissible humidity value;
- quality of the cut and its angle of inclination;
- wood density and core quality;
- number of knots per unit area of material;
- appearance and shade of blanks;
- age of the material, place of its cutting;
- damage by insects (bark beetles, beetles);
- the presence of fungus, mold, rot;
- warping along the edge;
- spiral curvature.
In addition, the grade depends on the weight, size of the lumber, and the ratio of the thickness and width of the boards. The gradation of the assortment takes into account business qualities, decorativeness, strength, resistance to rotting of different species, and the amount of shrinkage to actual sizes.
GOST prescribes requirements for such wood species as fir, cedar, spruce, poplar, pine, linden, aspen, alder, birch, beech, ash, larch, oak, hornbeam. Regarding knotiness, knots whose area does not reach half the tolerance are not taken into account. However, the higher the grade, the stricter the grading requirements.
READ What is veneer and what types does it come in?
The same requirements apply to cracking of workpieces along the edges and faces facing the end. Cracks should not cause damage to the integrity of the lumber.
Softwood lumber is made from spruce, fir, pine, cedar and larch. The most common and affordable is pine or spruce lumber. As a rule, for the production of edged lumber, round timber is not sorted and spruce and pine are offered for sale in a mixed form, since they also grow together in the forest. Sorting is not economically profitable - in other words, sorting will lead to an increase in the final cost of the material, but it is important to understand: the quality of pine and spruce boards is the same in their technical characteristics. That is, you can ignore this aspect - their physical characteristics are very similar, and for solving most construction problems, the quality and strength characteristics of spruce and pine will be identical.
According to the quality of structure and quality of processing, edged boards can be of five grades. There are four grades of softwood edged timber. The relative humidity of selected and 1-3 grade lumber cannot exceed 22%; by agreement with the customer, the indicators may change. The fourth grade has no restrictions on humidity. The grading is assessed taking into account the condition of the edge or face; only the worst part is taken into account when measuring. The surface roughness for selected and 1-3 grades should be less than 1250 microns; the fourth grade has no restrictions on this parameter. This is exactly what is very important. Often, cheaper lumber is sold under the guise of higher-grade lumber.
Softwood edged timber
Softwood edged boards
Edged timber, size according to GOST
The grade of lumber is also influenced by the criterion for limiting the natural defects of wood; we will talk about the general approaches of the standard to determining the class of wood. On our website there are many articles explaining highly professional terms and techniques that mean nothing to the average person. But even after studying the materials, experience is necessary; it is difficult for the average person to distinguish dozens of types of knots and irregularities in the structure of wood “by eye.” The best way to avoid being a victim of fraud is to buy edged boards or edged beams, relying on a trusted supplier. Our team is always ready to help you. We approach the issue of sorting honestly. Let us briefly consider the main differences between the varieties of edged boards and edged timber. The criteria by which it is worth distinguishing the types and quality of boards and timber are the presence of defects or defects.