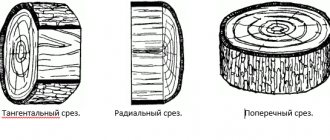
There is no construction project that could be completed without the use of lumber.
Therefore, there is a need to determine their exact number. You can calculate how many boards are in 1 cube using formulas, or you can use ready-made tables. These tables are called cubic tables.
Note that we are considering products made from softwood.
Types of lumber
In this section we will talk about lumber in the order in which they are obtained when cutting a log.
Obapole and croaker
For some reason, there is confusion with the definition of these materials: some claim that they are one and the same thing, and others claim that both sexes are made from slabs.
The proposed table will provide complete clarity.
As can be seen from the table, both sexes are not used in construction, so we will not consider it further.
The requirements for slab are standardized in accordance with OST 13-28-74. This means that croaker is a valuable building material.
The croaker is used:
- for installing a subfloor;
- roof sheathing;
- production of formwork.
Unedged board
It is sawn along two opposite surfaces, called layers. The edges are left uncut, hence the name.
Its standard dimensions are as follows: thickness - 25, 40 and 50 mm; length - 6 m.
The scope of application is wider than that of the slab.
Also used for construction:
- warehouses;
- utility rooms;
- temporary fences;
- awnings
In addition, it can serve as a base for clapboard lining, block house and other finishing materials.
Edged board
It differs from unedged in that it is propylene along the faces and edges.
Used as:
- roof sheathing;
- sheathing of walls of frame houses;
- racks and braces of frame houses;
- stairs;
- material for making country furniture, etc.
timber
This is lumber with a thickness of 100 mm or more with a difference in cross-sectional width and height of no more than twice. Usually the timber is of square section. The most used timber has a section of 100 × 100 mm and 150 × 150 mm.
Used:
- in the construction of frame houses in the form of posts and beams;
- as a material for external and internal walls of wooden houses;
- for the construction of stairs, fences, etc.
Bar
It differs from timber in that its maximum cross-sectional size is 75 mm. Like timber, it is most often made with a square cross-section.
Used for interior work such as device:
- stairs;
- railing;
- window sills;
- bases for finishing cladding;
- roof counter-lattices.
Calculation of cubic capacity of unedged boards
An unedged board differs from an edged one in that it is not processed on the sides, that is, one side has an irregular shape, and it is impossible to indicate the exact width of an unedged board. This is where difficulties arise with calculating the cubic capacity of unedged boards, which are easier to explain with a specific example.
Unedged board
Suppose you need to cover a rectangular building measuring 5*7 meters and 4 meters high with unedged boards. Your board is 50 millimeters (0.05 m) thick.
First, calculate the finishing area. To do this (remember the school), we multiply the perimeter of the building (two sides by 5, two sides by 7 - a total of 24 meters) by the height - 4 meters. We get 96 m2.
Now we multiply the area by the thickness of the material: 96*0.05=4.8 m3
It turns out that for cladding, the width of each cladding element has virtually no effect on the overall cubic capacity. There are no exact cubic capacity tables for unedged boards and there cannot be, since it is unknown from which part of the log the board was cut and what its thickness is on both sides, but some average data on the cubic capacity of unedged boards can be given:
Thickness of boards (length - 6000 mm) Average volume of one element 250.0294400.05500.071
How to calculate the number of boards in a cube
Edged board
As you know from the high school course, the volume of a rectangular parallelepiped (and that’s exactly what the edged board, beam and block are) is equal to the product of the lengths of its sides.
Calculated using formula 1:
V = L × b × h
where: V – volume; L – length; b – width; h – height (in our case thickness) of the board.
Having calculated the volume in this way, you can easily find the number of boards in a cube.
To do this, you need to divide one by the resulting number (formula 2):
N = 1 ÷ V
where: N – number of pieces, 1 – 1 cubic meter. m, V – volume.
We should not forget that the dimensions of edged materials are given in millimeters, so before calculation they must be converted to meters.
Example
There is lumber with the following parameters:
25 × 150 × 6000, where 25 is the thickness; 150 – width; 6000 – length.
Let's calculate the cubic capacity of the board.
To do this, convert millimeters to meters and substitute the resulting values into formula 1:
V = 0.025 × 0.15 × 6 = 0.0225
We substitute the resulting number into formula 2:
N = 1 ÷ 0.0225 = 44.4
The result is always rounded to whole numbers by discarding the decimal part.
Thus, one cube contains 44 whole boards.
Unedged board
Solving the previous problem in this case is more difficult.
The unedged one has a large difference in width on opposite layers, so when calculating the volume, you need to substitute the average width into formula 1: these two widths are added and the resulting amount is divided in half.
The measurement result is rounded to the nearest 10 mm, fractions up to 5 mm are not taken into account, and fractions of 5 mm or more are considered 10 mm.
In addition, uncut edges do not allow the board to be stacked tightly, and various increasing factors are used to calculate the exact volume.
The calculation method is not so much complicated as it is tedious, so it is easier to use the table from the next section.
Tongue and groove boards and lining
They differ from each other only in size, so the calculation method for them is the same.
They are mounted using the tongue and groove system, as shown in the figure.
In this case, the width b is taken to be the so-called “working” or “visible” width - the distance from the base of the tongue to the edge of the board (see figure). It is this size that should be substituted into formula 1.
Cubic capacity table
Ready-made tables are easy to find. Usually the ratio of the dimensions of the board and timber with cubic capacity and data on the mass of lumber and the mass of 1 cubic meter are given. And although the physical parameters of planed and unedged boards are somewhat different, in fact their useful area is the same. Therefore, the same tables are used for products of any type.
The number of boards in 1 cube with a length of 6 m can be found here.
With a length of 4 m, the number of boards will be as follows.
Tables of the number of boards in a cube
In order not to calculate the quantity and volume each time, special cube tables were compiled, in which for each size of material its quantity in one cubic meter is given.
4 meter boards
6 meter boards
4 meter timber
6 meter timber
Unedged material
Due to the wide range of sizes in length, thickness and width, it is impossible to calculate the exact amount of slab in one cube, so there is no cubature table for it.
Here is a table for converting the folded volume of a slab into a dense one.
In this case, we solve the inverse problem: we determine the actual volume of a known amount of slab.
To do this you need:
- Disassemble the slab into debarked (from which the thickest end closest to the tree root has been removed) and unbarked.
- Sort by length - up to 2 meters and more than 2 meters.
- If necessary, sort by thickness.
- Place in a bag, alternating thin and thick ends.
- Calculate the folded volume of the package.
- Select the appropriate coefficient from the table and determine the actual (dense) volume.
Cube for unedged boards.
Cube board: how to make calculations using different methods
Construction of a private house, cottage or any other building requires drawing up an estimate. It indicates the quantity of building materials and their cost. There are several methods that allow you to carry out the corresponding calculations. The board is a common material that is used everywhere. In order to determine how many boards are in a cube, you need to familiarize yourself with the calculation options and the nuances of this process.
The calculation of the cubic capacity of the board will depend on the degree of processing of the material, type and grade
Coverage area calculation
When the main construction is completed, it is time to begin finishing work: sheathing the walls and laying clean floors.
Now you need to calculate how much area can be covered with one cubic meter of material.
To do this, remember formula 1. When calculating the volume of one element, we write down the intermediate result - the product:
L × b = S (3)
where S is the area of this element.
Having calculated the quantity using formula 2, we multiply the result by the area.
How many boards are in 1 cube: calculation of the volume and weight of edged and unedged products
All photos from the article
Before starting any construction work, it is necessary to complete the project and draw up an estimate. The latter involves the calculation of materials, and lumber is always calculated in cubes. To help in this matter, we will next look at how to calculate the number of boards in 1 m3, and also provide a table with their sizes and quantity in one cubic meter.
Boards calculated by cubes
General information
As a rule, calculating the boards needed to perform certain jobs is not difficult for home craftsmen. But, as mentioned above, this material is sold by the cube, so before purchasing it, it is necessary to convert the number of pieces into volume.
If it is not so difficult to calculate the edged material with your own hands, thanks to the correct geometry of its shape, then finding out the volume of unedged material is much more difficult. In this article we will familiarize ourselves with the calculation features for each type of lumber.
Edged boards
Calculating the volume
Edged
As an example, let’s consider how many boards are needed for the floor in a room with an area of 20 m2, if they have the following parameters:
- cross section – 150x30;
- length 6 meters.
Volume formula V=a*b*c
The calculation instructions look like this:
- First of all, we find out the number of boards required for arranging a wooden floor. To do this, you need to divide the total area by the area of one plank. Therefore, first of all, we find out the area of the material 0.15x6 = 0.9 m2;
- Now you can count its quantity - 20/0.9=22.2~23 pieces. Of course, the material must be purchased with a small reserve, so we will increase the resulting value to 25 pieces;
- next you need to find out the volume of one plank by multiplying all its parameters - 0.03x0.15x6 = 0.027 m3;
- then you need to find out 1 cube of boards - how many pieces there are by dividing one cube by the previously obtained value - 1/0.027 = 37 pieces;
- Now it remains to find out the required amount of lumber in volume. To do this, you need to perform the following action - 25/37 = 0.67 m3.
Using this diagram, you can calculate the volume of lumber required for any type of construction work.
Note! If you purchase raw wood, you will need a much larger volume of it, since it will decrease in size during the drying process.
Now that the amount of lumber in 1 m3 is known, it will not be difficult to find out what the price of one plank is. To do this, the cost of the cube must be divided by the number of pieces per cubic meter.
Unedged lumber
Unedged
Calculating the volume of an unedged board is somewhat more difficult:
- The fact is that it is obtained by sawing raw logs. As a result, it has jagged edges called wane. Accordingly, the width along the entire length may not be the same. Therefore, the average width value is taken for calculation;
- If the spread of the width of the face is too large, the wood is sorted into several piles into which planks of similar length and width are placed;
- If you need to find out the volume required to cover the surface, then you should measure the area of this surface and then multiply it by the thickness of the material. In addition, there are some other calculation methods, but those described above are the simplest and most accurate.
In the photo - measuring the width with a tape measure
Advice! You can turn an unedged board into an edged one by removing the wane, for example, using a circular saw for wood. The yield of edged material from unedged material is 80 percent.
Table
As a rule, lumber has standard sizes, so all their parameters are known. Therefore, in order not to waste time on calculations, you can use the parameters that the table contains - how many pieces of boards are in 1 cube:
| Section size, mm | Boards 1 m3 with a length of 6 m, pcs. |
| 50x250 | 13,3 |
| 50x200 | 16,6 |
| 50x150 | 22,2 |
| 50x100 | 33,3 |
| 50x50 | 66,6 |
| 40x200 | 20,8 |
| 40x150 | 27,7 |
| 40x100 | 41,6 |
| 25x200 | 33,3 |
| 25x150 | 44,4 |
| 25x100 | 66,6 |
If the required section size is not here, you can refer to the reference literature, which contains more extensive data.
It should be noted that the table - how many boards in 1 cube is suitable for unedged lumber, the only thing, as mentioned above, is to focus on the average width. Of course, the data will be inaccurate, but, as a rule, high accuracy is not needed for such calculations.
Oak wood is the heaviest
Weight
Often, before purchasing a material, it is necessary to find out its weight. It is not possible to calculate this parameter yourself, since it depends on the density of the wood and humidity. Therefore, below is a table with the weight of different breeds:
| Wood type | Weight 1m3 at 10% humidity | Weight 1m3 at humidity 20% |
| Spruce | 440 | 460 |
| Pine | 430 | 450 |
| Aspen | 490 | 510 |
| birch | 630 | 650 |
| Larch | 660 | 690 |
| Ash | 670 | 610 |
| Oak | 680 | 720 |
| Beech | 670 | 690 |
Advice! It is better to purchase dry wood, since if it is dried on its own, it can crack and become deformed. Accordingly, the amount of usable material will decrease.
The optimal humidity is 8-12 percent.
Knowing how much 1m3 of wood weighs, you can calculate the number of vehicles that will be required to transport the material, and thus calculate delivery costs.
Here, perhaps, is all the basic information regarding the calculation of boards.
Conclusion
You can find out the basic parameters of boards, such as volume and weight, from reference literature. However, a table of how many pieces of boards are in 1 cube is not always at hand, so sometimes you have to perform the calculation yourself. It consists of several simple mathematical operations that make up the instructions.
You can find additional information in the video in this article. If after reading the material you have questions, you can leave them in the comments, and we will be happy to answer them.
rubankom.com