The variety of lumber presented on the modern market makes their choice difficult. The significance of any wooden building material depends on the cleanliness of its base. Types of wood are regulated by GOSTs, which specify the basic requirements for them. Based on the types of wood, you can choose the best option for boards of good quality and decent appearance. It is necessary to choose the type of timber with particular seriousness, since its cost, depending on the type, can differ significantly.
General information about lumber
Products of various types obtained by cutting tree trunks are usually called lumber. Depending on the type of tree, it can be coniferous or deciduous. Pine, spruce and larch logs are used to make coniferous materials. The most popular hardwood materials are birch, oak and aspen. Various defects arise in a growing tree due to climatic conditions and a number of other reasons. Therefore, wood brought from the forest almost always has defects (cracks, knots) that reduce the quality.
Depending on the number of various defects (in appearance and characteristics), the grade of wood is determined. In addition to raw trunks, dead wood is also sawn into lumber - dried but standing trees. Building material made from dead wood is best suited for the construction of wooden houses. In fairness, we must admit that all building materials have advantages and disadvantages. Alas, timber made from dead wood is no exception; it also has its pros and cons. The main disadvantage of such timber is considered to be high cost, since it is classified as an elite building material. For this reason, many developers cannot afford it.
Types of lumber depending on size, shape, structure
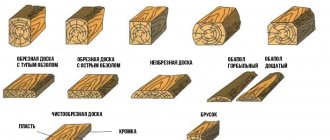
board
Board
- This is lumber up to 100 mm thick and more than twice the width. The main material for making boards is coniferous trees, such as larch, spruce and pine, but boards are also made from deciduous trees. The choice of one material or another depends on the purpose for which you intend to use the board.
Construction boards are divided into unedged and edged. An unedged board is lumber from which the tree bark has not been removed or has been partially removed. They are used for minor work: to create formwork, install scaffolding. This type of board usually has uneven edges.
Edged boards are lumber from which tree bark has been completely removed from all surfaces. Used for external and internal finishing of surfaces, floors, roof elements.
Board size chart
Thickness Width
| 16 | 75 | 100 | 125 | 150 | — | — | — | — | — |
| 19 | 75 | 100 | 125 | 150 | 175 | — | — | — | — |
| 22 | 75 | 100 | 125 | 150 | 175 | 200 | 225 | — | — |
| 25 | 75 | 100 | 125 | 150 | 175 | 200 | 225 | 250 | 275 |
| 32 | 75 | 100 | 125 | 150 | 175 | 200 | 225 | 250 | 275 |
| 40 | — | 100 | 125 | 150 | 175 | 200 | 225 | 250 | 275 |
| 44 | — | 100 | 125 | 150 | 175 | 200 | 225 | 250 | 275 |
| 50 | — | — | 125 | 150 | 175 | 200 | 225 | 250 | 275 |
| 60 | — | — | 125 | 150 | 175 | 200 | 225 | 250 | 275 |
timber
laminated veneer lumber
- this is lumber 100 mm thick or more, rectangular or square cross-section and a length many times greater than the width.
Timber is a natural, environmentally friendly and durable material. The timber is made mainly from coniferous trees. It is used for the construction of cottages, building frames, foundations, dachas, houses, furniture, and ships. The most used timber sizes are 100x100 and 150x150 mm. The small cross-section of this lumber allows us to guarantee high quality construction. It is also good as a wall material for wooden houses.
The timber is divided into regular unplaned, profiled, rounded and glued. We will talk about these types of timber in a separate article.
Bar
- This is lumber up to 100 mm thick and no more than twice the width. They are made from boards. The bars are used in carpentry, construction, and repairs. in the furniture industry. For coniferous trees, the thickness of the bars is from 16 to 75 mm, the length is from 1 to 6.5 m. Dimensions of the bars from deciduous wood: thickness from 19 to 100 mm, and length from 0.5 to 2 m.
Sleepers
Sleeper
- This is a support for rails in the form of bars. The width of the wooden sleeper is 23 - 25cm, depth 18 - 20cm, length - 275m. Houses made from sleepers are very heat-intensive; such construction is durable, as they are made from coniferous wood such as spruce, pine and fir. Sleepers are used for the construction of fencing structures, outbuildings, and as construction beams for the construction of residential buildings. This is an economical option. Due to the treatment of sleepers with creosote, they are not susceptible to rotting, damage by insects and fungus. But there is also a disadvantage of this treatment, since creosote contains toxic substances such as phenols and their esters, naphthalene and anthracene, which can contribute to the development of serious diseases. Creosote affects the nervous system and can cause headaches, weakness, and liver pain. That is why sleepers are very dangerous to use as construction timber for the construction of houses. However, they are still used in an attempt to use old materials, where the level of creosote is much lower.
Gorbyl
Gorbyl
- it is also called obapol, this is the side part of the log, having one sawn surface and the other not sawn or not sawn to the full length.
This is waste, part of a tree trunk that remains when sawing logs. On one side, the slab retains the natural surface of the wood, and on the other side it is flat. Used for the construction of fences, auxiliary rough structures, rough floors, formwork, pallets, and for kindling a stove. The main advantage of slab over other lumber is its low cost.
Wood and business croaker.
Wood slabs are only suitable for lighting stoves; they are no longer valuable as a building material.
Slab fence
The business one differs from the wood-burning one in that its sawn side is processed and polished. It can also be used to kindle stoves, but its condition allows it to be used in the construction of non-residential buildings, fences and enclosures.
Thus, all of the above types of wood can be used in different areas of construction, production, and life. It is virtually waste-free, environmentally friendly and relatively inexpensive. self-healing material.
Regulatory Requirements
Lumber used in the construction of houses is subject to fairly stringent requirements. They concern not only individual characteristics (sizes, shapes), but also the number of defects, as well as the level of humidity. The grade of wood depends on several parameters that are strictly regulated by the state standard; GOST 2140-81 contains a similar description of them.
When constructing a house, timber and lumber of the first or second grade, manufactured in accordance with GOST, are used. Most often these are types of coniferous wood, which have many advantages. For example, the high strength of materials is of great importance when constructing a frame. Meanwhile, soft pine wood is easier to process because it is very pliable. Hardwood is used mostly for making furniture. For example, solid beech woods are best suited for Viennese chairs.
What is commercial timber?
These wood-based panels (chipboard, fiberboard) can be made from fibers, shavings, sawdust and other sawmill waste. And for the manufacture of solid wood furniture, the raw material can only be high-quality industrial wood. This category includes raw materials made from the stem part of a tree. Of the total volume of logging, the yield of industrial wood is 72-85% (depending on the species and age of the trees).
The fibrous structure of the trunk can be studied from three main sections:
- end (transverse) - a cut across the fibers, perpendicular to the stem axis;
- radial - passing through the core of the barrel, at right angles to the end;
- tangential - applied parallel to the axis (at any distance from the core), tangential to the annual layers.
When a cross section of the trunk is made, the following layers are distinguished:
- bark, cork and bast layer - external protection of the tree;
- cambium - a thin layer between the sapwood and bark;
- sapwood - porous wood through which water and nutrients rise up the trunk from the roots to the crown;
- core (which includes the core);
- medullary rays;
- annual circles.
More information about timber grades and assortments
Wood used for the production of various building materials is classified by grade. This parameter depends on the characteristics of the wood and the quality of its processing. According to GOST 2140-81, lumber is divided into four grades based on wood quality. Classification of wood by grade involves a numerical designation from 1 to 4. Depending on the varieties and number of defects, various products are assigned a specific grade.
A grade 1 board or timber must have clean surfaces with a minimum number of flaws. In material assigned grade 2, a small number of defects are allowed that do not spoil its appearance. Third-rate products may contain any type of defect.
According to European standard
The grade of lumber is indicated by the letters A and B. On products with the sign A, wormholes, rot, wane and the presence of knots of any size are not allowed. Grade B allows the presence of all types of defects on the wood in small quantities, with the exception of rot.
Russian entrepreneurs engaged in the production of lumber often determine the grade of their products according to unwritten standards that differ from generally accepted GOST standards. For example, you can find building materials of the following types:
- Extra. These materials must meet requirements that are much stricter than those for GOST 1st grade products. In principle, they should not have any defects. This material is very rare, so it is quite expensive.
- Prima. It is similar to DIN grade 1.
- Variety AB. These materials have characteristics that are variety-determining for extra and prima.
- Grade C. These wood products may contain any type of defect that does not violate their integrity.
Timber and wood products
Round timber
divided according to thickness into small ones (diameter 8... 13 cm); medium (diameter 14...24 cm); large (diameter 26 cm or more). The grade of round timber is determined depending on the thickness and presence of wood defects.
Lumber,
obtained by longitudinal sawing of logs.
The face of the board or bar facing the core is called the inner face, and the face facing the bark is called the outer face. According to their location in the log, they distinguish between middle (containing the core), central (adjacent on both sides to the center plane) and side boards and slabs.
Planed lumber
dried before planing. Planed boards can be grooved or folded. Often the comb is replaced with an insert strip. In this case, grooves are selected on both edges of the board.
The lining is used for covering railway cars. It is also used in civil engineering. Rustic is used for wall cladding. Its profile is more complex than the lining profile.
Moldings
have a given cross-section profile and length, limited mainly by transportation conditions. Molded materials include platbands, skirting boards, fillets, layouts, bars, glazing beads, figured slats, handrails for handrails, boards for finished floors.
Platbands are used for edging door and window openings. Skirting boards and fillets are used to design corner joints between the floor and walls, walls and ceiling. Layouts cover the joints of sheets of facing material.
Products for parquet floors
can be divided into parquet dies, piece and type-setting parquet, parquet boards and panels.
Parquet blocks are made mainly from hardwood: oak, beech, birch, ash, maple, birch bark (elm), elm, elm, hornbeam, chestnut, cherry, white acacia, honey locust, mahogany, etc.
Block parquet consists of individual planed dies with grooves and ridges on all four edges.
Stacked parquet is produced in the form of a set of dies, selected by color and texture. The relative position of the dies must be preserved during installation, so they are fastened either with a sheet of kraft paper glued to the set from the front side, or with a sheet of special lining material (made of polyethylene foam, cork, etc.) glued to the bottom. After laying the parquet, the paper along with the glue is removed. The lining material remains under the decking and serves as a shock absorber, insulation and sound insulator.
Parquet boards consist of a base in the form of a tongue-and-groove board and parquet blocks glued to it. The base is most often made of glued planed bars or planks, which can be located both along and across the board. The length of parquet boards usually does not exceed 3 m, width - 200 mm. Laying the floor with parquet boards is less labor-intensive than laying piece and stacked parquet. At the same time, the quality of the flooring is higher.
Parquet boards, like parquet boards, consist of a wooden base and a front covering of parquet blocks. Their difference from parquet boards lies in the design and shape (usually square) of the base. The base of the parquet boards consists of a frame frame and filler bars. The connection of the panels to each other can be tongue-and-groove or keyed (using keys inserted into grooves on all edges of the panel). The dimensions of parquet panels usually do not exceed 800×800 mm.
Sliced veneer -
These are thin (no more than 1 mm thick) sheets of deciduous or coniferous wood, obtained by planing timber or vanches on special machines. Veneer is intended for veneering (cladding) commercial wood products. Based on texture, sliced veneer is divided into radial, semi-radial, tangential and tangential-end (from build-ups).
Peeled veneer
obtained by peeling churaks (parts of
a ridge
- a piece of trunk less than 4 m long) on peeling machines. Churaks are boiled in water before peeling. From a block rotating in the machine, a uniformly moving caliper with a knife cuts (peeles) a long continuous strip of veneer with a thickness of 0.55 to 1.50 mm.
Peeled veneer is used for the manufacture of plywood, bent blanks and lining joinery. In order to enrich the texture, conical peeling is used, in which the block in the peeling machine is clamped at an angle to the longitudinal axis. Peeling of wood with a knife with a wavy blade is also used. The resulting wet corrugated veneer is straightened between hot plates under pressure.
Plywood
- sheet material obtained by gluing together under pressure several sheets of peeled veneer. The fibers in adjacent layers of plywood must be mutually perpendicular. The edges of the finished plywood are cut on all four sides. Based on the number of layers, three-, five- and multi-layer plywood is distinguished. Plywood bends easily and is less susceptible to warping and cracking. It is considered to be made from the type of wood from which its outer layer is made. The length of the plywood sheet is taken in the direction of the fibers of the outer layer. Plywood is called longitudinal if the length of the sheet (1,220...2440 mm) is greater than the width of the sheet (725...1,525 mm), and transverse if the length of the sheet is less than the width of the sheet. Plywood can be sanded (on one or both sides).
Veneered plywood has one or both outer layers of sliced valuable wood veneer. Accordingly, it is called one-sided or two-sided. Based on the texture of the face layer, radial, semi-radial and tangential plywood are distinguished.
Decorative plywood is made from peeled veneer with a polymer film coating and the use of decorative paper or without it. Plywood with an applied melamine-formaldehyde or urea-melamine-formaldehyde film is pressed with polished steel spacers, resulting in a glossy, dense surface with increased water resistance.
Bakelite plywood consists of an odd number of layers of peeled birch veneer, glued together with a mutually perpendicular arrangement of fibers in adjacent layers with phenol-formaldehyde resin (bakelite). This plywood has increased water resistance, weather resistance and strength.
Joiner boards
consist of a slatted panel covered on both sides with veneer in one or two layers. The slabs can be faced on one or both sides with sliced veneer, which is sanded or left unsanded.
Fiberboards
(Fibreboard) is made from crushed wood and special additives. Wood processing waste is first crushed into chips, and then boiled in a 1-2% solution of caustic soda, washed with hot water and crushed to fibers using defibering machines or a hammer crusher. The slabs are pressed at a temperature of 150... 165 0C under a pressure of 1 to 5 MPa. Wood fibers are compressed into a solid mass under high pressure and high temperature. The main binding element in boards is lignin, which is released from wood when heated. Depending on the pressure, slabs of varying hardness and density are obtained - from 250 to 950 kg/m3. When obtaining super hard slabs, a binder (synthetic resins) is added. Soft boards are used as thermal insulation. Thin-sheet solid material - hardboard - is used in the construction of floors and partitions, cladding walls and ceilings.
MDF boards
(MDF - Medium Density Fiberboard) are a foreign analogue of fiberboard. MDF boards are highly environmentally friendly and are used in the manufacture of kitchen furniture and for interior decoration.
Chipboards,
just like wood-fiber ones, they are made from wood processing waste, but in addition, special flat shavings are used, obtained from round timber of non-commercial healthy wood on special flaving machines. Wood filler is mixed together with a synthetic binder in an amount of 6... 12% by weight of the chips. The slabs are pre-compacted in a cold press. Curing of the binder occurs in a hot pressing press at a temperature of 135... 140°C and a pressure of 0.5... 2 MPa, depending on which the specified density of the slab is obtained.
The surfaces of the plates can be polished. In the manufacture of three-layer slabs, special flat chips are used for the top layers, and chips from the machine and crushed particles are used for the middle layer.
In addition to flat-pressed chipboards with a horizontal fiber arrangement, extrusion boards with a vertical arrangement (perpendicular to the surface) are produced. These slabs are either solid or multi-hollow with round channels. They are lined with paper, veneer, and the surfaces are sanded.
Particle boards are used for the manufacture of door panels and built-in furniture, wall and ceiling cladding, flooring, and partitions.
Solid wood shields
(plank) are glued together from boards (plots) no more than 100 mm wide, selecting them so that the annual layers in adjacent plots have a counter or perpendicular direction. This reduces warping of the shields, but does not eliminate it.
Pasted boards
are divided into hollow and filled.
A hollow covered board consists of a frame with a middle and plywood glued to it on both sides .
Its main advantage is its small weight.
In laminated boards with infill, the space inside the frame is filled with bars or slats. They can either be fitted and glued together, or assembled into a lattice, or laid without fitting and gluing. Other fillers may be used.
How to choose the right variety
Before choosing the grade of wood, you need to decide what the products made from it are needed for. But you should not use only selected class lumber for construction and finishing, but where possible, build from second-class or even third-class material. For the frame of the house, load-bearing structural elements and rafter system, the quality of the material is undoubtedly of great importance, so in this case it is preferable to use Extra or Prima timber. Whereas, in enclosing structures, edged boards are quite suitable.
For interior partitions, roof sheathing and subfloors, as well as for the construction of temporary structures, grade 2 lumber can be used. For structural elements not intended to bear heavy loads, third-grade material is suitable. The main thing is that the products are free from fungal infections and rot.
Assortment and assortment
Construction lumber is made primarily from wood from coniferous trees such as pine, cedar, spruce, larch and fir. GOST 24454-80 describes the parameters that the characteristics of lumber (assortment) must correspond to, as well as division according to functional criteria (assortment).
GOST 24454-80 specifies the assortment of softwood lumber according to geometric parameters. The table given there indicates their nominal sizes. This standard does not apply to valuable wood species. At the customer's request, it is possible to manufacture products according to individual sizes that are not in the table.
The range of lumber used for construction consists of the following products:
- edged and unedged boards;
- croaker;
- timber;
- plates;
- quarters;
- logs