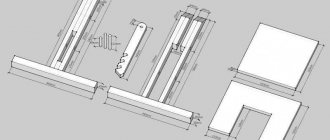
Carpentry workbench frame
Take smooth pine boards without large knots with a cross-section of 50x150 mm. Dry the raw lumber: the lower the moisture content of the boards, the less likely the structure will warp. The carpentry workbench in question is designed for comfortable work by a craftsman with a height of 170–180 cm. To change the height of the structure, make the legs higher or lower.
Drawing of a carpentry workbench (front view).
Workbench drawing (side view).
Table 1 - list of frame parts
| № | Name | Finish dimensions, mm | Material | Quantity | ||
| thickness | width | length | ||||
| A | Leg detail | 46 | 70 | 820 | pine | 4 |
| B | Lower spacer | 46 | 70 | 100 | pine | 4 |
| C | Upper spacer | 46 | 70 | 680 | pine | 4 |
| D | Cross leg | 46 | 70 | 366 | pine | 2 |
| E | Cover cross member | 46 | 70 | 458 | pine | 2 |
| F | Longitudinal leg | 46 | 70 | 1400 | pine | 2 |
| G | Longitudinal drawer | 46 | 70 | 1308 | pine | 2 |
| H | Bottom shelf | 16 | 504 | 1258 | Chipboard, MDF | 1 |
| I | Table top spacer | 50 | 50 | 366 | pine | 2 |
All elements of the base of the carpentry workbench are paired, so mark two parts of the same length on a 150 mm wide board at once.
Saw all the wooden pieces to length, with the exception of the spacers: it’s easier to cut the short ones already planed, and the long ones should be sawed off later “in place.”
Measure the width of the board, subtract the thickness of your circular saw blade and divide the result in half. Set the calculated size on the measuring scale and make sure that the saw blade is perpendicular. Unfold the boards exactly in the middle.
Board cutting diagram.
Sharpen the parts and sand them with medium-grit sandpaper.
File the bottom spacers and sand the ends. After cleaning the surfaces from dust, apply glue to the small leg and to the end of the leg.
Squeeze the parts together with a clamp, wipe off the squeezed out glue and drill holes with a countersink drill.
Fasten the workpieces with 6.0x70 screws. Prepare the remaining legs of the woodworking bench frame.
Bevel the bottom ends to reduce the likelihood of the wood splitting when the workbench moves.
Prepare the joints connecting the legs with the longitudinal legs for gluing. Fasten the parts with screws, setting a right angle.
Screw all four legs into place.
Place the frame halves and longitudinal drawers on the floor, measure the length of the upper spacers.
File the parts and secure them with glue and screws.
Assemble the top frame of the woodworking bench on a flat surface. Fasten the bars with wood glue and 6.0x80 mm screws, drilling guide holes for them.
Assemble the lower frame of the workbench, using clamps and auxiliary boards for convenience.
Replace the top frame and level the entire structure. Connect the frame parts with screws.
Cut out the bottom shelf from sheet material 16 mm thick and secure it to the bars
Installation of additional equipment
After the table is ready, additional equipment is installed on it:
- Board clamps. Usually mounted from two bars. Clamps are installed at both ends of the tabletop. For convenience, it is worth installing several clamps of different thicknesses: 5 cm, 10 cm, 15 cm and 20 cm. The clamps are installed exactly opposite each other.
- Vise for parts. Ideally, there should be several vices: 2 or 3 pieces. They are designed for small and large parts.
- Stops for cutting parts. This is optional equipment. Stops are usually small blocks on the countertop.
- Lower shelves for tools. They will create comfort during work and significantly save time. It is better to place heavy, large tools on the bottom shelf. Place boxes with small items a little higher. It is better to make drawers for small things retractable.
- Additional lighting. Without it, work will be uncomfortable. Typically, a long LED office lamp is mounted on the desk. To prevent shadows from your hands from interfering with your work, you should attach two lamps on different sides.
Don't forget about the lighting. We suggest considering fluorescent lamps or LED strip as an additional lighting source.
Workbench table top for carpentry work
Use sheets of MDF, chipboard or plywood 16–20 mm thick for the workbench cover. Glue the slabs in two layers and get a tabletop 32–40 mm thick.
Drawing and arrangement of the workbench cover: 1 – edge strips (birch, maple); 2 – working surface (hard fiberboard); 3 – load-bearing board (chipboard, plywood or MDF).
For the countertop, you can take sheets of chipboard left over from unnecessary furniture. For example, the walls of a wardrobe will do. Take them as a base and add small pieces so that the carpentry workbench lid measures 670x1940 mm.
Place narrow slabs toward the back wall and toward the center of the workbench. Place large sheets in the top layer of the countertop. Glue the cut pieces together.
Fasten the sheets with self-tapping screws, deepening them into the countersunk holes. Trim the edges with a hand-held circular saw 20mm from the edge.
Align the tabletop with the frame and secure with screws.
Sharpen slats for edge trims. Saw off the 45° bevels and cut the planks to length. Place a piece of fiberboard on the lid of the workbench, add a flat panel on top and secure it all with clamps.
This makes it easier to attach the pads. Align the ends with the edges of the tabletop and press the rail against the panel - the top plane will be flush with the workbench lid. Holding the bar with one hand, drill pilot holes and secure the parts with screws.
Move the device to the other side and install the remaining pads. Sand the slats with a sander.
Drill a hole in the corner of the slab so that the fiberboard can be easily pushed out of its recess when replacing it.
Clean the surfaces from dust and cover the wooden parts of the frame with stain. Place the fiberboard in the recess of the lid. If you are using pieces of material, secure them with double-sided tape. Place a carpenter's vice on your workbench.
Boxes for storing tools in a carpentry table
When filling the space under the cover of a carpentry workbench, use a modular principle. It’s easier to make individual blocks and more convenient to change them later when you need space for a new tool. There will be a certain waste of material, but the weight of the workbench will increase and its stability will be enough to work with power tools.
Scheme of organization of storage places: 1 – full extension drawer; 2 – spacious plywood box; 3 – chipboard container; 4 – wide box; 5 – compartment for a portable tool box; 6 – space for cases and workpieces.
Use boxes from old furniture
Select suitable sized drawers from an unnecessary desk or chest of drawers.
Label the wooden elements and carefully separate them. Clean the glue from the spikes and eyes.
Trim the planks to width, removing worn corners and cracked grooves. If the original bottom of the box is flimsy, prepare thicker plywood or fiberboard. Make new grooves on a circular saw.
Assemble the box “dry”, adjust the parts if necessary. Clean the surfaces and glue the structure. Use mounting angles to accurately assemble right angles.
Once the glue has dried, sand the corners and sides of the box, securing it in place for ease of work.
Prepare guide strips and calculate the dimensions of the module.
Calculation of a block for three drawers
File the bottom, top and side panels. Screw the guide rails with screws.
Assemble the panels into a module and test the movement of the drawers. Place the block inside the workbench with supports underneath it.
Drill pilot holes, countersink and tighten the screws. Attach the chipboard to the top beams and to the legs of the workbench.
Install front covers on the drawers. Having marked the location of the housing, secure it with one screw. Insert the drawer into place and adjust the position of the panel. Carefully remove the drawer and tighten the remaining screws.
Secure the remaining linings - the module with wide drawers is ready.
Types and design
All homemade work tables for carpentry work can be divided into three types:
- Mobile workbenches have a weight of up to 30 kg, dimensions of less than 1 m in length and up to 70 cm in width, are equipped with only a vice and are made partly from metal elements. Such machines are intended for working with small, lightweight workpieces or minor repairs of wooden products. A mobile desktop is an excellent option if there is a lack of space and can be installed in any room in the country house or on the balcony. Often, mobile workbenches have a folding design.
Homemade carpentry workbench with mobile designIf there is no need for a stationary, professional workbench, then for minor repair work or the manufacture of small parts you can convert an old desk.
- A stationary carpentry workbench is made with reference to a specific location and is not intended to be moved during operation.
Equipment of this type allows you to process parts of any size and weight. A stationary carpentry workbench is a reliable, stable structure, arranged in accordance with the preferences of the owner and the characteristics of the room - The compound type machine is the most difficult to manufacture.
However, due to its variability, this design is the most practical and functional structure. If necessary, individual parts of the workbench can be easily replaced, since the elements of the workbench are connected to each other by bolted joints. A composite workbench is a structure that can be adjusted to any requirement
Carpentry table compartment for portable box
The middle module is made to the full height of the bench to enhance the rigidity of the carpentry workbench. For the body, take 16 mm thick chipboard and cut out two sides, a bottom and a lid.
Middle module housing: 1 – frame diagram; 2 – side wall; 3 – lower and upper panels.
Attach the guide strips to the sides, assemble the frame with screws and install it close to the right block.
Prepare the parts for the drawer.
Drawings of box elements: 1 – long wall; 2 – short wall; 3 – bottom; 4 – front pad; 5 – rail.
Use a circular saw to select grooves in the walls, which can be done with a regular disk. Set the cutting depth to 6 mm and the width to 8 mm. Run all four parts through. Move the saw fence 2 mm and make a test cut. Check the groove and adjust the stop if necessary. Run the rest of the workpieces.
Assemble the module and install slats at the bottom that protect the edges of the chipboard from chipping and provide a “smoother” operation.
Secure the front panel with screws and place the drawer in place.
How to make modules with convenient drawers
The design of the housings of these modules is identical to the previous designs. The retractable container placed on roller guides is made taking into account the installation gap, so its width will be 26 mm less than the internal size of the case (for common guides with a thickness of 12 mm).
Module structure and box parts: 1 – assembly diagram; 2 – back and front walls; 3 – front panel; 4 – bottom; 5 – side walls.
Before assembling the case, secure the restrictive wooden slats and metal guides to the sides.
Installation diagram of guides on the walls of the housing.
Secure the finished module under the workbench lid.
To install the drawer rails, unclip the latches and pull out the small rails.
Fasten the parts to the walls. Determine the required distance from the edge to the guide yourself based on the specific design and the 10 mm gap between the wall of the box and the top panel of the frame.
Pull out the middle rails all the way.
Insert both rails at the same time, holding the middle rails with your fingers. If the drawer is too tight, take it out and try again.
Replace the front trim.
Materials
The working surface of the carpentry table is made of hardwood. The main qualities of raw materials are high strength and wear resistance. The service life of the workbench depends on the durability of the working surface. The product should last as long as possible without replacing the countertop. Its minimum thickness should be 6 cm.
Characteristics of a table that extends from under the tabletop, selection criteria
The carpentry table supports can be made from softwood. Pine and linden will do. For greater stability, it is permissible to supplement the structure with longitudinal dies made of the same material. Supports can also be made from metal pipes.
Decorative and additional elements are made from any durable raw materials.
Tools are usually hung on the front of the workbench and a vice is placed. Therefore, it is advisable to make it from hardwood. If you choose a soft variety, there is a risk of the surface “sagging” under the vice. The back part can be made of any material. The main thing is that it can withstand the installation of drawers and additional functional elements.
How to make a carpentry workbench drawer from plywood
Saw the box body blanks from 10mm plywood, and for the bottom take a 5mm thick sheet.
Scheme of cutting parts for two plywood boxes: 1 – front panel; 2 – rear liner; 3 – side wall; 4 – front liner.
Sand the workpieces with a grinder.
Make grooves for the plywood bottom in the side walls, back and front liner. Remove burrs with sandpaper.
Glue and screw together the parts of the front and back walls.
Apply glue to the joints and into the groove.
Assemble the structure using angles and clamps.
Fasten the parts with screws, drilling guide holes.
Assemble the second plywood box with your own hands.
Install a panel on the back wall of the carpentry workbench designed to increase the rigidity of the structure and to accommodate hand tools.
Cover the drawers and cut ends of the particle boards with finishing compound.
Connect power to your homemade workbench and start filling the containers with tools.
Rear and front clamps
Rear and side (front) screw clamps are those elements without which no workbench simply can fulfill its main purpose. Therefore, this part of the structure should be built first.
The rear clamp is designed to hold lumber while planing. As shown in the diagram, its vice blocks move along the front edge of the workbench, allowing the workpiece to be securely secured using lead screws.
The side screw clamp (which, due to its special location, is called the front clamp by many) has the same purpose as the rear clamp. And these elements differ from each other only in their location. Here are the drawings of a carpentry table for making it yourself.