In the old days, only craftsmen could make beautiful things from wood using hand tools, but when the modern lathe was invented and adapted for carpentry, the situation changed. Now any person who has learned the basics of working on a machine is able to create almost works of art using wood turning.
In recent years, woodworking has become not only the production of any wooden products at enterprises, but also a hobby for many thousands of people who like to turn wood crafts on their personal woodworking lathe.
If you make any part from wood with a hand tool, then such an activity will take a lot of time, but the same craft on a machine can be done much faster, and even better. Only a master of his craft can make beautiful things from wood by hand, but anyone can master the basics of such a craft as wood turning, and he will produce very beautiful crafts. Let's try to tell you a little about this craft.
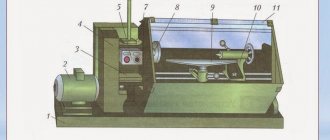
Design and principle of operation of a wood lathe
The main components of a wood lathe
The main difference between a wood lathe and its counterpart, on which metal blanks are processed, is that instead of a mechanical device for bringing the cutter to the workpiece, it has a tool rest - a device for holding chisels.
A lathe for woodworking is simple. The headstock and tailstock are located on the device frame. There is a spindle in the headstock; various devices are inserted into it, with the help of which the left end of the wooden workpiece is attached. The tailstock serves to support the right end of a long workpiece. A tool rest is installed between the left and right headstock, which serves to support the tool with which the workpiece will be processed.
The spindle is driven by an electric motor. The rotation speed can be adjusted. By the way, some turning work can be performed on milling machines, but this should be discussed in a separate article.
The workpiece is secured in a chuck mounted on a spindle. Then she presses up with the tailstock. If the tailstock support device is stationary, then it is lubricated with machine oil before installing the workpiece. Before you begin to install the workpiece, you need to accurately calculate and mark the center in it. The easiest way to find it is to use a corner finder. If the workpiece is not fixed in the center, then when the spindle rotates, this will cause it to “beat”, and it will not be possible to turn the part well.
Turning while clamping at one end
A special approach requires processing wood on a lathe when clamping at one end. This is how all kinds of boxes, decorative bowls and glasses, and wooden plates are made. For these purposes, fastening between centers is not suitable; one cartridge is needed that will hold the part during processing.
The workpiece is fixed using various holders. Most often used:
- holder with screw;
- cup holder;
- lock with key;
- three-jaw chuck.
In addition to the above clamps, a combination holder is widely used. Its design combines all known methods of fixing a workpiece, making it a universal tool.
Material selection and preparation
Wood species
Wood is a malleable material for making a wide variety of crafts. However, it must be borne in mind that not all types of wood are equally easy to turn. The easiest parts to process on a lathe are walnut, hornbeam, beech, linden, birch and pear. Conifers, as well as oak and ash, are much more difficult to turn. When selecting material for a workpiece, you should choose blanks that are free of cracks, falling knots, tar and other defects.
It should be noted that different types of wood have their own unique beautiful texture. Knowing the internal texture of each type of tree, it is easier to select the necessary blank for making a particular craft. From walnut wood you can carve a beautiful powder compact, a round box, and from acacia wood you can make a magnificent salt shaker. The texture of the wood must be taken into account when turning a particular product.
Before putting the blank on the lathe, you need to adjust its size to the future product as much as possible using a hand tool, for example, an ax. There is no need to install a thick log in the centers if you have to carve a thin part. It should be trimmed. If the workpiece has a square cross-section, then the corners can also be cut off with a hand tool, giving the blank a more rounded shape.
Selection and preparation of workpiece
The basis of the future product is a square block. The timber must be free of knots, cracks and other mechanical damage. Using a ruler and pencil, mark the centers. Finding the center is not difficult; just draw two diagonals at each end of the block.
Before attaching the blank to the lathe, it must be given a shape close to cylindrical. You should not try to sharpen a solid block; you may break the tool or get injured if large chips fly out. But it is not necessary to create a perfect cylinder; it is enough to cut off the corners, turning the block into an octahedron. This can be done with a hatchet or a plane.
Sometimes, not a block is used as a base, but a workpiece with a cross-section close to a circle, for example, a piece of log. In this case, a slightly different technology is used. There is no need to give the log a round shape, but difficulties arise in finding the centers. Here you can’t do without a special carpenter’s tool - a center finder.
Devices for fastening wooden workpieces
The most commonly used device for fastening blanks is a driving chuck. Most often, two types of such devices are used for wood turning.
Diagram of a chuck with teeth
The first version of such a device is a cartridge with teeth. The workpiece is secured in such a device as follows: you should drill a small hole in the marked center of the blank, insert the central tooth of the chuck into it, of course, having first removed it (the chuck) from the spindle, after which you should lightly hit the shank of the device, thereby driving the remaining teeth into wood.
In this way, the location for installing the blank in the cartridge is marked. We install it on the spindle, after which we install the workpiece according to the markings, press the tailstock quill - you can start turning the wood.
The second option for driving a wooden block is to use a faceplate. This device is a metal round disk. In the middle there is a hole for putting on and attaching to the lathe spindle.
Through holes are located in the correct order over the entire area of the disk. Through these holes, the workpiece is attached to the faceplate with bolts or screws (self-tapping screws). First you need to mark the center of the workpiece, and then install it. You can’t do without using a faceplate when you need to turn the wood of the end of a workpiece, and you can’t use the tailstock for stop.
Studying the machine
Before you start creating a wooden masterpiece, it is worth studying the structure of the machine. It consists of four main parts.
Firstly, this is the frame, the frame on which all components and assemblies are mounted.
The next important part of the lathe is the headstock. Rotation from an electric motor is transmitted to it through a pulley system or gear transmission. At its output there is a spindle with a rotating center or faceplate for fixing the workpiece. In an industrial machine made for the right hand, it is on the left.
The tailstock is a passive part, which is a free-rotating pointed shaft. Its purpose is to fix a long workpiece. The headstock can be moved to work with parts of different lengths and be securely fixed in any position.
A tool rest or chisel holder is most often a metal table on which a chisel or wood chisel rests. Its design allows you to move freely for ease of use.
Before turning on the lathe, it is worth understanding the controls, understanding the operating principle and task of each part, this will allow you to avoid mistakes and, possibly, an accident.
Wood turning tool
Most often, turning chisels are used for processing wood on machines. Compared to conventional chisels, turning chisels have longer handles, and their cutters are made only from high-quality tool steel. That is, the chisel consists of two parts - a handle and a metal blade mounted on it with a blade sharpened at a certain angle or a double-edged blade.
There are different types of chisels for different tasks. For a beginner in turning, in order to start working with wood, it is enough to learn how to use these two chisels:
Chisels for turning
- Reyer - this chisel has a semicircular blade, which is made of a thick plate; it is intended for rough turning of the workpiece;
- meisel - this type of chisel is intended for finishing the part; the blade is sharpened obliquely, on both sides.
Most of the other types of turning chisels are classified as shaped tools. They give the final appearance of a turned part. For example, decorative grooves can be cut out on a turned salt shaker. Here are some types of such chisels:
- chisel-hook - with such a cutter you can carve a recess at the end of the workpiece;
- chisel-comb - with its help you can cut internal and external threads or apply many decorative grooves;
- ring chisel - you can do the same thing with it as with a hook.
There are a great many types of shaped cutters. Experienced turners come up with their own cutters for a specific task and make them themselves.
Wood turning cutters
Turning cavities
Before creating a recess in the part, it is rough processed. It is more convenient to do this with conventional center-to-center fastening. During rough processing, the outer surface of the product is formed and the parameters of the recess are outlined.
The tailstock of the machine is removed; it will not be needed. Cut the workpiece to the required length and install it in the headstock clamp. Check the reliability of the fastening. The tool rest is turned perpendicular to the workpiece, and the machine is turned on. Using a semicircular cutter, turning of the cavity begins.
Important! You only need to work with that part of the workpiece that moves from top to bottom, otherwise you may drop the tool or even get injured.
It is more convenient to work if you pre-drill a hole of the required depth in the center of the workpiece.
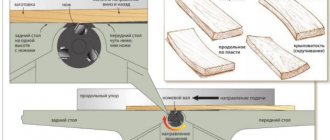
Lathe technology
It is advisable that the workplace in front of the lathe be equipped for a specific worker - for his height. The workpiece should be at elbow level. Before starting to work, the turner must take a stable and comfortable stance in front of the machine.
The wooden piece must be securely fastened either in the centers or on the faceplate. Next, you should bring the tool closer to the workpiece, turn the shaft with the blank - it should not touch it. The upper part of the tool rest should be located five millimeters below the axis of rotation.
Now you can start the engine. The more finishing work is done, the higher the spindle rotation speed should be. We rest the body of the chisel blade against the tool rest, and slowly bring the cutter closer to the rotating workpiece. The chips must be removed in a thin layer; the cutter must not be allowed to penetrate deeply into the body of the blank - this is unsafe. Hold the blade of the chisel with one hand, and its handle with the other. It is advisable to press the elbow tightly against the body; in this manner, a stronger and more immovable emphasis is created.
Types of jobs
Such units allow the following types of turning work:
- turning of various types;
- grinding;
- cutting off excess part of the workpiece;
- drilling end holes.
Turning has three types:
- longitudinal;
- transverse;
- corner.
Longitudinal turning involves smooth movement of the cutting tool at a constant speed of rotation of the wooden blank. The turning tool moves at low speed parallel to the axis of rotation. Transverse turning is performed as a result of the movement of a turning tool under a certain force perpendicular to the axis of rotation. Angular turning is used to obtain complex shapes. In this case, the tool is directed at a certain angle to the surface of the workpiece. These methods produce the most complex sample shapes. It should be remembered that in order to properly sharpen a wooden workpiece, you should clarify its density, select the spindle rotation speed and the necessary cutting tool.
To work with one of the types of turning, the following methods of tool placement are used:
- lower;
- top;
- straight (perpendicular or at an angle).
By choosing one of the techniques, you can carve a given shape or make the necessary groove at any angle.
Compliance with safety rules when working on a lathe is a prerequisite
Without mastering the safety rules for working on a machine, you should not even approach it, otherwise the worker may lose his health and not get pleasure from a well-made part. The basic safety requirements when carrying out wood turning are outlined below:
Safety precautions
- the turner must be dressed in overalls, which must be tightly fastened with all buttons;
- hair must be covered with a headdress;
- Be sure to wear safety glasses and lower the protective screen;
- the handles of chisels should not have cracks;
- the workpiece must be securely secured in the chuck;
- the workpiece must not be damaged;
- the machine must be grounded;
- all adjustment manipulations (measuring the size, moving the tool rest towards the part, etc.) must be performed with the machine turned off.
There are other points of safety requirements that can be set out either in the production instructions or in the documentation of the lathe manufacturer.
Purpose and characteristics of a lathe
Modern manufacturers offer turning equipment capable of performing many machining operations. Depending on their list, the purpose of the unit is determined. The main characteristics of wood processing machines include:
- installed engine power;
- weight of the entire machine;
- dimensions;
- list of acceptable cutting tools;
- number of possible processing operations;
- maximum size of the workpiece;
- Availability of automation and software control tools.
Each type of machine provides a specific industry. If it is necessary to produce a large number of similar parts from wood, their production is entrusted to specialized automatic lathes and machines with numerical control.
Classification
Lathes are divided into:
- center ones with mechanized feed. It is possible to perform work on this equipment using hand-held cutting tools (when installing a special tool rest on the frame). An oblong piece of wood is held by a spindle and a movable tailstock. The longitudinal feed of the caliper is mechanized. These machines can be used to work with a copier. When working with short, light workpieces, the tailstock fastening may not be used. When processing the inside of a wooden part, a faceplate serves as a fastener. The moving elements in the operating mode on these lathes are the cutters moving along the piece of wood being processed and the rotating spindle.
- Lathes are used to produce parts on a flat, wide wooden base. Beautiful multi-level carvings, bas-reliefs, high reliefs - this is what can be produced on machines that work with a wide faceplate, on which the workpiece is mounted. Work is carried out only on the front part of the part. The rest of the revision will be done manually.
- round-sticks process wood, giving it a shape with a round cross-section. When working on this equipment, the workpieces do not rotate or move. The only moving parts of the machine are the heads with the cutters. There are also machines in this group for processing long products. Then they will feed the workpieces with rollers under the cutters.
Shaping wood occurs by rotating the material being processed and using a cutting tool.