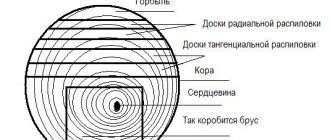
Before sawing round timber, it is necessary to calculate how much volume will be left for further use, and how much material will be spent on processing.
This is important because it affects the final cost of the product. The amount of untrimmed wood you get will depend entirely on what type of wood is used. At the same time, there are certain measures to increase the yield of lumber after cutting.
What is the yield percentage and its dependence on the diameter of lumber
To understand this, it is necessary to unpack the concept itself.
The percentage of lumber yield from roundwood is all the useful wood after sawing. The rest is waste that is sent for further processing to produce materials such as MDF, fiberboard, chipboard. It is worth understanding that the volume that will be obtained as a result of cutting wood is calculated for each individual diameter and selected cutting option.
Output table
It is worth understanding the question of why the parameter under consideration depends on the diameter of the forest.
Everything here is extremely simple: the fewer cuts there are on the tree, the higher the volume value will be. Of course, a lot will also depend on the cutting technology and on the sequence in which the cutting was carried out. The correct sequence will be shown in Fig.
2. It should be understood that small lumber is obtained from small species of wood, and thick boards and beams are made from large timber. It is also worth considering the average diameters with approximate rates of volumetric flow rate:
- 14 – from 45 to 50%; 20 – about 52%; 25 – on average up to 57%; 34 – this is the diameter of timber timber, which has the highest value of the volume fraction, equal to 66%; if the forest has a diameter of more than 40 cm , then there is a sharp decrease in the materials received.
Output of lumber from roundwood at a band sawmill
> Treatment >
When sawing round timber, boards, beams and sleepers of various sizes are obtained. The resulting amount of lumber is called the output. Manufacturers strive to obtain large quantities of product with a minimum of waste. Proper calculation allows you to obtain the highest yield of lumber from round wood on a band sawmill. This can be done using a log cutting map.
Equipment and tools
The choice of means for processing wood is influenced by the quantity of the planned product and its quality. The following tools can be used in logging:
- With a circular saw you can make cuts in any direction. The tool copes with any thickness of logs. The saw is used both at home and in production.
- A chainsaw is used in cases where it is necessary to process small volumes of lumber. Most often used on private farms. For ease of operation, it can be equipped with cutting guides and log holders.
- The band sawmill produces a large volume of high-quality wood. Its advantage is the low percentage of waste at the output.
- A special feature of the frame sawmill is its mobility. It can be moved freely to any location and can be installed in close proximity to logging sites.
- A disc machine is used to produce unedged material.
- In production, a bark stripping machine is often used. The tool has a high cost, but is quickly purchased due to its efficiency.
When there is a small amount of round timber, a circular saw is most often used. For industrial scale, there are entire complexes that allow processing wood of any quality.
Types of wood cutting
Before you start cutting logs, you need to decide on the quantity and type of future lumber. Cutting can be carried out according to the following schemes:
- Waddle. As a rule, it is produced on trunks of medium thickness, mainly deciduous trees. During cutting, the log is passed through the sawmill once. The result is unedged boards and slabs.
- Sawing wood with lumber. The log is passed through the frame 2 times. First, unedged material and timber are cut out. Then the timber is sawn, producing edged and unedged boards.
- Segmental or sector method. Allows you to obtain up to 8 different elements from one barrel that meet the necessary requirements. The log is divided into sections, which are subsequently sawn in a tangential or radial direction.
- Circular method. During processing, the wood is rotated 900 after each pass through the frame. This method allows you to remove defective areas of wood in a timely manner.
In addition to cutting lumber, there are several types of sawing:
- Radial. With this method, sawing occurs perpendicular to the trunk, across the annual rings. The board turns out to be of excellent quality with an even pattern. The downside is the low yield percentage.
- Tangential. The cut is made along a tangent line relative to the growth rings. Thus, a board with different patterns is obtained.
- Rustic. The cutting is done at different angles. Wood defects are often visible on the cut of the board. This method is used to produce cheap materials.
In production, the method of cutting and sawing round timber is reflected in the technological map. It is drawn up before starting work and will allow for preliminary calculation.
Routing
The percentage of lumber yield is the amount of wood suitable for further use obtained from 1 m3 of forest. Industrial waste in the form of sawdust is used for the production of particle boards. The calculations take into account the type of intended product, the diameter of the logs and the method of sawing them.
All data is entered into the log cutting map. It will allow you to calculate the norms for the volume of finished lumber at the output, as well as the amount of waste. In this way, the final cost of the product can be determined.
You can create a technological map yourself. For this purpose, there are reference books on the topic of sawmilling. For industries where products are produced in large volumes, special computer programs have been developed.
Yield percentage
The average volume of output that should be obtained can be calculated in the following ways:
- According to the diameter of the trunk. Suitable in cases where all the sawlogs are the same size. To make the calculation, calculate the volume of one trunk and multiply it by the entire cubic capacity. The method has a slight error. The downside is that it takes a lot of time and human resources to accept products.
- By volume of transport. With this method, the volume of finished lumber for each type of transport is calculated separately. The method is used for large volumes of lumber, as it significantly speeds up calculations. Has a large percentage of error.
- Using measuring frames. This method has a high level of accuracy. When measuring, the curvature and thickening of the trunk are taken into account, which is impossible when calculating manually. The method also allows for immediate sorting of lumber, taking into account its further consumption.
- By multiplying the stack volume by a certain factor. The calculation has a high level of error. The method is used when measurements need to be carried out urgently.
Correct calculation of output affects the cost of future products. This indicator largely depends on the type of wood and how the wood was cut.
Ways to increase the ratio
There are technologies that allow you to increase the final volume of material:
- If possible, it is best to calculate the yield using special programs. Manual counting has a low level of accuracy, which entails a high percentage of defects.
- The use of high-quality equipment will reduce the share of waste and defects.
- Before starting work, you should check and configure the equipment.
- Cutting narrow timber takes a long time. It is better to use wide workpieces in your work. The same goes for the length of the log.
- Preliminary sorting of the wood will significantly speed up the work.
The yield of the finished material often depends on the type of wood being processed. Coniferous forest gives a higher yield coefficient, in contrast to deciduous forest. Such sawlogs have smoother trunks with a low level of defects and rot.
For the processing of hardwood, cutting is carried out mainly using the tumble method using a band sawmill. This approach allows you to increase the yield volume by up to 70%.
Sorting timber allows you to separate logs not only by diameter and curvature. With its help, trunks with defects, rot, and sapwood are separated. They are usually sawn into timber. The use of 1st grade timber increases the volume of finished lumber by 3–4%. Lower varieties reduce this figure by 2 to 7%.
The working tool must be regularly checked for faults. On circular and frame saws, it is important to monitor the presence of soldering, sharpening angles, and rolling.
Dependence of the final yield percentage on sawing technology
Optimizing the cutting procedure significantly increases the percentage of final product yield:
- Initially, high-quality wood without defects is processed.
- At the second stage, logs with damage on the end part are processed. Before starting work, these places are cut off.
- Next, trunks with signs of rot at the core are sawed. It is removed before work. The remaining part is cut into the necessary elements.
A high percentage of yield is obtained by cutting large-diameter round timber. The coefficient can reach up to 2.1, depending on the size, sorting and quality of the equipment.
Average yields when sawing round timber of various diameters are:
- Up to 4 cm - from 45 to 50%.
- 20 – 25 cm – up to 57%.
- 34cm – about 66%.
- With a diameter above 40 cm, a sharp decrease in the percentage of yield is observed.
When producing moldings, it is necessary to take into account shrinkage from 8 to 14% for each cube of lumber. To obtain more accurate indicators, it is better to focus on log sawing tables.
The number of saws also plays a role. The fewer cuts on the trunk, the higher the volume of the final product. Small logs are used for small boards. Using large wood, beams and thick boards are obtained.
The most rational indicators are considered to be in the production of timber. In this case, with a minimum number of saws and high operating speed, the highest yield of lumber is obtained with a minimum amount of waste.
Approximate yield by variety
The following tree species are preferable for the manufacture of lumber:
- deciduous - beech, aspen, poplar, birch, alder, linden.
- conifers - pine, spruce, cedar, fir, larch.
For each breed, the yield differs in percentage. Indicators characteristic of coniferous forest:
- When working with a circular saw with a circular saw, output volumes of up to 85% are achieved.
- When sawing using machines, 70% of edged lumber is obtained.
- When cutting with a chainsaw, about 30% of unedged lumber is obtained.
When processing deciduous wood, about 60% of unedged boards are obtained. The reason for such a high rate is the curvature of the source material. To solve this problem, special additional equipment is installed on the machines. The resulting production lines increase yield by 20%.
The percentage of lumber yield depends on many factors. This indicator is influenced by the quality and size of raw materials, tools for work, and processing method. With the right approach, you can achieve fairly high results.
Output of sawn timber from roundwood at a band sawmill Link to main publication
Volume of waste after sawing
In order for the finished product to have a large percentage, everything should be calculated and prepared correctly. And the work process itself must be carried out in full accordance with technology. It is worth taking into account that a round forest of coniferous and deciduous trees will produce different yields of lumber from unedged boards per m3.
In what sequence should round timber be cut?
Note! Coniferous wood is considered the best option due to the fact that they have a straight trunk and a relatively larger diameter. In addition, such wood is not as susceptible to decay, which leads to less waste.
When working with hardwood, 2 processing methods are used:
- Using a 375 or 363 band sawmill. In camber. This technology involves cutting out a half-beam, which is subsequently passed through a multi-saw device.
In this case, the first method allows you to get approximately 40-50% of the output. But the collapse technique differs in a slightly larger volume - up to 70%.
The disadvantage of this technology is that its costs are relatively high. When sawing round lumber 3 m long, you can notice a fairly high level of defects. However, the remaining wood will not be immediately useful due to the fact that it requires an additional processing process.
Cutting process
It is worth noting that there are very few marriage options. A wormhole can interfere with processing, as it is not suitable for most woodworking. As a result of sorting, the volume of material is only 20-30% of the wood that was obtained as a result of sawing.
Hello dear readers and subscribers of the blog, Andrey Noak is in touch with you! Today I will tell you about the yield of lumber when sawing round wood.
Cutting sawlogs into lumber
Some nuances of cutting logs into lumber
The stage of dividing sawlogs into blanks can be considered the main one in sawmill production. This article will be from the “how it’s done” series; we’ll take a quick look at the sawmill and try to explain some relevant terms that the average consumer periodically comes across.
It is at this stage that boards and beams, molded products are obtained, which then become blanks or parts that we use in everyday life or on the construction site. The quality and performance characteristics of lumber products, as well as the grade of products, the percentage of value yield of products and the resulting non-business waste depend on what cutting scheme the manufacturer chose and what equipment he used. The rationality of sawing round timber largely determines the economic efficiency of sawmill production as a whole.
Raw materials
Round timber (sawlogs, round timber) is the raw material for the production of lumber. Logs and ridges made of coniferous or hardwood are brought to the sawmill for subsequent cutting. A log is the upper and middle part of the whip, and a ridge is its lower butt part. The logs are used mainly for the creation of special products (such as veneer and shavings, barrels, shoe lasts, skis, parts of ships and aircraft, gun elements...). Logs are used to create general-purpose lumber - boards, beams/timbers, and construction moldings.
As for the concept of “whip” - in logging this is the name given to the entire trunk of a tree that has been felled, without roots and branches.
Interestingly, the quality and technical characteristics of sawlogs are subject to state standards. For example, GOST 9463 - 88 “Round softwood timber. Technical specifications") contains information on dividing sawlogs into grades - grades 1, 2 and 3 are distinguished. The regulatory document shows us the optimal thickness and length of round timber for specific areas of use. It also gives the optimal allowances and defects that can be allowed in the sawlog of each of the three grades. By size, round timber is divided by GOST into small (6-13 cm in diameter), medium (14-24 cm), large (24 or more centimeters). Similar data on other species are collected in GOST 9462 - 88 (Round hardwood timber).
To obtain high-quality timber or boards, responsible manufacturers use exclusively living and healthy wood, which by all criteria complies with the provisions of current state standards. As practice shows, it is not possible to obtain durable and reliable structures from dead wood and burnt wood, since such wood is often severely damaged by insects, is prone to rotting, and has low strength characteristics.
Log cutting methods
In principle, two approaches to cutting round timber can be distinguished. This is sawing and milling. In some cases, these technologies are combined. Milling occurs on beam machines, which usually process round timber from all sides at the same time, producing beams with a given profile section or four-edged (when all four sides are flat). Quite often, milling is combined with sawing.
Sawing cutting is carried out on several types of lines and machines - vertical frames, band machines, disk machines with one or more circles. Depending on how many tools are used in each pass, cutting is classified into:
- Group,
- Individual.
During group cutting, several saws/discs are used, which split the log into several products at once, which have a cross-section corresponding to the distances between the knives set by the operator. During individual sawing, a single piece of equipment sequentially cuts out individual pieces from round timber.
There are several types of cutting round timber depending on the direction of the longitudinal cuts and the number of passes.
1. The “waddle” method consists of parallel arrangement of cuts, which are made with several saws (frames, several circles) or with one saw - accordingly, it can be done in one pass or in several. In this way, an unedged board with different grain directions is usually obtained; its edges with a sharp wane can then be cut off to produce an edged board. The tumble method is considered optimal when working with saw logs with a diameter of up to 180 mm or if the log has a curvature.
2. The “with lumber” method is used for cutting lumber with different cross-sectional sizes and different orientations of fibers in products. Large lumber (from 24 cm) is mainly used as raw material. The essence of the method is at least two passes, when initially a two-edged beam is produced from a log (only 2 sides are sawn), and then it is cut into unedged boards of the same or different thickness. In thick round timber with a diameter of 300 mm or more, several beams can be cut.
3. The “timber-beam” method is similar to rumble cutting, only here, in addition to the edge unedged boards, a large middle part of the log is also obtained in the form of a two-edged beam, which is then cut using the “with edging” method.
4. Sector and segment methods , as a rule, are used to divide ridges in order to obtain special-purpose products with a tangential or radial arrangement. These two methods are characterized by preliminary cutting of round timber into segments or sectors, which are then cut into boards or beams using the tumbled or trussed method.
5. The circular method is most often used when large sawlogs with a diameter of more than 32 centimeters are used, the core of which is affected by rot inside, or if it has a false core. Using this approach, craftsmen manage to cut high-quality lumber, leaving defects in the waste. They make a circular cut using an individual method - with one piece of equipment. First, one slab is separated, the log is laid on the resulting plane, and the next pass is made perpendicular to it. Then the workpiece is turned over, a longitudinal cut is made at 90 degrees to the previous plane.
There are several dozen more cutting methods that are not used so often. Standing out among them are the options designed to create lumber glued from cutting sections of different shapes.
Cutting planning
When dividing sawlogs into boards and beams, waste inevitably appears in the form of shavings, trimmings of end sections, slabs and slats with wane, cut out defects and defects... With a competent approach to planning work, a manufacturer can increase the yield of business products by using valuable raw materials more rationally.
To achieve optimal cutting in accordance with technical conditions, first of all, it is also necessary to correctly evaluate the initial characteristics of the round timber. In general, an important factor may be:
- Diameter and length of the log.
- Tenacity, the size of the core of the log.
- Curvature of saw logs.
- The presence of critical flaws and defects.
- Wood species.
- Humidity of raw materials.
- The required characteristics of the output product are the specification (arrangement of fibers, cross-sectional shape, length...).
- Manufacturability of production facilities.
Based on an analysis of the available raw materials, a decision is made on choosing a sawing method in order to use the log as fully as possible, including its running part. These works are now increasingly carried out using special programs that take into account the assigned tasks and the priority of sections, and at the output they produce maps of optimal cutting suitable for the specific type of equipment used. Using such maps, the sawmill operator collects the supplies and makes the cutting.
A supply is a combination of saw equipment and spacers, which ensures the production of lumber of specified sections. In essence, a postav is a plan diagram for subsequent division.
Most often, it is easier to display the characteristics of a delivery in a series of numbers. For example, the following option for tumbling sawing is possible: 20-20-40-40-20-20 - where in the center we have two boards 40 mm thick, and at the edges there are two boards 20 mm thick. And this is what the set of saws for cutting with blocking looks like:
- 1st pass 20-20-150-20-20 (one double-edged beam 150 mm and 4 boards).
- 2nd pass 19-32-40-40-32-19 (six boards will be obtained from the central beam).
Introduction
This parameter is one of the most important indicators in sawmilling. The efficiency of sawing timber depends on this indicator. Many beginners mistakenly believe that the higher this ratio, the better.
In fact, this is not always the case; most specialists know about this, but remain silent. I repeat once again - a high percentage of lumber yield per cubic meter of forest is not always good.
I described in detail why this is so in my book “Organization of sawmilling at a modern enterprise,” but for readers I will lift the veil on this issue at the end of the article.
This is a truly unique e-book, there are definitely no such things in Russia!!! It provides simply colossal information gained from personal experience as a technologist in a large production.
Percentage of round timber
Calculated using the formula:
Kout=Vpil/Vbr
Where K, % is the percentage of lumber yield.
Vpil, m3 - volume of lumber obtained. Calculated:
Vpil = L*H*B*n1+L*H*B*n2 + …
- where L is the nominal length of the finished lumber; H is the thickness of the board; B is the width of the board; n is the number of boards of each size.
Vbr, m3 - volume of logs from which lumber is obtained. It is determined by the cubature, which can be downloaded from me on this page.
The useful percentage of lumber in production is calculated for each diameter of the forest and for each sawing technology.
I can only give general recommendations, and improvements need to be done in specific places.
Why does the useful percentage depend on the diameter of the wood being cut?
It's very simple, the fewer cuts to obtain wood, the higher the percentage. Of course, it also depends on the useful use, but once again I will say that it is very important how many saws you have to get a board. As a rule, small boards are cut from small wood, and timber or thick boards are cut from large wood.
The company's performance in the production of timber is especially good; its cubic capacity is good, sawing speed is maximum (there are fewer saws after all) and cutting tool consumption is minimal.
Below are the approximate diameters with consumption rates:
- 12 - 16 cm - yield 45 - 50%; 18 - 22 - on average 52% 24 - 26 - about 57%; 28 - 40 - this is timber timber and the best results are obtained when obtaining timber - 66%; 42 - 60 — in this range there was a decrease in the percentage of boards made from wood. Since this wood is used to produce boards and beams that are not so large, and therefore the number of cuts with a saw becomes many times greater.
These consumption rates are approximate and are valid for the production of such lumber as:
- 25*150*6,0;35*150*6,0;50*150*6,0;180*180*6,0;200*200*6,0.
Based on the type of equipment, these standards can be adopted for band sawmills, sawmill frames and circular saw equipment.
Ways to increase the ratio
There are technological tricks, which I partially talked about in this article. But as they say, repetition is the mother of learning, here are some of them:
- Using shorter commercial wood; Using specialized programs, read about this here. In short, we can say that you need to use the program to find the optimal cost of boards obtained from logs. On the one hand, a high useful yield means a large cubic capacity, and on the other hand, a high indicator means obtaining a larger volume of low-quality wood. The use of thinner saw blades through double-spindle circular saws, the use of stellite tips. The use of sorting round timber by diameter, species, defects.
And now in more detail about everything.
The shorter the wood, the higher the percentage of lumber obtained. In Europe they know this well and therefore the cutting lines there are calculated at 1.5 - 2 meters. Our sawmill frames can only cut 4-meter logs.
Using programs in production, we calculated our supplies for each season, increasing the amount of low-quality wood during periods of demand (summer, autumn), and increasing the amount of high-quality wood during periods of increased demand for them (winter, part of spring).
I think everything is clear about using a saw blade with the best characteristics. It is also necessary to monitor the quality of the resulting cutting tools. On frame and circular saws, you need to constantly monitor the presence of all solder tips, sharpening angles for each season, and rolling on both types of saws.
Sorting allows logs to be separated by diameter, defects and blemishes.
For example, with rot in the core, then the log is sorted and sawed into lumber, instead of being turned into timber. Or vice versa, if the sapwood is rotten, but a beam emerges from the central part, and the log is a timber log, we sort it for sawing into timber. You need to think similarly in terms of blueness and curvature.
Yield of sawn timber when sawing round timber: by round timber grade
Hello dear readers and subscribers of the blog, Andrey Noak is in touch with you! Today I will tell you about the yield of lumber when sawing round wood.
Introduction
This parameter is one of the most important indicators in sawmilling. The efficiency of sawing timber depends on this indicator. Many beginners mistakenly believe that the higher this ratio, the better.
In fact, this is not always the case; most specialists know about this, but remain silent. I repeat once again - a high percentage of lumber yield per cubic meter of forest is not always good.
I described in detail why this is so in my book “Organization of sawmilling at a modern enterprise,” but for readers I will lift the veil on this issue at the end of the article.
This is a truly unique e-book, there are definitely no such books in Russia :-)!!! It provides simply colossal information gained from personal experience as a technologist in a large production.
Percentage of round timber
- Calculated using the formula:
- Kout=Vpil/Vbr
- Where K , % is the percentage of lumber yield.
- Vpil , m3 - volume of lumber obtained. Calculated:
Vpil = L*H*B*n1+L*H*B*n2 + …
- where L is the nominal length of the finished lumber;
- H - board thickness;
- B - board width;
- n is the number of boards of each size.
Vbr , m3 - volume of logs from which lumber is obtained. It is determined by the cubature, which can be downloaded from me on this page.
The useful percentage of lumber in production is calculated for each diameter of the forest and for each sawing technology.
I can only give general recommendations, and improvements need to be done in specific places.
Why does the useful percentage depend on the diameter of the wood being cut?
It's very simple, the fewer cuts to obtain wood, the higher the percentage. Of course, it also depends on the useful use, but once again I will say that it is very important how many saws you have to get a board. As a rule, small boards are cut from small wood, and timber or thick boards are cut from large wood.
The company's performance in the production of timber is especially good; its cubic capacity is good, sawing speed is maximum (there are fewer saws after all) and cutting tool consumption is minimal.
Below are the approximate diameters with consumption rates:
- 12 - 16 cm - yield 45 - 50%;
- 18 - 22 - average 52%
- 24 - 26 - about 57%;
- 28 - 40 - this is timber timber and the best results are achieved when obtaining timber - 66%;
- 42 - 60 - in this range there was a decrease in the percentage of boards made from wood. Since this wood is used to produce boards and beams that are not so large, and therefore the number of cuts with a saw becomes many times greater.
These consumption rates are approximate and are valid for the production of such lumber as:
- 25*150*6,0;
- 35*150*6,0;
- 50*150*6,0;
- 180*180*6,0;
- 200*200*6,0.
Based on the type of equipment, these standards can be adopted for band sawmills, sawmill frames and circular saw equipment.
Ways to increase the ratio
There are technological tricks, which I partially talked about in this article. But as they say, repetition is the mother of learning, here are some of them:
- Use of shorter commercial timber;
- Using specialized programs, read about it here. In short, we can say that you need to use the program to find the optimal cost of boards obtained from logs. On the one hand, a high useful yield means a large cubic capacity, and on the other hand, a high indicator means obtaining a larger volume of low-quality wood.
- The use of thinner saw blades due to double-spindle circular saws and the use of stellite tips.
- Use of sorting round timber by diameter, species, defects.
And now in more detail about everything. The shorter the wood, the higher the percentage of lumber obtained. In Europe they know this well and therefore the cutting lines there are calculated at 1.5 - 2 meters. Our sawmill frames can only cut 4-meter logs.
Using programs in production, we calculated our supplies for each season, increasing the amount of low-quality wood during periods of demand (summer, autumn), and increasing the amount of high-quality wood during periods of increased demand for them (winter, part of spring).
I think everything is clear about using a saw blade with the best characteristics. It is also necessary to monitor the quality of the resulting cutting tools. On frame and circular saws, you need to constantly monitor the presence of all solder tips, sharpening angles for each season, and rolling on both types of saws.
Sorting allows logs to be separated by diameter, defects and blemishes. For example, with rot in the core, then the log is sorted and sawed into lumber, instead of being turned into timber. Or vice versa, if the sapwood is rotten, but a beam emerges from the central part, and the log is a timber log, we sort it for sawing into timber. You need to think similarly in terms of blueness and curvature.
Approximate yield by variety
The situation regarding varieties is quite interesting. It turns out that the percentage of yield of high-grade products depends on the following factors:
- The coefficient of production of lumber from round timber. Grade depends not directly, but indirectly. The fact is that after some golden mean, the more planks we get per cubic meter, the higher the amount of low-grade wood with wane;
- The larger the diameter, the higher the likelihood of getting more high-quality boards;
- The presence of wood defects, such as curvature, rot, blueness and others; the fewer there are, the higher the percentage of obtaining a high-quality board;
- The shorter the finished product, the higher the percentage of high-quality boards.
Now let’s estimate, approximately based on the diameter, the percentage of first-class lumber obtained from the total volume of boards produced. To do this, I made everything in the form of a small table.
Table 1 - yield of boards when sawing round timber
| Diameter, cm | Yield of premium grades, % |
| 12 — 16 | first grade yield 40% |
| 18 — 22 | on average 50% |
| 24 — 26 | about 50% |
| 28 — 40 | log timber, during the production of timber you can get indicators of about 70% |
| 42 — 60 | about 60 - 70% |
How does the percentage of lumber production depend on sawing technology?
In addition to diameter, grade, defects (curvature) and length, the percentage of board yield depends on the technology of sawing wood and the type of equipment.
There are two types of sawing technology:
- Individual cutting, the percentage of useful yield approaches 75%;
- Group cutting, depending on other parameters, the useful yield can also reach 70%.
And the equipment for sawing can be the following:
- Band sawmills produce lumber products with minimal wood consumption rates;
- Tire sawmills produce lumber with increased consumption when sawing logs, since the thickness of the chain is much greater than the strips.
- Sawmill frames. It is quite inconvenient to process thin wood using this type of equipment. Therefore, sawing is mainly done from a diameter of 20 - 22 cm;
- Milling canter lines. This type of equipment has both an advantage and a disadvantage over other technologies. He only cuts graded wood;
- Circular saw equipment cuts according to individual cuttings - this is a big plus for the resulting materials, both in quality and quantity.
Approximate yield by variety
The situation regarding varieties is quite interesting. It turns out that the percentage of yield of high-grade products depends on the following factors:
- The coefficient of production of lumber from round timber. Grade depends not directly, but indirectly. The fact is that after some golden mean, the more boards we get per cubic meter, the higher the amount of low-grade wood with wane; The larger the diameter, the higher the probability of getting more high-quality boards; The presence of wood defects, such as curvature, rot, blueness and others, the fewer there are, the higher the percentage of obtaining a high-quality board; The shorter the finished product, the higher the percentage of obtaining a high-quality board.
Now let’s estimate, approximately based on the diameter, the percentage of first-class lumber obtained from the total volume of boards produced. To do this, I made everything in the form of a small table.
Table 1 - yield of boards when sawing round timber
Diameter, cmYield of the highest grades, %12 - 16yield of the first grade 40%18 - 22on average 50% 24 - 26 about 50% 28 - 40timber timber, when producing timber you can get indicators of about 70% 42 - 60about 60 - 70%
How does the percentage of lumber production depend on sawing technology?
In addition to diameter, grade, defects (curvature) and length, the percentage of board yield depends on the technology of sawing wood and the type of equipment.
There are two types of sawing technology:
- Individual cutting, the percentage of useful yield approaches 75%; Group cutting, depending on other parameters, the useful yield can also reach 70%.
And the equipment for sawing can be the following:
Band sawmills produce lumber with minimal wood consumption rates; Busbar sawmills produce lumber with increased consumption when sawing logs, since the thickness of the chain is much greater than the strips. Sawmill frames. It is quite inconvenient to process thin wood using this type of equipment.
Therefore, sawing is mainly done from a diameter of 20 - 22 cm; Milling cant lines. This type of equipment has both an advantage and a disadvantage over other technologies. It only cuts sorted timber; Circular sawing equipment cuts according to individual cuts - this is a big plus for the resulting materials, both in quality and quantity.
Video on the topic
And now I’ll answer why a high yield is not always good, but everything is simple at very high rates, the amount of boards with wane increases.
The result is low-grade lumber and its total cost from a log at a certain point becomes lower than the cost of high-quality materials.
And selling low-quality material can be more difficult.
Good luck and see you again, Andrey Noak was with you.
When sawing wood, it is important to immediately calculate what the consumption will be, as this will affect the cost of lumber. The yield of finished products may vary. It all depends on the quality of the wood used and whether measures are taken to optimize cutting.
There are special measures to increase work efficiency, make the output better, and the quality of sawing higher. Before sawing, you need to pre-calculate everything. This is not as difficult as it might seem, but the consumption of round timber will be optimal and profitable to obtain an excellent result.
Options for cutting round timber.
Sawdust yield when sawing wood examples
The norm is a sawlog consumption of 1.5 to 2.0 cubic meters of round wood to obtain a cubic meter of lumber. Sawlog consumption depends on the following factors:
- Curvature of wood. Wood diameter. Delivery (number and dimensions of installed lumber). Wood sawing technology. Log length, allowances. More details in the article “Sawing logs according to European standards.”
The sawlog consumption is calculated to obtain a cubic meter of lumber using the following formula: Kpil = Vbr/Vpil Where K, % is the sawlog consumption coefficient.
Vpil, m3 - volume of lumber obtained. Vbr, m3 - volume of logs from which lumber is obtained.
Output of lumber from roundwood - by grade and depending on the diameter of the logs
/ Andrey Noak Date: 2016-05-10
Loading.
Hello dear readers and subscribers of the blog, Andrey Noak is in touch with you!
I repeat once again - a high percentage of lumber yield per cubic meter of forest is not always good. I described in detail why this is so in my book “Organization of sawmilling in a modern enterprise”,
Output boards from round timber table
To obtain a high percentage of lumber from round logs, several different technologies are used, including certain cycles of actions. The time required for sawing round timber and the labor intensity of the process varies, depending on the chosen processing method, the location of the work, and the season.
Thus, some enterprises build workshops for the primary processing of raw materials near the timber harvesting site and save on this.
Roundwood harvesting Not only trunks, but also large branches are processed.
Roundwood logs are sorted by size and presence of bark. The trunks that have not been sorted are subsequently used for rough work (making scaffolding, etc.).
When accepting raw materials from the supplier, not only the cubic capacity is checked, but also the presence of damage, rot, knots - such materials do not meet the technical specifications. Defects in wood reduce the percentage of finished products at the output, and knots can damage equipment.
How to calculate wood balance?
/ Andrey Noak Date: 2014-04-12
Loading.
Hello dear readers and subscribers of Andrey Noak's Blog!
Wood balance is the yield of all components from the log after sawing. Today we will look at how to calculate it correctly.
ContentsIn the book you will learn how to organize sawmilling production most efficiently. It also provides more detailed information on calculating wood balance and methods for increasing efficiency.
Each wood sawing technology has its own advantages and disadvantages.
And accordingly, different sawing technologies lead not only to different quality of the resulting lumber, but also to different percentage yields of the following items:
- Gorbyl.
- Technological chips.
- Sawdust.
- Lumber.
By the way
Calculation of the amount of sawdust when sawing unedged boards Text of a scientific article on the specialty “Medicine and Healthcare”
WOOD PROCESSING INDUSTRY UDC 674.093 I. N. Kukharenko, Minsk, in 1974-1988.
Junior Researcher, Head of the Laboratory of the Department of Lumber Technology BTI named after.
S. M. Kirov I dedicate to the 85th anniversary of my alma mater: thanks. and contrary to .“T. TO." CALCULATION OF THE QUANTITY OF SAWDUST WHEN SAWING UNEDGED BOARDS 11 2 The inevitability of wood loss when sawing logs in the form of sawdust is obvious. The article provides the derivation of strict mathematical formulas for calculating the amount of sawdust when sawing unedged boards.
Their quantitative yields are given as a percentage of the volume of logs with run-off coefficients of 1.10-1.40 for cut widths in the range from 0.005 to 0.050 of the diameter of the upper end of the log with a gradation of 0.001.
How much waste is generated when sawing wood?
Unedged boards…………………………………………….
The materials have scientific and practical application in solving issues of the validity of rational cutting of sawn raw materials. Key words: unedged boards, sawdust, formulas, quantity, tables, examples.
13 Business croaker………………………………………………….
n. The total amount of bark obtained from debarking wood at enterprises, taking into account the loss of bark during logging, varies from 10 to 14.5% of the volume of marketable wood.
When transporting wood by rafting, part of the bark falls off and the actual yield of bark is on average 8... For example, with rot in the core, then the log is sorted and sawn into lumber, instead of obtaining timber from it.
Or vice versa if the sapwood
Sawing round wood: cutting map, necessary tools
Forest sawing is a cycle of actions using a variety of technologies aimed at obtaining lumber from round timber suitable for further use in industry. The duration and labor intensity of the process depend on the chosen method of processing round timber, as well as the time of year. Trunks and large branches are used for production.
All material is divided into groups according to thickness and presence of bark. Often, timber processing enterprises have workshops near the harvesting site, in which machines for the initial processing of wood are installed.
Manual debarking of wood The wood that has not passed the debarking stage can be used on floors or as ridge beams in the corresponding interior, or as a supporting device during construction.
Industrial debarking of the forest If another option for using the wood is planned, then sawing is carried out, resulting in the following
Stages of sawing round timber
To obtain a high percentage of lumber from round logs, several different technologies are used, including certain cycles of actions.
The time required for sawing round timber and the labor intensity of the process varies, depending on the chosen processing method, the location of the work, and the season.
Thus, some enterprises build workshops for the primary processing of raw materials near the timber harvesting site and save on this.
Roundwood logging Not only trunks are processed, but also large branches. Roundwood logs are sorted by size and presence of bark.
The trunks that have not been sorted are subsequently used for rough work (making scaffolding, etc.).
When accepting raw materials from the supplier, not only the cubic capacity is checked, but also the presence of damage, rot, knots - such materials do not meet the technical specifications.
How to optimize the yield of lumber from roundwood
When sawing wood, it is important to immediately calculate what the consumption will be, as this will affect the cost of lumber. The yield of finished products may vary.
It all depends on the quality of the wood used and whether measures are taken to optimize cutting.
There are special measures to increase work efficiency, make the output better, and the quality of sawing higher. Before sawing, you need to pre-calculate everything.
This is not as difficult as it might seem, but the consumption of round timber will be optimal and profitable to obtain an excellent result.
Options for cutting round timber.
In order for the yield of lumber to be significant, it is necessary to use special measures to increase the efficiency of the process: Calculation should be carried out only when using special programs; manually it will have low effectiveness, and the percentage of rejects will be high. The round timber must first be sorted so that processing is carried out correctly.
For cutting it is necessary to use high quality equipment.
Sawing lumber
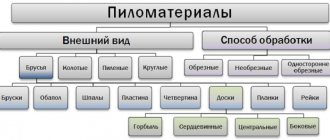
Sawing lumber is a fundamental process in wood processing.
First, we need to recall a few terms that are used in the woodworking industry and that are defined: Materials that have one or more straight sides. Depending on the ratio of length to width and the number of parallel sides, beams, bars, boards, obapol and sleepers are distinguished. Bars - thickness less than 100 mm, width does not exceed double thickness.
Slats also belong to this category, only their linear dimensions are much smaller. Beam - thickness more than 100 mm, width does not exceed double thickness.
Boards - the width exceeds two thicknesses, can be edged (all four sides are trimmed) or unedged (the sides are not trimmed).
Sleepers are timber with strictly defined dimensions, used during the construction of railways, and are currently used
Determining the percentage of lumber yield when sawing timber, in particular round timber
Before sawing round timber, it is necessary to calculate how much volume will be left for further use, and how much material will be spent on processing. This is important because it affects the final cost of the product.
The amount of untrimmed wood you get will depend entirely on what type of wood is used. At the same time, there are certain measures that make it possible to increase the yield of lumber after cutting. To understand this, it is necessary to expand on the concept itself.
The percentage of lumber yield from roundwood is all the useful wood after sawing.
The rest is waste that is sent for further processing to produce materials such as MDF, fiberboard, chipboard. It is worth understanding that the volume that will be obtained as a result of cutting wood is calculated for each individual diameter and selected cutting option.
Output table It is worth understanding the question of why the parameter under consideration depends on the diameter of the forest.
You might also be interested in:
Guidelines for determining the volume of secondary wood resources
1.2.
Secondary wood resources in the forestry, woodworking and pulp and paper industries include logging waste - twigs, branches, tips, tips, peaks; waste from sawmilling and woodworking - slabs, scraps of lumber and logs, pencils, veneer scraps, veneer scraps, slats, plywood scraps, chipboards and fibreboards, sawdust, shavings, sanding dust, bark; pulp and paper production waste - bark, chip screenings, sawdust, log trimmings, osprey, technical lignosulfonates.
1.3. The standards given in these guidelines were developed without taking into account irrecoverable losses.
1.4. The general standard for pulp and paper wood waste is represented by the sum of all wood waste and bark generated during the mechanical preparation of wood (sawing, debarking, felling, sorting, transportation, taking into account losses during storage), which is due to the fact that most enterprises burn debarking waste and wood waste together (screening out chips and sawdust).
Otherwise, the amount of waste will be large, and the quality of the resulting lumber will be low.
It is best to cut wide lumber first; narrow lumber takes longer to process. It is not recommended to take long logs. Before work, you should set up the equipment.
It is also worth considering the average diameters with approximate rates of volumetric flow rate:
- 14 – from 45 to 50%; 20 – about 52%; 25 – on average up to 57%; 34 – this is the diameter of lumber, which has the highest volume fraction of 66%; if the forest has a diameter of more than 40 cm, then there is a sharp decrease in the materials obtained.
In order for the finished product to have a large percentage, everything should be calculated and prepared correctly.
Rational cutting of round timber: diagrams, maps, tables
This scheme makes it possible to obtain unedged boards with different arrangement of layers relative to the annual layers.
The method is rational when cutting logs up to 18 cm in diameter and for sawlogs with curvature of trunks (most often used in cases of cutting birch raw materials, which in 70% of cases have simple or complex curvature).
Unedged boards obtained after tumbling cutting are processed into edged boards or transferred for cutting into unedged blanks.
If the predominant amount of finished products must have established cross-sectional dimensions, the cutting method with blocking is used. This scheme is also used for cutting large-diameter logs in the production of general-purpose lumber. Sawing with timbering is carried out on multi-rip equipment in two passes.
How to increase cutting efficiency
In order for the yield of lumber to be significant, it is necessary to use special measures to increase the efficiency of the process:
- The calculation should be carried out only when using special programs; manually it will have low results, the percentage of defects will be high. The round timber must first be sorted so that the processing is carried out correctly. For cutting, high-quality equipment must be used. Otherwise, the amount of waste will be large, and the quality of the resulting lumber will be low. It is best to cut wide lumber first; processing narrow lumber takes more time. It is not recommended to take long logs. Before work, you should set up the equipment.
The yield of finished lumber may vary. It must be remembered that at the first stage boards are obtained, then they are sorted. As a result, the percentage decreases even more; for example, for deciduous trees it can be only 10-20%.
Sequence and dimensions of cutting round timber.
To increase the yield of lumber, the cutting process must be optimized. This applies primarily to those workpieces that have significant curvature. To cut a crooked round timber, you need to perform a number of steps:
First, only suitable wood is selected for work. If the remaining logs have rot, sprouts, or cracks at the ends, then it is necessary to trim off some sections. If a rotten core is discovered during work, you can carefully remove it, and then saw the remaining part. This will allow you to avoid large losses and obtain boards with a length of 1 m or more with the required quality. It is recommended to use logs with a larger diameter so that the yield percentage is higher.
The coefficient can be 1.48-2.1, but it all depends on the diameter, quality of the round timber, sorting, and equipment. For frame shops this coefficient will be 1.48-1.6, and for lines with milling equipment - 1.6 for large timber. With a round log diameter of 12 cm or more, the coefficient can exceed 2.1.
Cutting wood
Before choosing a tool, you need to decide on the type of cut, focusing on the annual rings of the log. There are several types:
- radial (along the radius);
- tangential (the cut is parallel to one radius and touches the annual rings);
- the fibers are located parallel to the cutting being performed.
Among the cutting methods, the one that is most suitable for a particular case is selected:
- Waddle. Sawing wood in this way is carried out for deciduous trees with a small trunk thickness, and is considered the simplest processing. Output: unedged elements and slabs.
- If you have another forest processing machine, then it is possible to cut up to 65% of the material to produce edged boards of equal width. First, the double-edged timber and boards on the sides are cut, and then a certain amount of edged lumber is obtained from the timber.
- More specific methods are sector and segment sawing. The number of elements in the first method varies from 4 to 8, and depends on the thickness of the trunk. After dividing, elements are cut from each sector along a tangential or radial line. The second method begins with the timber coming out of the central part, and boards are cut from the side segments in a tangential direction.
- For individual cutting of wood, the circular method is suitable. It is based on turning the log along the longitudinal line by 90° after each sawn board. This allows you to monitor the quality of the wood and promptly remove affected areas of the trunk.
Volume of waste after sawing
In order for the finished board to come out with a high percentage, everything must be prepared correctly, the work must be carried out only in accordance with the technology. Roundwood of coniferous and deciduous species produces different yields.
In the latter case, the volume is smaller, even if special additional equipment is used. Needles are considered more convenient for sawing, since their trunk is straight and the log has a larger diameter. Coniferous wood is not so susceptible to rotting, so there is less waste. For hardwood, 2 cutting technologies are usually used:
Types of lumber from roundwood.
- using a band sawmill on Z75, Z63; in camber, when a half-beam is cut out in the core of the material and passed through a multi-saw machine.
The volume of a band sawmill is 40-50%. When using technology for collapse, the yield is different, it can be increased up to 70%, but the costs of such work are higher. If you cut round timber, the length of which is 3 m, you can see that the percentage of rejects is quite large, and the remaining material requires processing.
This applies to the bulk with boards 22x105(110, 115)x3000 mm. There are many options for such a marriage. For example, it could be a wormhole, which is no longer suitable for most jobs.
After sorting, the volume of hardwood material, which belongs to grade 0-2, will be only 20-30% of the amount obtained after sawing.
This means that of the total mass of harvested round timber, the yield of normal boards will be only 10-20%. The remaining materials are mainly used for firewood. For coniferous round timber, the yield will be different, but attention should be paid to what average values of the resulting volume are observed.
Lumber output
In order for the yield of lumber to be optimal, numerous conditions must be taken into account.
To calculate correctly, you can consider the example of round timber yield. The data was obtained from the real experience of specialists and from the performance of sawmills. This makes it possible to compare percentages and calculate optimal average numbers.
For conifers, the following solution is possible:
The name of the board in the sawn log.
For unedged boards and other unedged materials during sawing, the yield will be 70%. This is the amount of material obtained during processing; the amount of waste will be equal to 30%. For edged material, when using sawmills of 63, 65, 75, there will be a lower yield of lumber, only around 45%.
For band sawmills, the yield is usually up to 55-60% of the finished material. If you use means to increase efficiency, you can reach 70%, although this requires a lot of experience. From a circular sawmill you can get lumber in the amount of 70-75%, although using methods to increase efficiency it may well be 80-75%. But work experience is required.
According to GOST 8486-86, for grade 0-3, the yield percentage, not taking into account sorting, is approximately 70%.
Another 30% can be left for rejecting the finished material. The rejected material is not thrown away; it is used for the manufacture of other types of lumber, which allow for the presence of certain defects.
For deciduous roundwood, a different yield percentage is observed:
- For unedged material - 60%. For edged material - up to 35-40%, since the curvature of the original hardwood forest is usually large.
The output can be increased; additional equipment is used for this. This could be a special multi-sawing machine, an edge trimming machine, or a slab machine. In this case, the yield of lumber will increase by about 20%.
The given percentage is given based on data on obtaining boards of grade 0-4. When sorting grades 0-1, the percentage of lumber obtained is 10%. To get a cube of finished edged hardwood material, you need to cut 10 cubes of the original round wood.
The yield of lumber from roundwood may vary. It all depends on the original type of wood used by the sawmill. Special measures to increase efficiency allow you to get a higher percentage than is possible, but for this you must have some experience.
When sawing wood, it is important to immediately calculate what the consumption will be, as this will affect the cost of lumber. The yield of finished products may vary. It all depends on the quality of the wood used and whether measures are taken to optimize cutting.
There are special measures to increase work efficiency, make the output better, and the quality of sawing higher. Before sawing, you need to pre-calculate everything. This is not as difficult as it might seem, but the consumption of round timber will be optimal and profitable to obtain an excellent result.
Options for cutting round timber.
Manual work: using a chainsaw
For home cutting of several trunks, it is not advisable to purchase a tool whose cost is several times higher than the price of finished products. If you have the necessary skill, then it is more efficient and cheaper to do all the necessary work with a conventional chainsaw or chain equipment powered by electricity. Of course, such work requires much more physical effort and time, but the cost of the issue is significantly reduced.
Working on a garden plot requires pruning fruit trees, and it also becomes possible to additionally produce material for outbuildings without resorting to the services of specialists, so any thrifty owner will prefer to buy a chainsaw. Most often, coniferous wood is harvested for the home, and this tool does an excellent job of cutting it. Thanks to straight trunks, it is easier to mark cutting lines, which increases the speed of work. Professionals, by the way, most often use a chainsaw, since it is more powerful than an electric one and can be used anywhere, regardless of whether there are power sources at the cutting or cutting site.
To use a chainsaw to cut logs, you will need a device such as a saw attachment, as well as cutting guides and base-trunk fasteners. The frame-shaped attachment is attached to the tool so that it remains possible to adjust the distance between the chain and the frame itself. This is done to make it possible to produce finished lumber of different thicknesses. For the role of a guide, you can take either a profile of the required length, or a flat wooden plank with sufficient rigidity. A special chain is selected for the tool, designed to cut the trunk lengthwise. Its difference from the others lies in the teeth sharpened at a certain angle.
Before you start work, you need to not only prepare all the necessary tools. Regardless of whether a woodworking machine or a manual device is intended for processing the trunk, the first thing you need to do is familiarize yourself with the cutting map. This is done in order to minimize the percentage of waste and increase the yield of useful products.
The first thing you need to worry about when cutting longitudinally is the uniform density of the finished boards. To do this, a competent sawyer directs the tool from the east side of the log to the west, or in the opposite direction. This is explained by the higher density of round timber in its northern part than in the southern part.
Next, use a chainsaw to remove the slab from both sides so as to obtain a double-edged beam. It, in turn, is sawed in accordance with the cutting pattern chosen at the beginning of the work. The solution is an unedged board. If there is a certain percentage of defects in the trunk, then a circular cut is possible with the trunk turning at a right angle or 180°.
How to increase cutting efficiency
In order for the yield of lumber to be significant, it is necessary to use special measures to increase the efficiency of the process:
- The calculation should be carried out only when using special programs; manually it will have low results, the percentage of defects will be high. The round timber must first be sorted so that the processing is carried out correctly. For cutting, high-quality equipment must be used. Otherwise, the amount of waste will be large, and the quality of the resulting lumber will be low. It is best to cut wide lumber first; processing narrow lumber takes more time. It is not recommended to take long logs. Before work, you should set up the equipment.
The yield of finished lumber may vary. It must be remembered that at the first stage boards are obtained, then they are sorted. As a result, the percentage decreases even more; for example, for deciduous trees it can be only 10-20%.
Sawing map
The sawing map is a calculation of the optimal amount of finished lumber from one log. You can calculate it yourself for each specific log diameter, or you can use a computer program that greatly facilitates the calculation, and the price of which is quite affordable.
Material yield after cutting wood
Or the source could be a regular sawmill reference book. The result is a table that is used as a basis. The sawmill attachment should always be oriented to its data in order to obtain more lumber of any type of wood.
How to optimize cutting
Sequence and dimensions of cutting round timber.
To increase the yield of lumber, the cutting process must be optimized. This applies primarily to those workpieces that have significant curvature. To cut a crooked round timber, you need to perform a number of steps:
First, only suitable wood is selected for work. If the remaining logs have rot, sprouts, or cracks at the ends, then it is necessary to trim off some sections. If a rotten core is discovered during work, you can carefully remove it, and then saw the remaining part. This will allow you to avoid large losses and obtain boards with a length of 1 m or more with the required quality. It is recommended to use logs with a larger diameter so that the yield percentage is higher.
The coefficient can be 1.48-2.1, but it all depends on the diameter, quality of the round timber, sorting, and equipment. For frame shops this coefficient will be 1.48-1.6, and for lines with milling equipment - 1.6 for large timber. With a round log diameter of 12 cm or more, the coefficient can exceed 2.1.
Volume of waste after sawing
In order for the finished board to come out with a high percentage, everything must be prepared correctly, the work must be carried out only in accordance with the technology. Roundwood of coniferous and deciduous species produces different yields.
In the latter case, the volume is smaller, even if special additional equipment is used. Needles are considered more convenient for sawing, since their trunk is straight and the log has a larger diameter. Coniferous wood is not so susceptible to rotting, so there is less waste. For hardwood, 2 cutting technologies are usually used:
Types of lumber from roundwood.
- using a band sawmill on Z75, Z63; in camber, when a half-beam is cut out in the core of the material and passed through a multi-saw machine.
The volume of a band sawmill is 40-50%. When using technology for collapse, the yield is different, it can be increased up to 70%, but the costs of such work are higher. If you cut round timber, the length of which is 3 m, you can see that the percentage of rejects is quite large, and the remaining material requires processing.
This applies to the bulk with boards 22x105(110, 115)x3000 mm. There are many options for such a marriage. For example, it could be a wormhole, which is no longer suitable for most jobs.
After sorting, the volume of hardwood material, which belongs to grade 0-2, will be only 20-30% of the amount obtained after sawing.
This means that of the total mass of harvested round timber, the yield of normal boards will be only 10-20%. The remaining materials are mainly used for firewood. For coniferous round timber, the yield will be different, but attention should be paid to what average values of the resulting volume are observed.
Tools and equipment
Trunks and large branches are used for production. All material is divided into groups according to thickness and presence of bark. Often, timber processing enterprises have workshops near the harvesting site, in which machines for the initial processing of wood are installed.
Manual debarking of wood
Wood that has not passed the debarking stage can be used on floors or as ridge beams in the corresponding interior, or as a supporting device during construction.
Industrial debarking of forests
If another option for using the wood is planned, then sawing is carried out, resulting in the following segments:
- unedged and semi-edged (rough material from which the bases of the floor, walls or ceiling are mounted);
- edged (intended for finishing flooring).
The cutting can be carried out by a mobile organization that has all the necessary tools.
Wood cutting map
Rational use of the material is ensured by compliance with the cutting map. This allows you to reduce costs due to waste, the percentage of which the card can significantly reduce. The tools and types of forest processing equipment used depend on the volume, desired quality and size of the finished lumber.
Wood sawing machine
The most commonly used are a circular saw and various machines:
- The circular saw allows you to make precise cuts in various directions. Suitable for both professional and home use, it copes well with above-average round timber diameters;
- chainsaw;
- machines for clean bark removal;
- sawing on a band sawmill makes it possible to process dense logs; it is considered the most popular, since the output is high-quality material and a small amount of waste;
- disk machine: production of double-edged timber and unedged boards;
- a frame sawmill does not require a foundation, the technology using it allows you to install the equipment in close proximity to the felling site;
- the fine gauge is processed by universal machines, the output is high-quality building materials even from low-grade logs;
- sawing of round timber at a large woodworking enterprise should be carried out with the largest amount of lumber, differing from the rest in its special quality and precise dimensions. For this purpose, special lines are installed for sawing.
At the sawmill, timber and edged boards are obtained by cutting logs up to 7 m long and 15-80 cm in diameter along the longitudinal line. A circular saw has one or more disks and processes wood of different diameters according to their number.
If you need to process a small amount of wood at home, you can use a regular chainsaw.